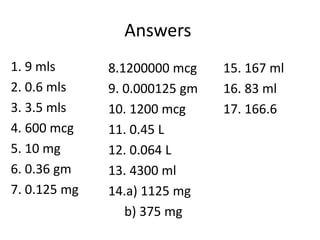
This document outlines how to perform various drug calculations, including metric conversions, dose calculations based on patient weight, and infusion rate calculations. It provides examples of each type of calculation and questions to practice the skills. Metric conversions involve moving the decimal place to convert between kg, g, mg, and mcg units. Dose is calculated by multiplying the prescribed mg dose by the patient's weight in kg. Infusion rates are calculated by dividing the total volume by the number of hours to get a hourly rate in ml/hr and then converting to drops per minute based on the giving set calibration.