The document provides a detailed exploration of various mathematical set concepts, including cardinality, finite and infinite sets, equivalent and unequal sets, and null and singleton sets. It includes specific examples and solutions related to cardinal numbers, properties of sets, and the relationships between them. The document serves as an educational resource for understanding and teaching the fundamental principles of set theory in mathematics.














































![Solution :
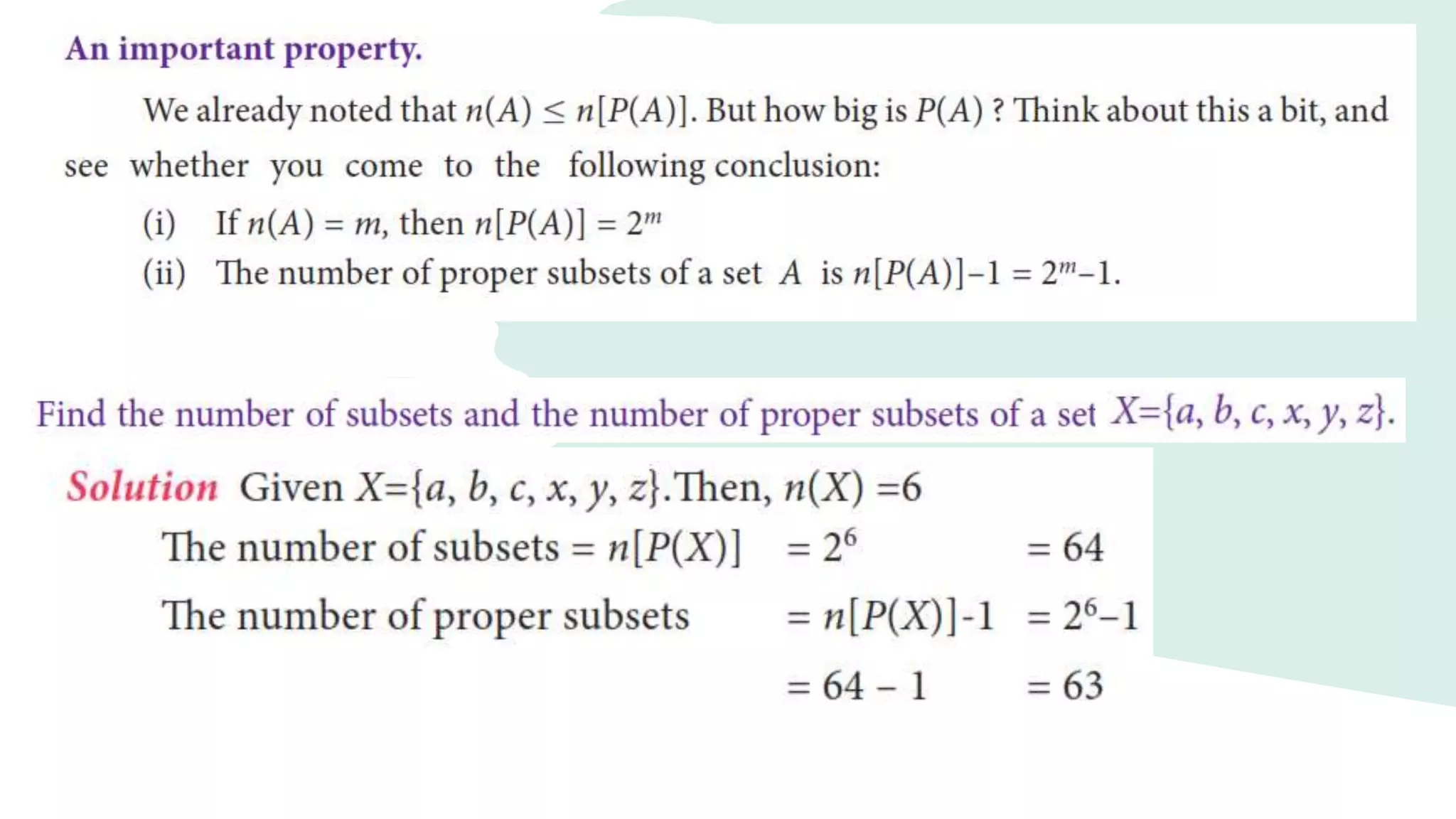
The number of proper subsets of a set A is
n [P(A)] – 1 = 2m–1
n(A) = 3
n [P(A)] – 1 = 23–1
= 8 - 1
Number of proper subset :
n [P(A)] – 1 = 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1b-201019053240/75/1b-Pedagogy-of-Mathematics-Part-II-Set-language-introduction-and-ex-1-2-58-2048.jpg)
![(ii) X = { x2 : x ∈ N, x2 ≤ 100}
X = {22, 32, 42, 52, 62, 72, 82, 92, 102}
n (X) = 10
n [P(A)] – 1 = 210 – 1
n [P(A)] = 1024
Number of proper subset :
Number of proper subset = 1024 - 1 = 1023](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1b-201019053240/75/1b-Pedagogy-of-Mathematics-Part-II-Set-language-introduction-and-ex-1-2-59-2048.jpg)
![Question 10 :
(i) If n(A) = 4, find n [P(A)].
Solution :
n(A) = 4, find n [P(A)]
n [P(A)] = 24
= 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1b-201019053240/75/1b-Pedagogy-of-Mathematics-Part-II-Set-language-introduction-and-ex-1-2-60-2048.jpg)
![(ii) If n(A) = 0, find n [P(A)].
Solution :
n [P(A)] = 2m
= 20
= 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1b-201019053240/75/1b-Pedagogy-of-Mathematics-Part-II-Set-language-introduction-and-ex-1-2-61-2048.jpg)
![(iii) If n[P(A)] = 256, find n(A).
n [P(A)] = 256
2m = 256
2m = 28
m = 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1b-201019053240/75/1b-Pedagogy-of-Mathematics-Part-II-Set-language-introduction-and-ex-1-2-62-2048.jpg)
