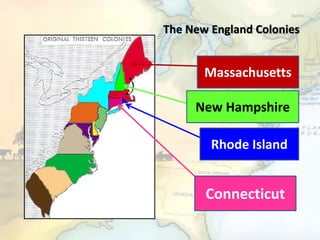
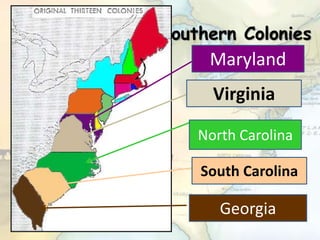
The document provides information about the founding, industries, cities, origins of names, and dates of statehood for each of the 13 original colonies. It discusses the different regions of colonies - New England, Middle, and Southern colonies - and some of the reasons the colonies were established, including religious freedom, opportunities for trade and manufacturing, and the profitable cultivation of cash crops. The development of democratic ideas that began in the colonies, such as the Mayflower Compact, Virginia House of Burgesses, and Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, established principles of self-government and representative democracy.