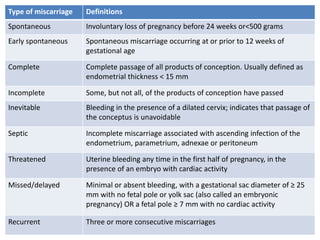
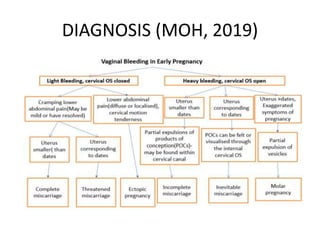
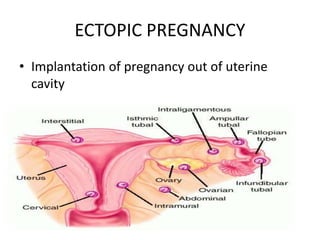
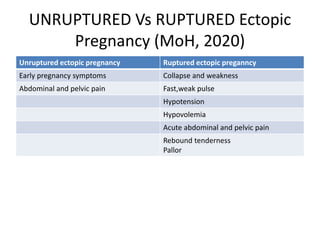
First trimester bleeding is common, occurring in 25% of pregnancies. While often resulting from miscarriage, it can also be caused by ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, or non-obstetric conditions. Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of pregnancy before 24 weeks gestation or fetal weight under 500 grams. Risk factors for miscarriage include increased maternal age, smoking, alcohol, caffeine, obesity, toxins, radiation, prior miscarriages, uterine defects, and infections. Diagnosis involves pregnancy tests, ultrasound, and bloodwork. Complications can include infection, shock, and anemia. Treatment depends on the type and severity, ranging from observation to medication and surgical evacuation. Follow up care and family planning counseling








































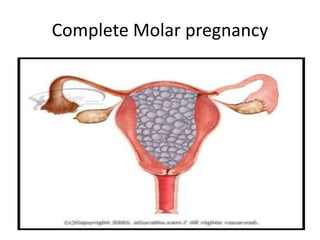



![Management
• Aspiration under Ultrasound guidance
• Cross match and book blood for possible transfusion
• Administer Oxytocin during aspiration
• Products of evacuation should be sent for Histology
Examination
• Hysterectomy
• Signs of trophoblastic proliferation
• serum human chorionic gonadotropin [hCG]levels
>100,000 milli-international units/mL
• ovarianthecaluteincysts>6cmindiameter
• Age>40years](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1623901744851firsttrimesterbleeding-220916134748-9c72192d/85/1623901744851_FIRST-TRIMESTER-BLEEDING-pptx-52-320.jpg)


