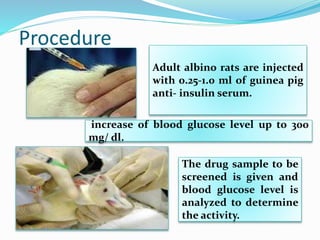
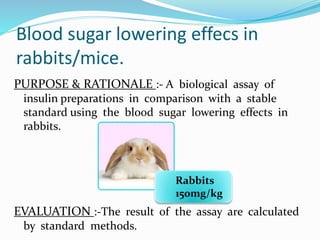
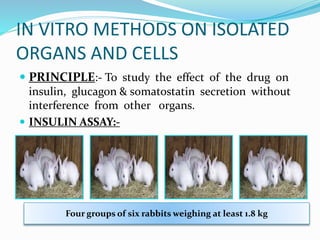
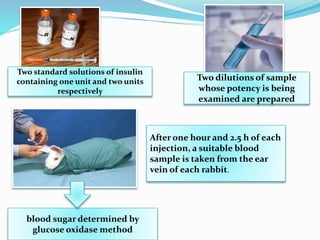
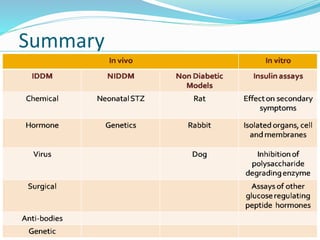
The document discusses various in vivo and in vitro models used to study diabetes and evaluate potential antidiabetic drugs. It describes methods like streptozocin-induced diabetes in rats to study effects on blood glucose levels and cataract formation. Insulin antibody-induced diabetes in guinea pigs is also presented. In vivo blood glucose lowering effects are evaluated in rabbits/mice following oral administration of test compounds. In vitro assays include testing effects on insulin secretion using isolated organs and cells as well as insulin receptor binding assays.


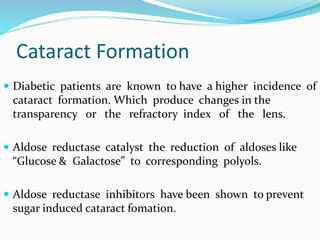



![Streptozotocin induced DM
Streptozotocin [60 mg/kg body weight] is prepared in citrated buffer [ph 4.5]
Albino rats of either sex weighing 150-200 g are injected i.p with above solution.
Animals showing fasting blood glucose levels > 140mg/dl after 48 hours of
streptozotocin administration are considered diabetic.
After six weeks of treatment blood samples are collected from 6 hour fasting
animal
Serum is separated by centrifuge (3000 rpm) under cooling (2-4 °C) for ten
minutes
Serum glucose level is estimated by glucose- peroxidase method [GOD-POD
kit] using autoanalyser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypoglycemicamandeep-170318080933/85/screening-of-hypoglycemic-agent-8-320.jpg)

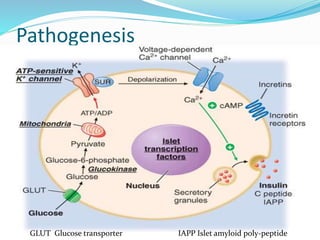
![Insulin antibody induced diabetes
Principle: - A transient diabetic syndrome can be
induced by injecting guinea pigs with anti insulin
serum.
Preparation of antibody
Bovine insulin, dissolved in acidified water [ph 3.0] at a dose
of 1mg /ml
Anti insulin sera is collected after two weeks of antigenic challenge
Injected into guinea
pigs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypoglycemicamandeep-170318080933/85/screening-of-hypoglycemic-agent-10-320.jpg)