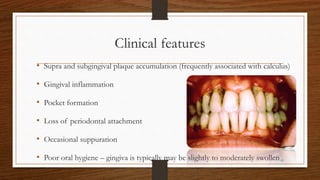
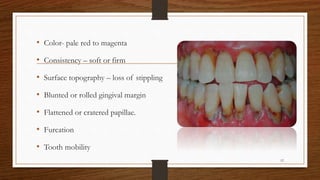
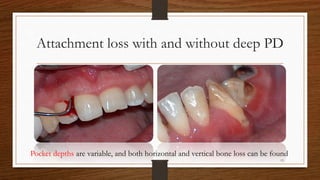
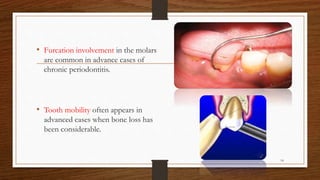
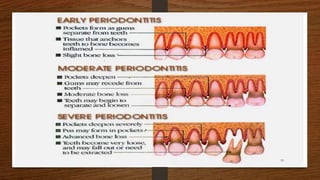
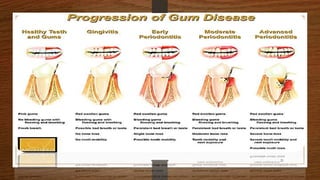
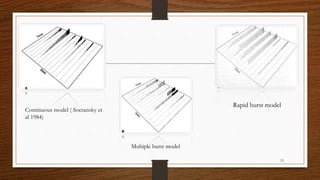
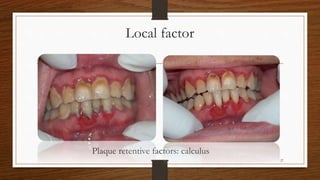
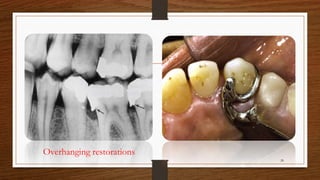
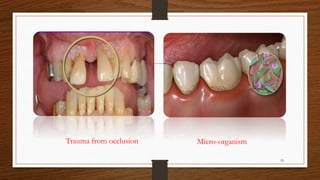
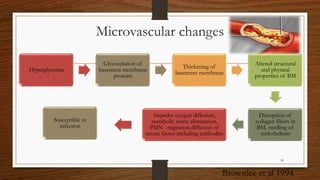
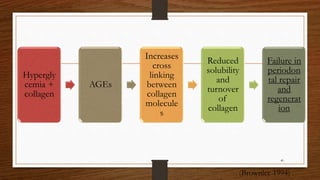
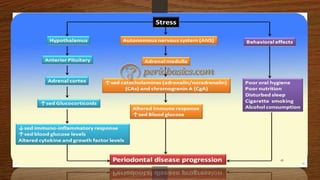
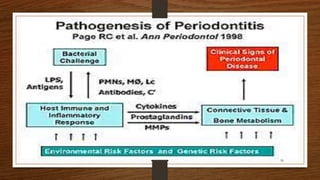
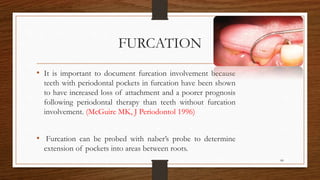
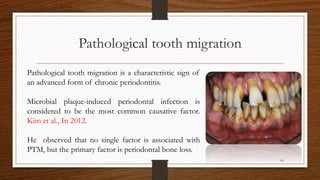
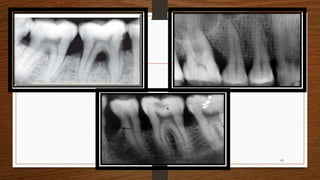
Chronic periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that causes the destruction of the tissues that support the teeth. It is caused by bacterial plaque accumulating at and below the gumline. It is characterized by pocket formation, attachment loss, and bone loss. The disease progresses slowly over time and is generally classified as slight, moderate, or severe depending on the amount of attachment loss. A clinical diagnosis involves measuring pocket depths and looking for signs of inflammation, recession, and bone loss. Radiographs can also help assess bone level changes over time. Risk factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and genetic factors. Treatment involves nonsurgical debridement or surgical procedures to reduce pockets and regenerate lost tissues.







































































![• PROGNOSTIK [Dentsply]
It detects the presence of serine proteinase and elastase in
GCF samples.
• PERIOGARD [Colgate]
It detects the presence of Aspartate Aminotransferase in GCF
sample.
• EVALUSITE
This chair side immunoassay detects periodontal pathogens
such as Aa commitans , P gingivalis , P intermedia .
90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicperiodontitis-221024065918-23da8ad0/85/chronic-periodontitis-pptx-90-320.jpg)
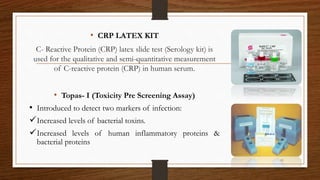

![• BIOLISE
Recently a software has been made Biolise [SLT-Lab instruments, Craitsheim,
Germany] which is used to detect the elastase activity in GCF.
[Hermann et al 2001].
• GLUCOMETER
It is used for Blood glucose measurements using gingival crevicular blood.
93](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicperiodontitis-221024065918-23da8ad0/85/chronic-periodontitis-pptx-93-320.jpg)