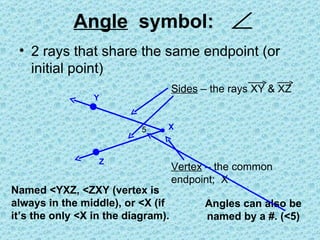
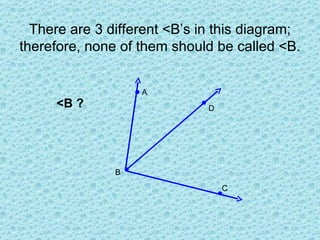
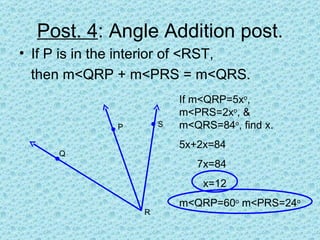
1. An angle is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint called the vertex. Angles can be named using symbols like ∠XYZ or a number like ∠5.
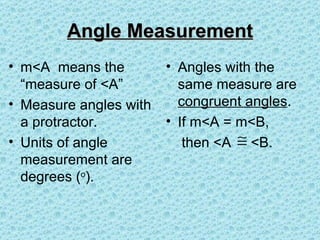
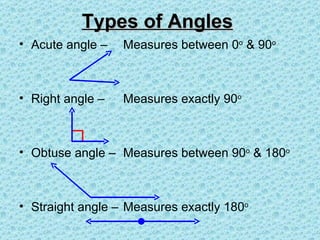
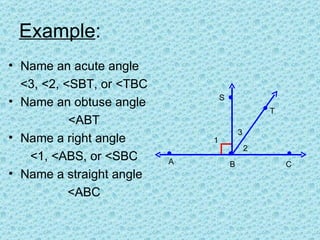
2. Angle measures are reported in degrees (°) as measured using a protractor. Angles with the same measure are congruent.
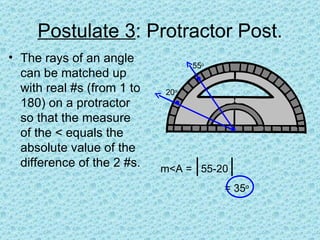
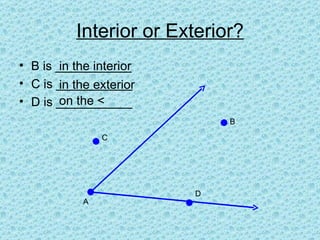
3. The measure of an angle is the absolute value of the difference between the two numbers the angle rays align with on a protractor. Interior angles are inside the angle lines, exterior are outside, and an angle on a line is on the angle.