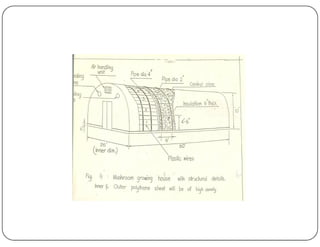
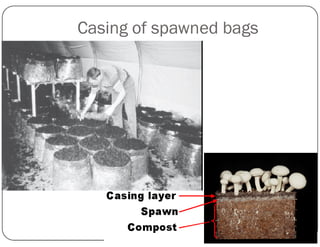
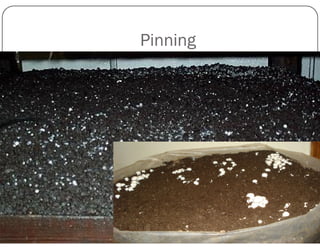
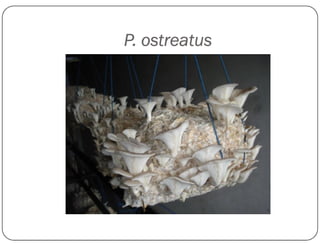
This document discusses mushroom cultivation techniques. It covers the background and economic potential of mushroom cultivation in India. It then describes the three step process of cultivating the most popular white button mushroom: 1) producing spawn, 2) preparing compost, and 3) cropping. It also discusses cultivation techniques for other mushrooms species grown in India like oyster mushroom, paddy straw mushroom, and milky mushroom. It concludes by emphasizing the need for more training, compost production units, and exploitation of medicinal mushrooms in India.