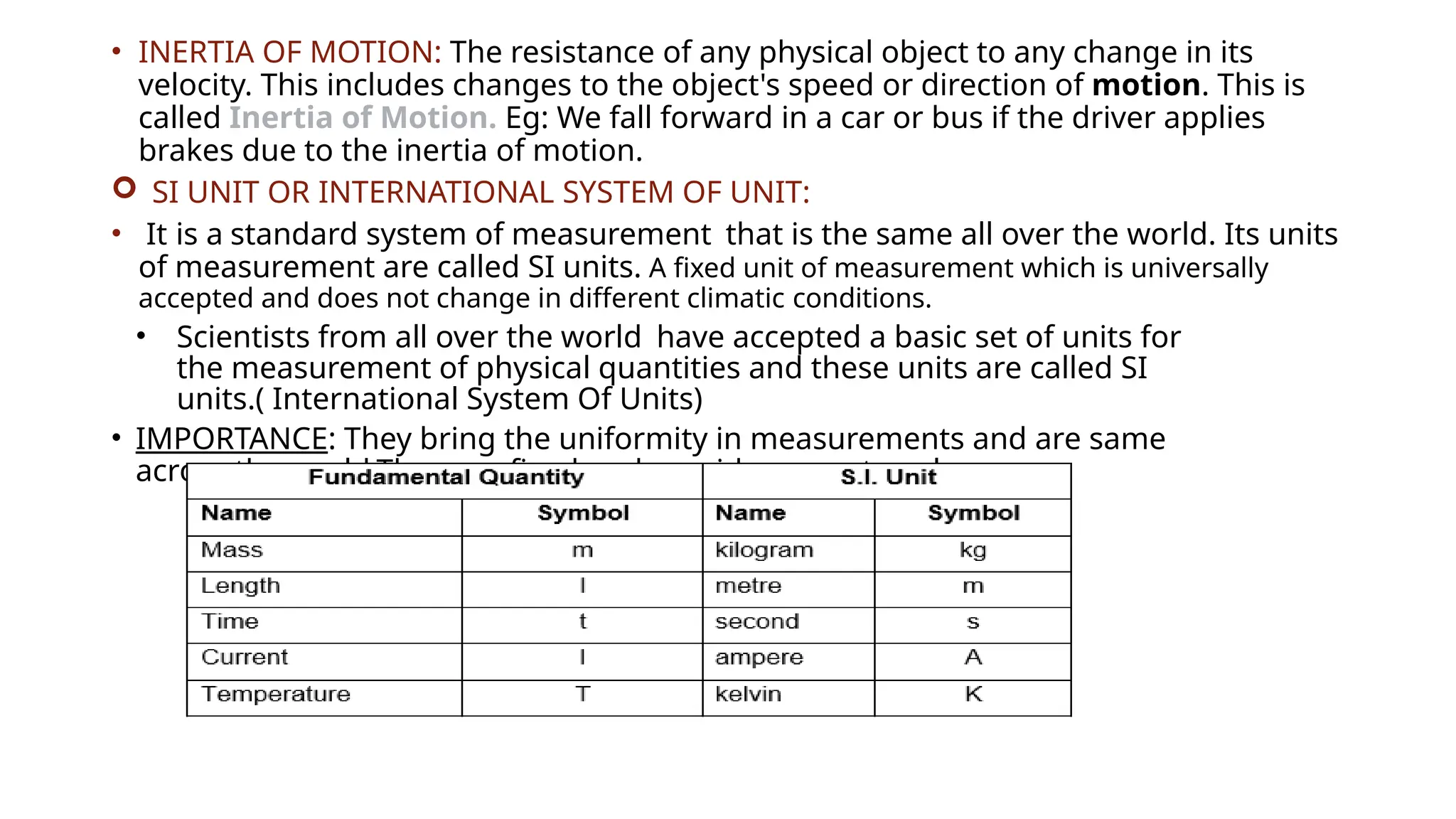
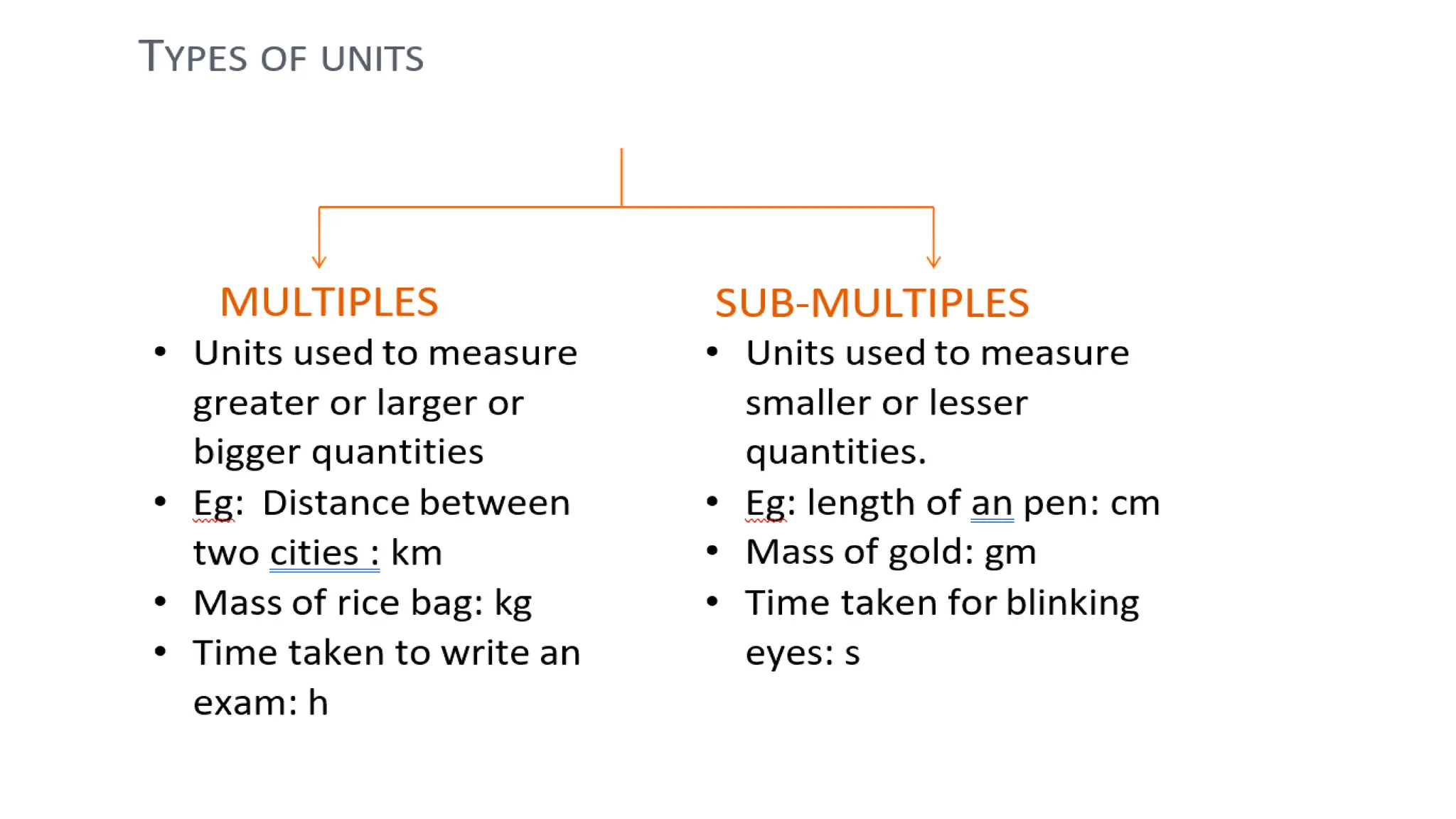
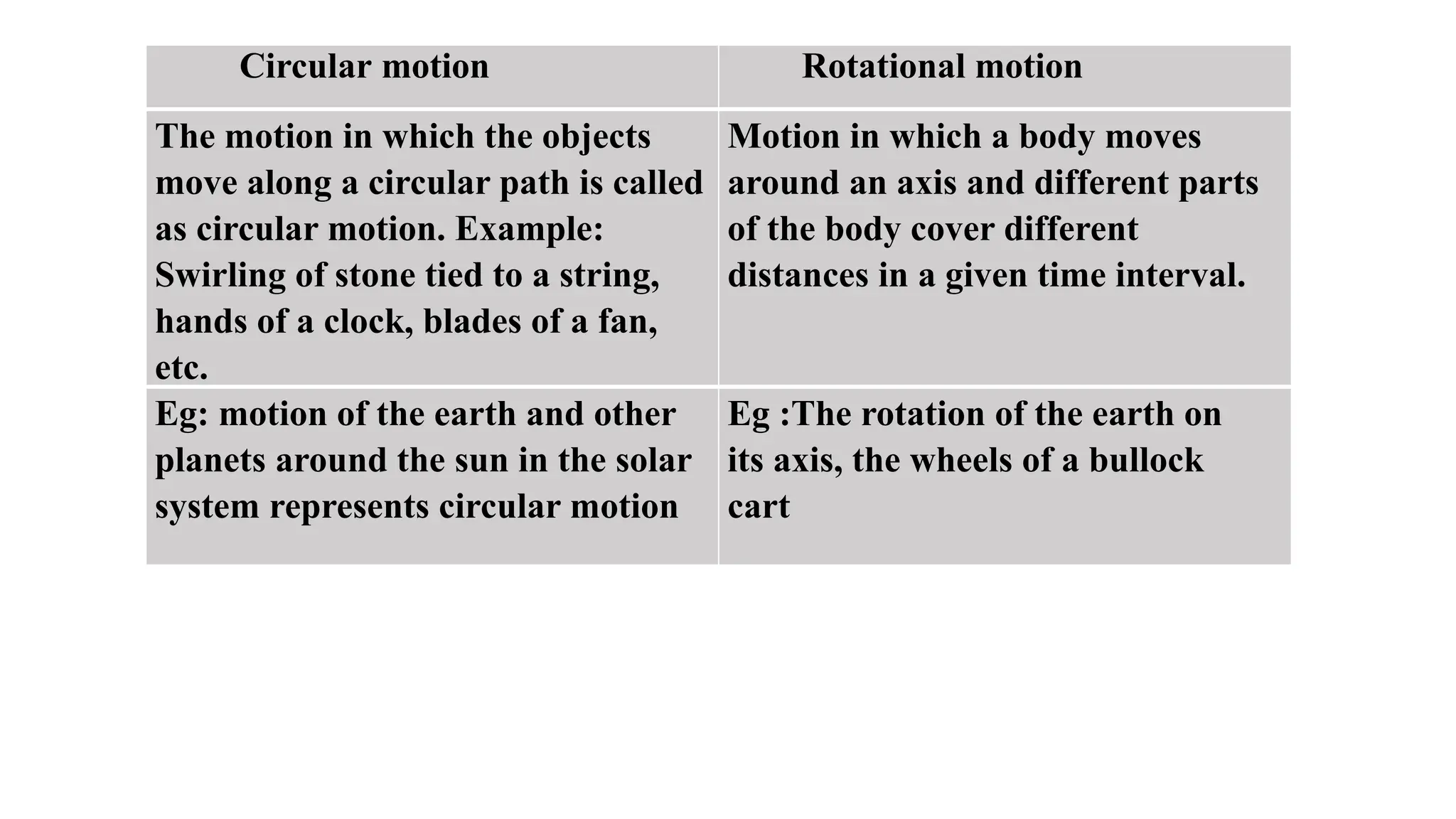
The document provides definitions and explanations of motion, rest, and inertia, along with essential concepts of measurements, including the International System of Units (SI units) and unit conversions. It discusses different types of motion such as rectilinear, curvilinear, circular, oscillatory, and random motion, as well as parallax error and the importance of standard measurement units. Additionally, it includes questions and answers about transportation, measurement, and various motion types, alongside numerical examples for conversions.