This document summarizes different mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in prokaryotes:
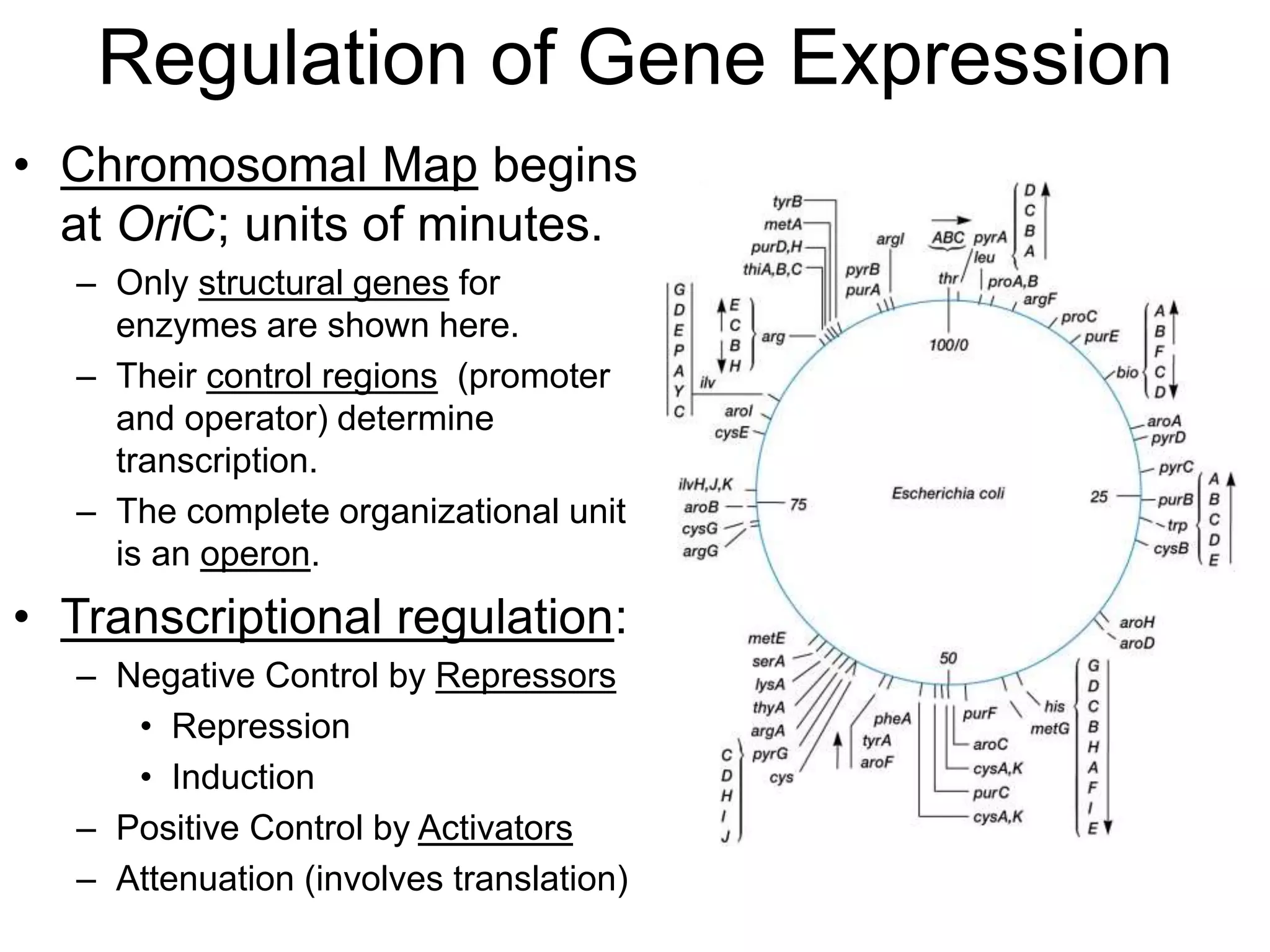
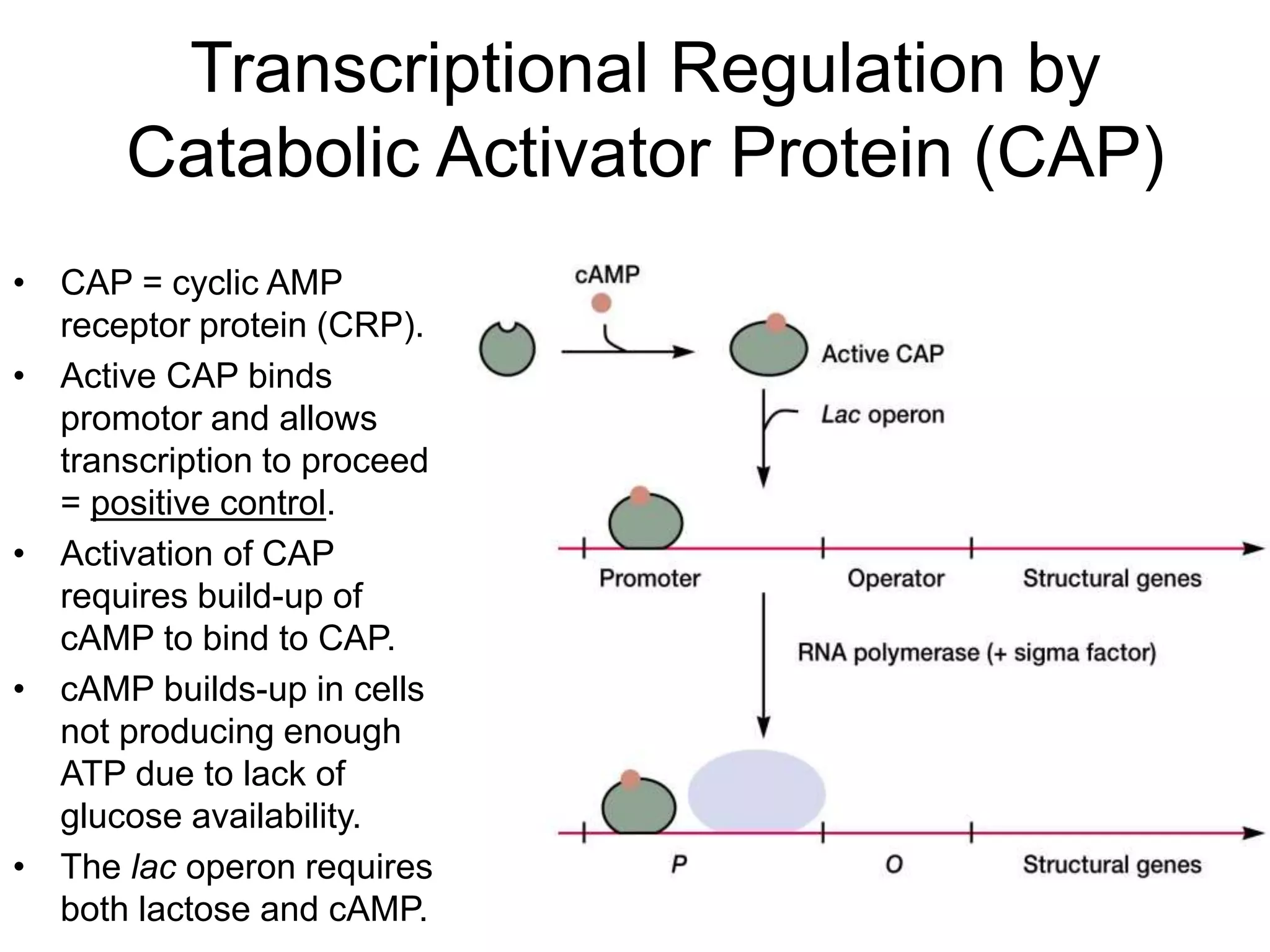
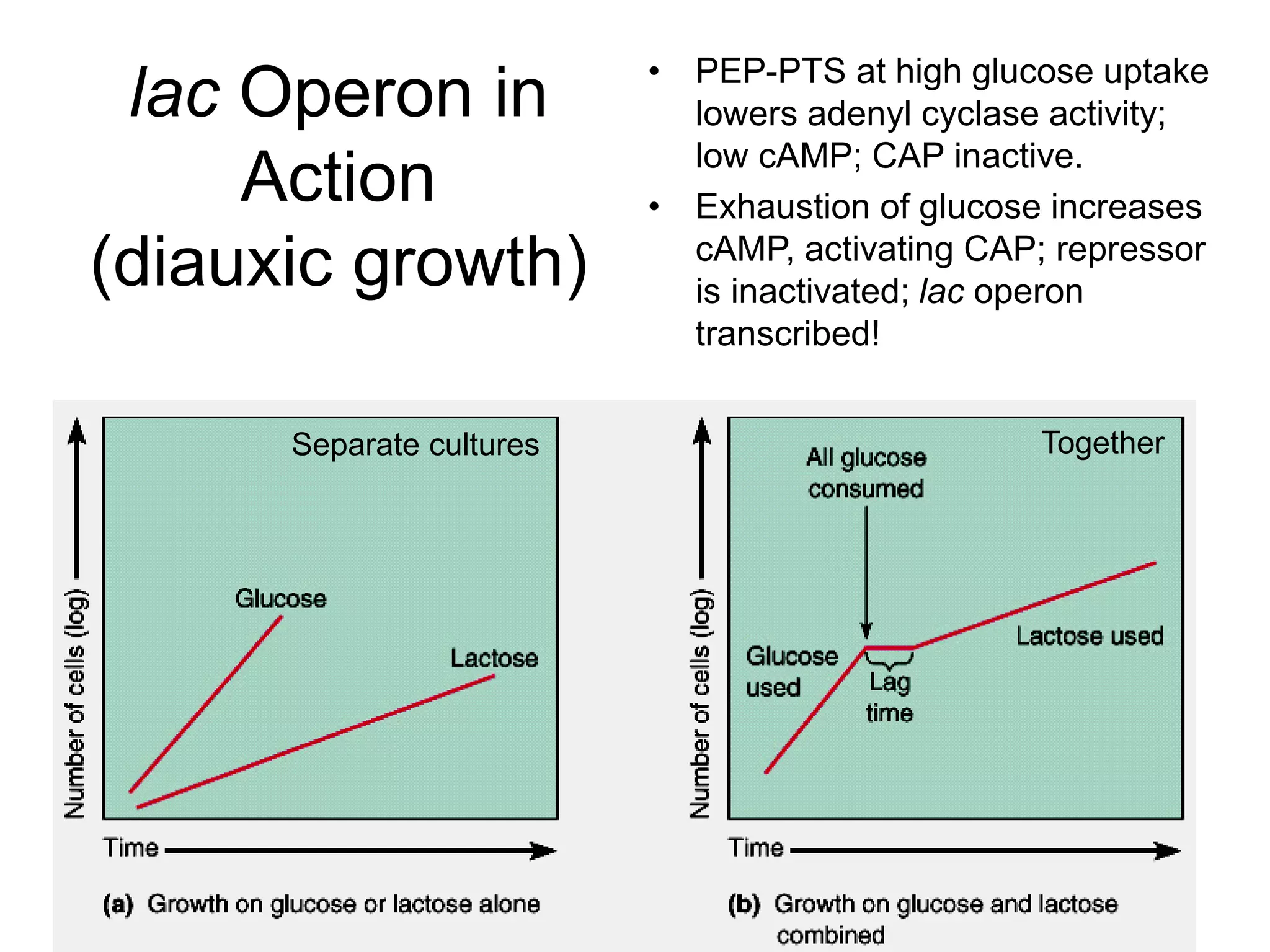
- Gene expression is controlled by promoter and operator regions located near structural genes organized into operons. Transcription can be regulated positively by activators or negatively by repressors binding the operator.
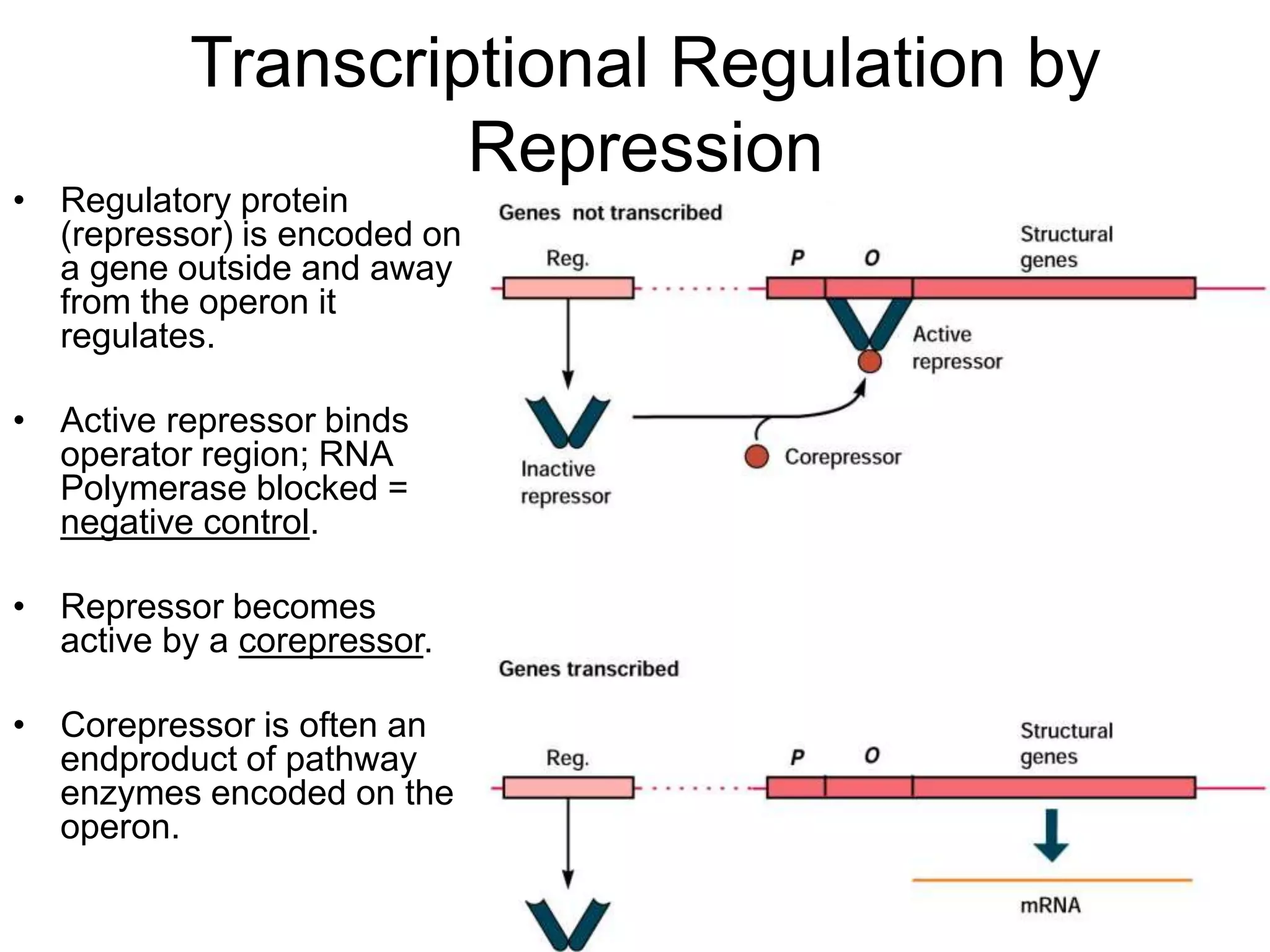
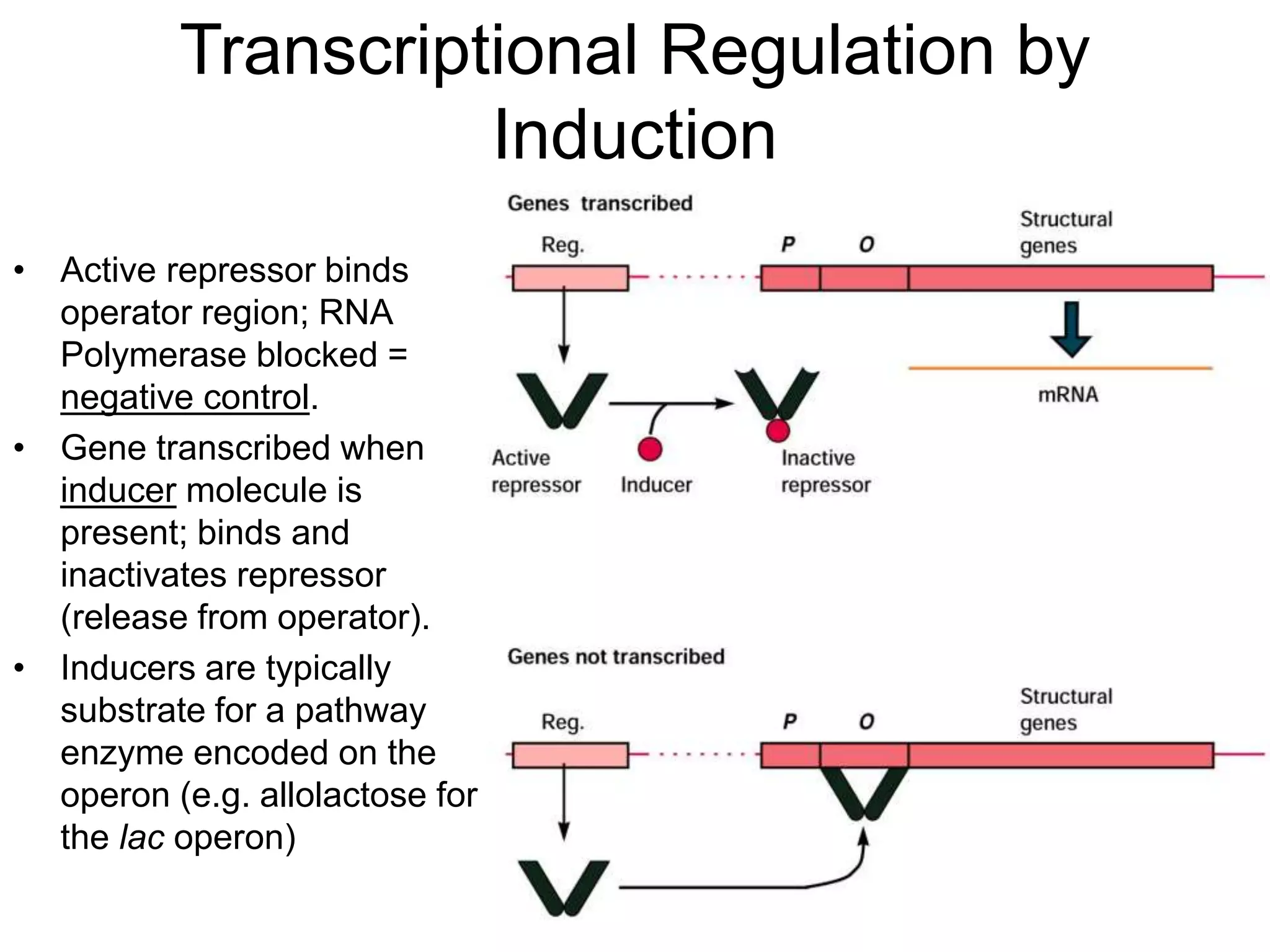
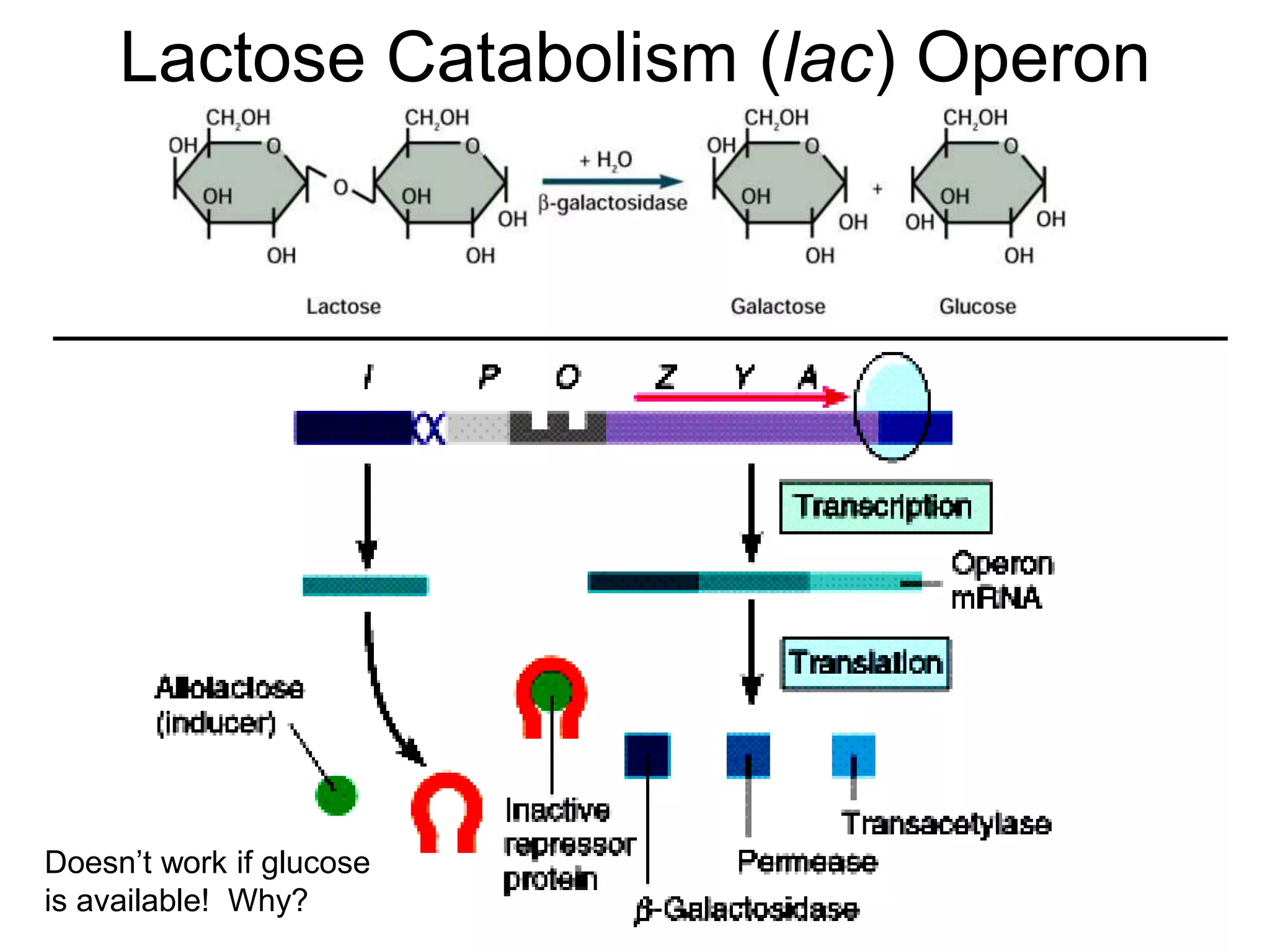
- Repression involves a repressor protein binding the operator and blocking transcription until an inducer molecule inactivates the repressor. Induction allows transcription in the presence of an inducer like allolactose.
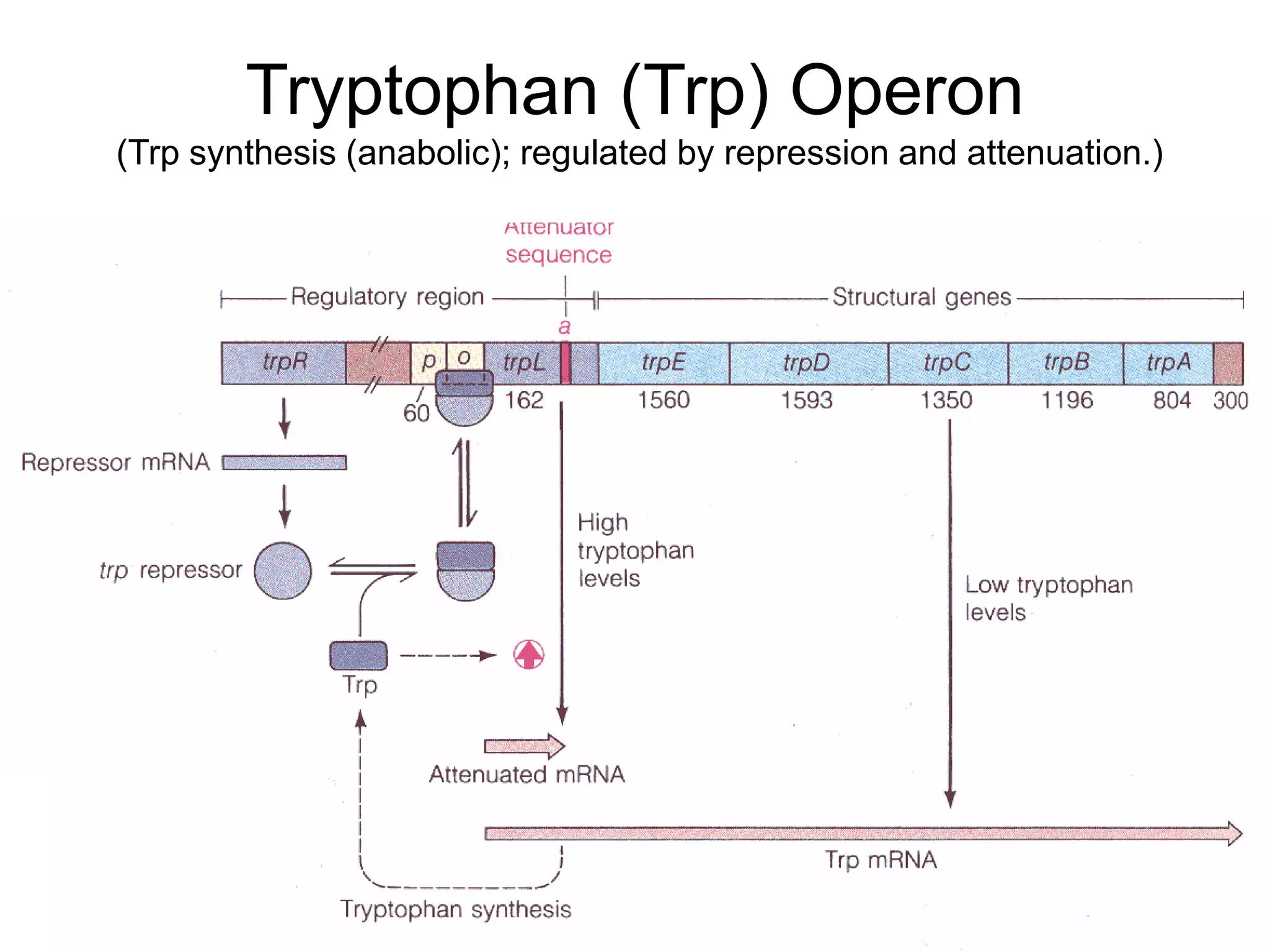
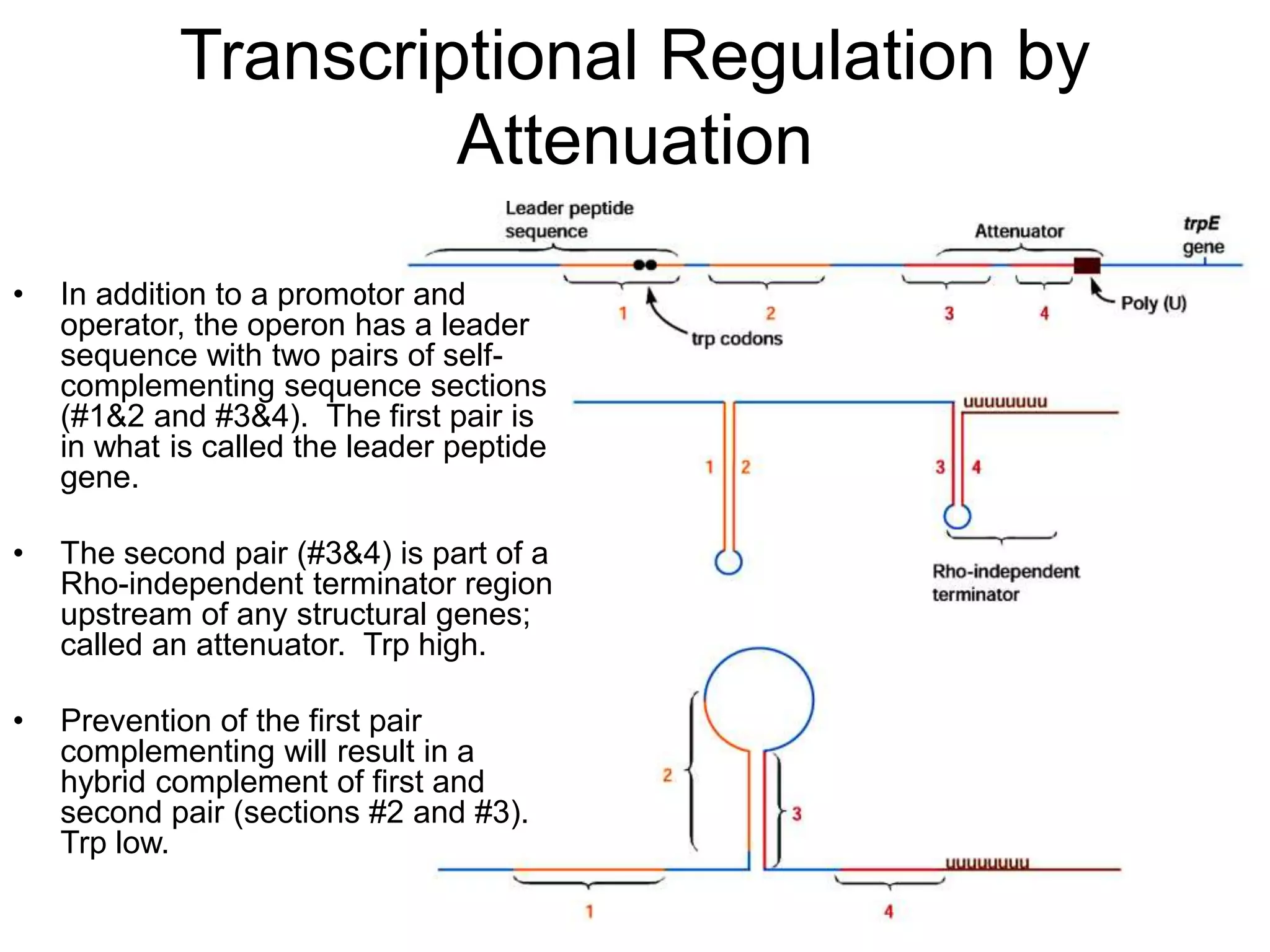
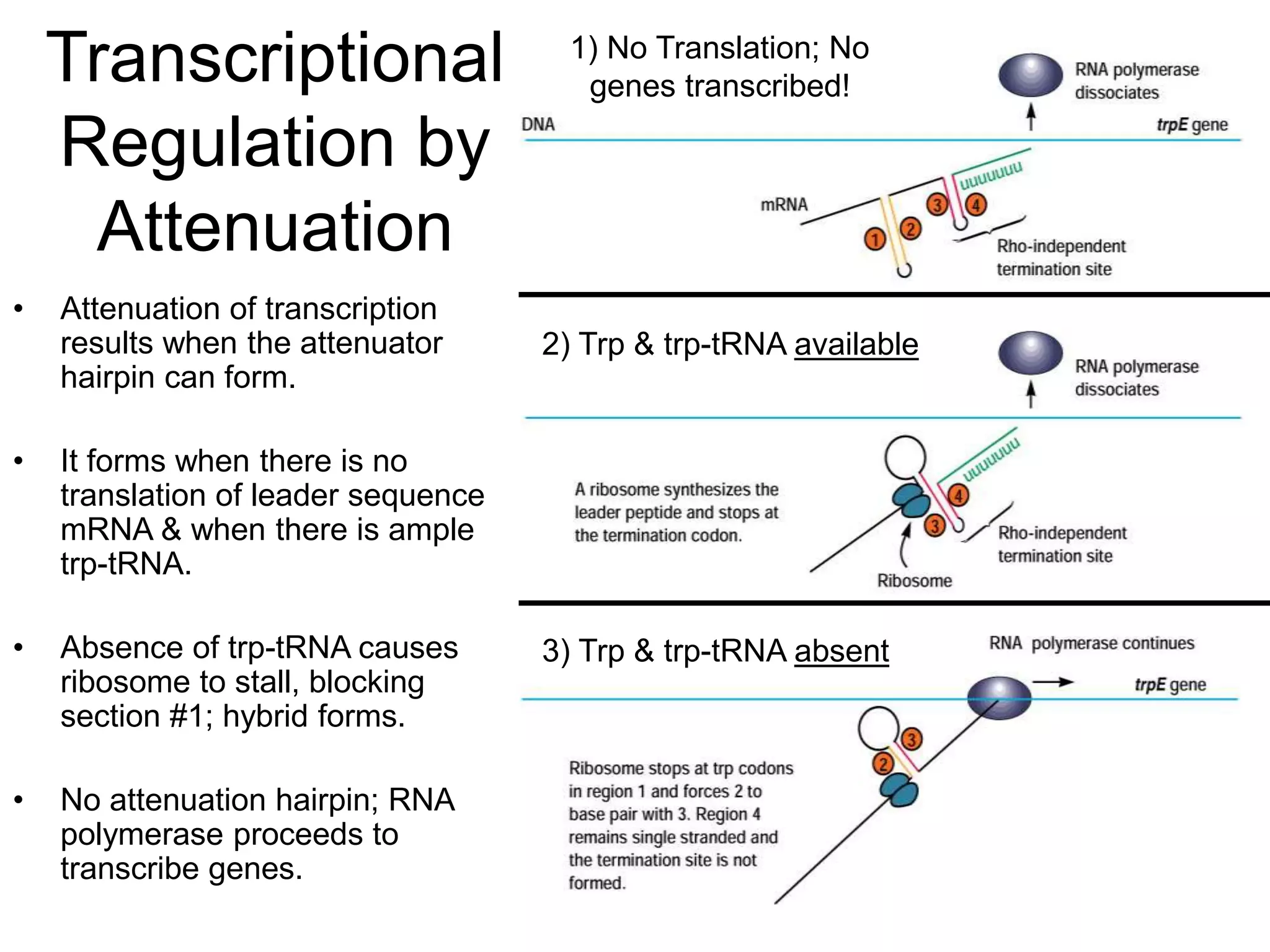
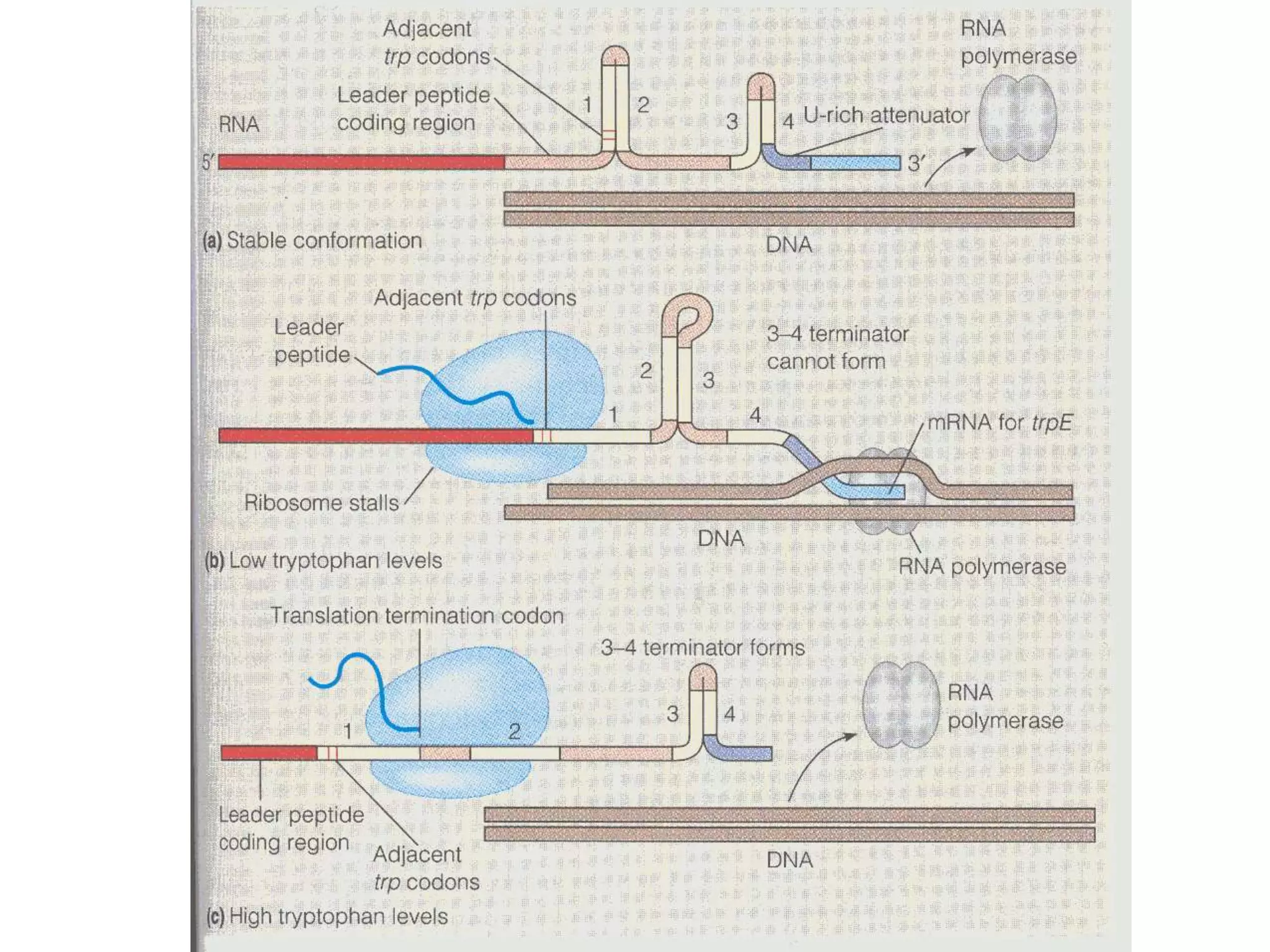
- Attenuation regulates transcription based on whether a ribosome stalls while translating the leader peptide due to lack of a tRNA, allowing transcription, or whether it terminates, forming a hairpin to terminate transcription.