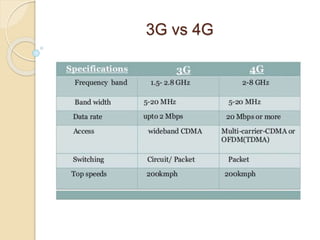
This document discusses the evolution of wireless network technologies from 1G to 4G. 1G networks provided basic call functionality with poor voice quality. 2G introduced digital encryption, text messaging, and improved roaming. 3G enabled higher data rates and multimedia services like maps and video calling. 4G offers even higher speeds of 100Mbps, lower costs, support for WiFi, and capabilities for video streaming, online gaming, and mobile TV broadcasting. The conclusion states that wireless networks are becoming a critical global infrastructure connecting 1G through 4G systems.