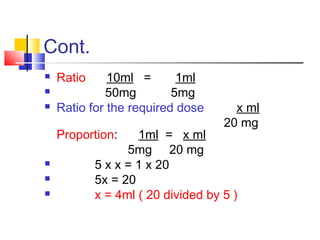
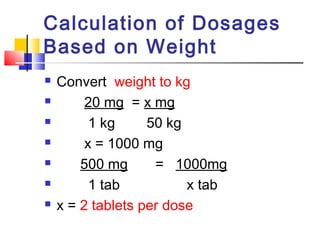
The document discusses various methods for calculating medication dosages using ratios, proportions, conversions between measurement systems, and calculations based on weight. It provides examples of calculating dosage amounts from given concentrations in vials or syringes. It also addresses calculations for intravenous infusions and piggyback infusions, including drip rates and time required.