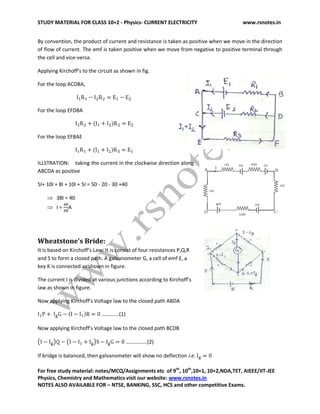
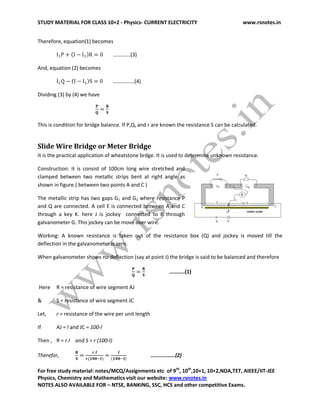
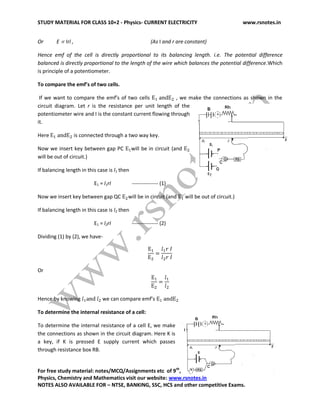
1. The document provides study material on current electricity, defining it as the branch of physics dealing with the flow of electric charges.
2. It defines electric current as the rate of flow of electric charges across any cross-sectional area of a conductor. Current is directly proportional to charge and inversely proportional to time.
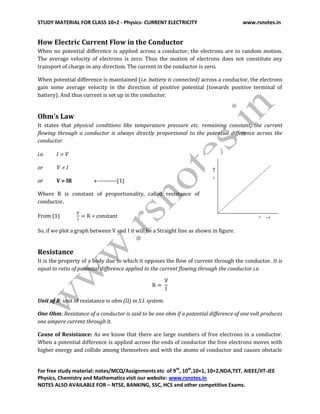
3. Ohm's law is described, stating that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, if the physical conditions like temperature and pressure remain constant.