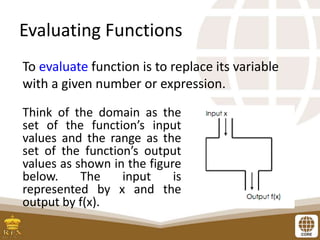
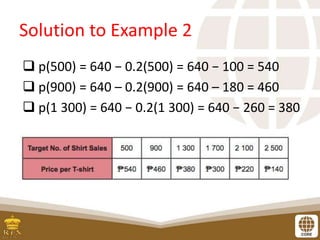
This document discusses evaluating functions by substituting values for variables. It provides examples of evaluating various functions, including price functions. Students should be able to evaluate functions and solve problems involving function evaluation. Functions can be even, odd, or neither based on whether f(-x) = f(x) or f(-x) = -f(x). Examples are provided to identify functions as even, odd, or neither. Exercises include evaluating functions for given values and determining function parity.