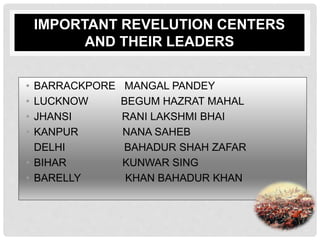
The 1857 revolt was a major uprising against British rule in India. It began as a mutiny of Indian soldiers (sepoys) in the town of Meerut in May 1857 and erupted into wider rebellions across northern and central India. The rebellion posed a serious threat to British power but was eventually contained after the defeat of rebel forces in Gwalior in June 1858. Key leaders of the revolt included the Rani of Jhansi, Nana Sahib of Kanpur, Kunwar Singh, and Maulvi Ahmadullah. The revolt marked the end of East India Company rule and the direct governance of India by the British crown.