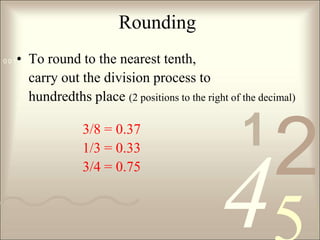
This document provides a math review for nursing students, summarizing guidelines for abbreviations, rounding, volume and concentration, conversions, setting up dosage calculation problems, and other topics. It discusses acceptable abbreviations, rounding to the nearest tenth, relationships between volume, concentration and dosage, common conversions between metric and other systems, and how to set up and solve dosage problems using dimensional analysis. It also reviews dividing doses, reconstituting drugs, and tips for taking quizzes.