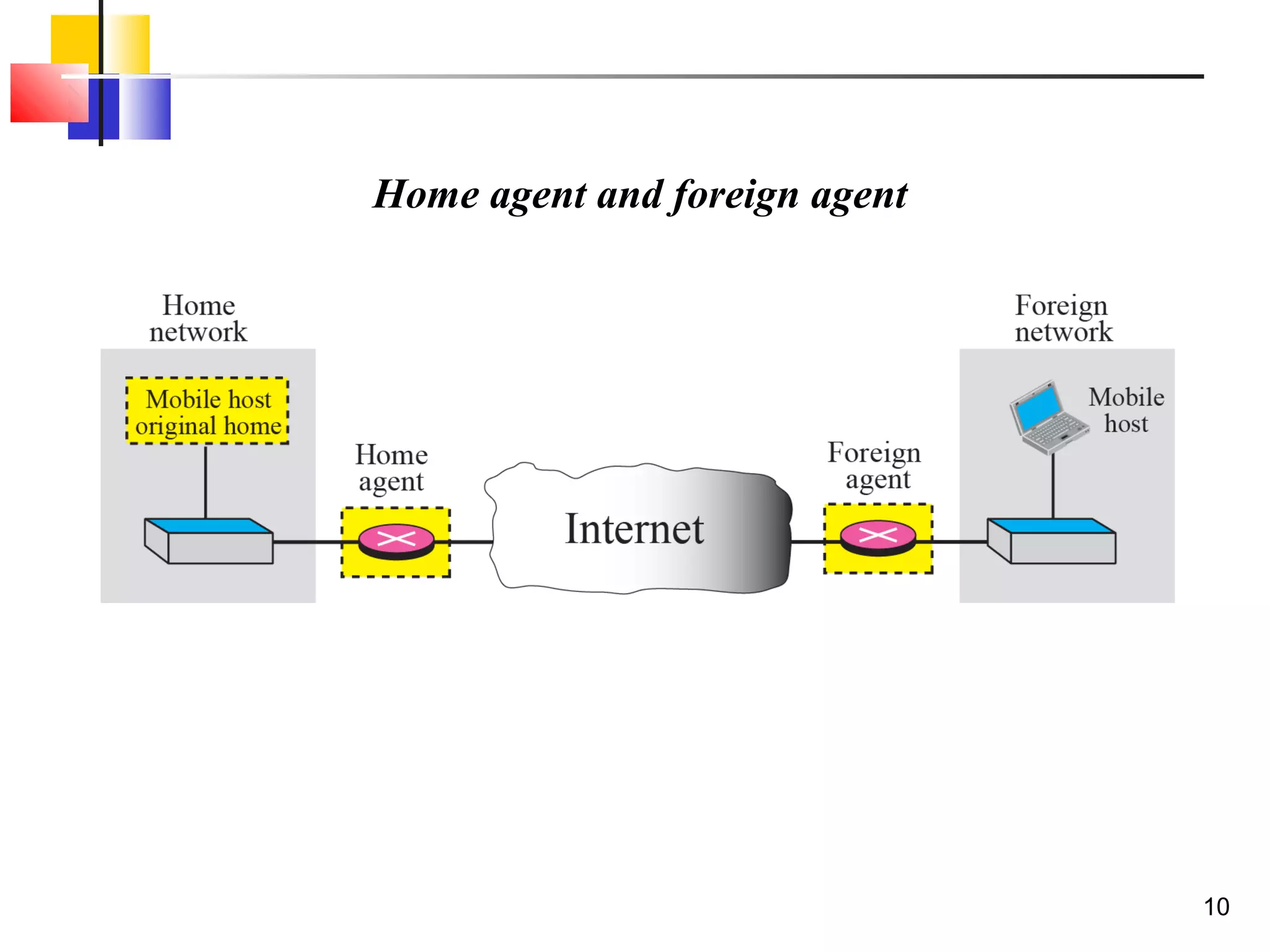
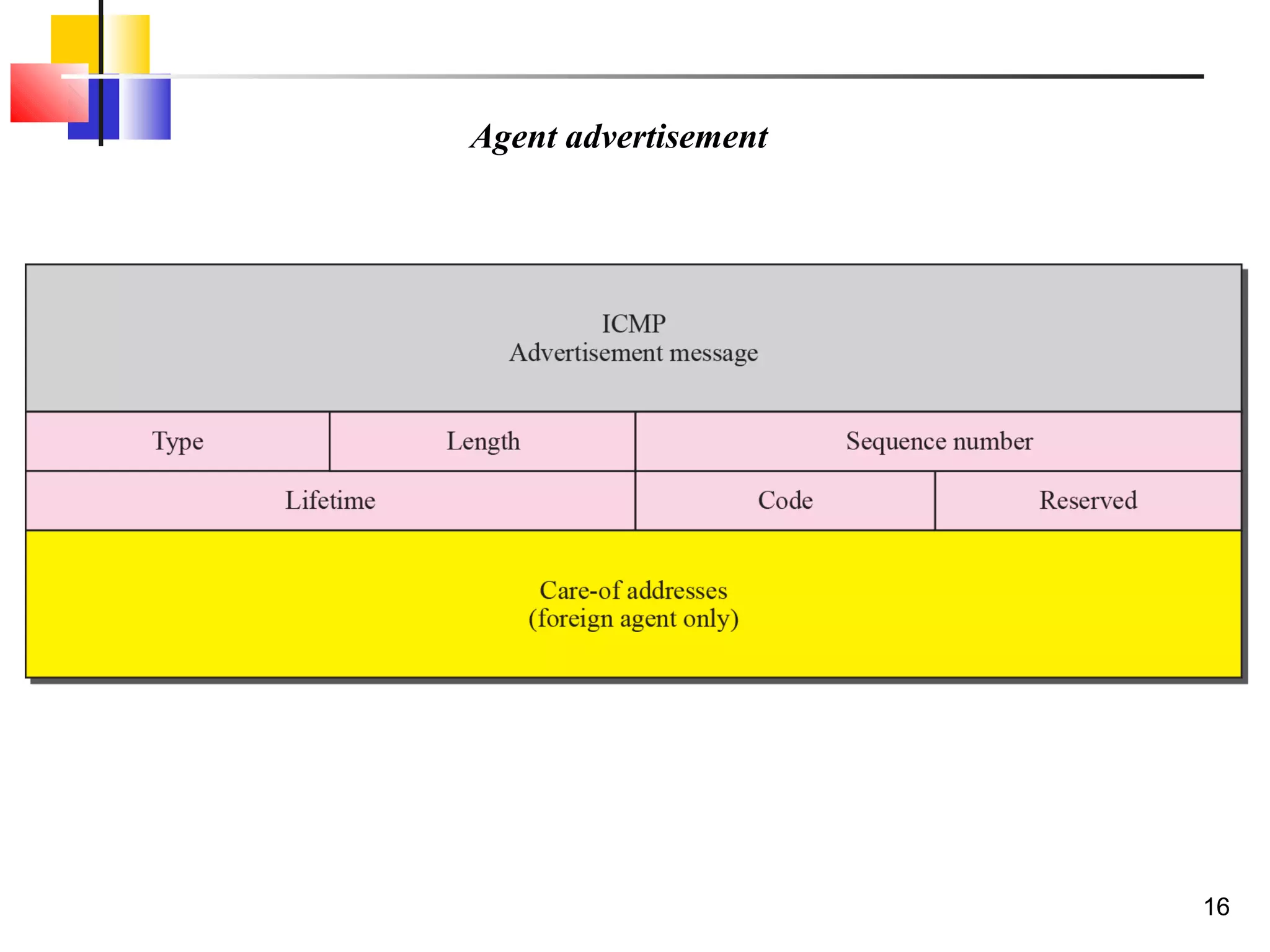
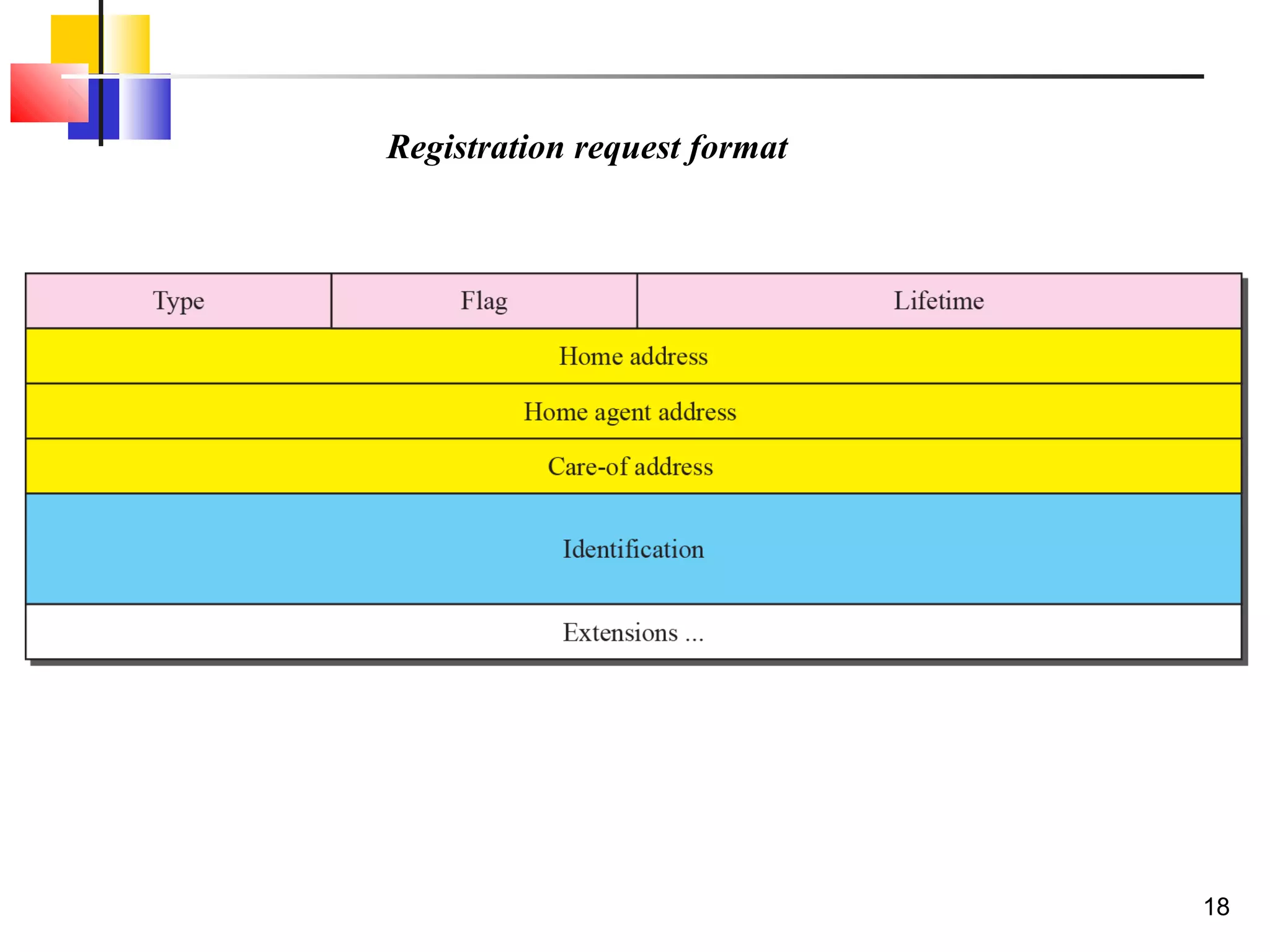
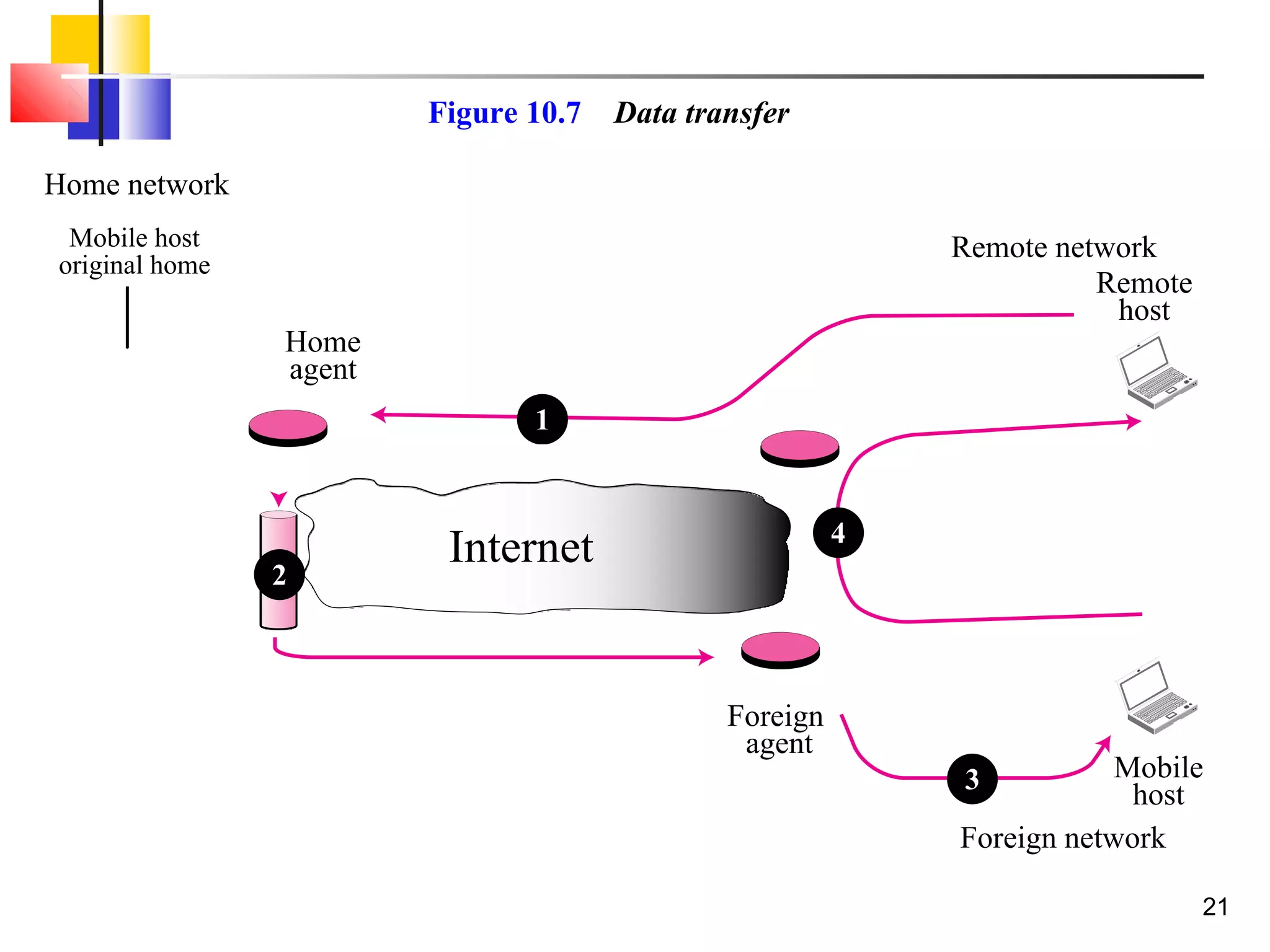
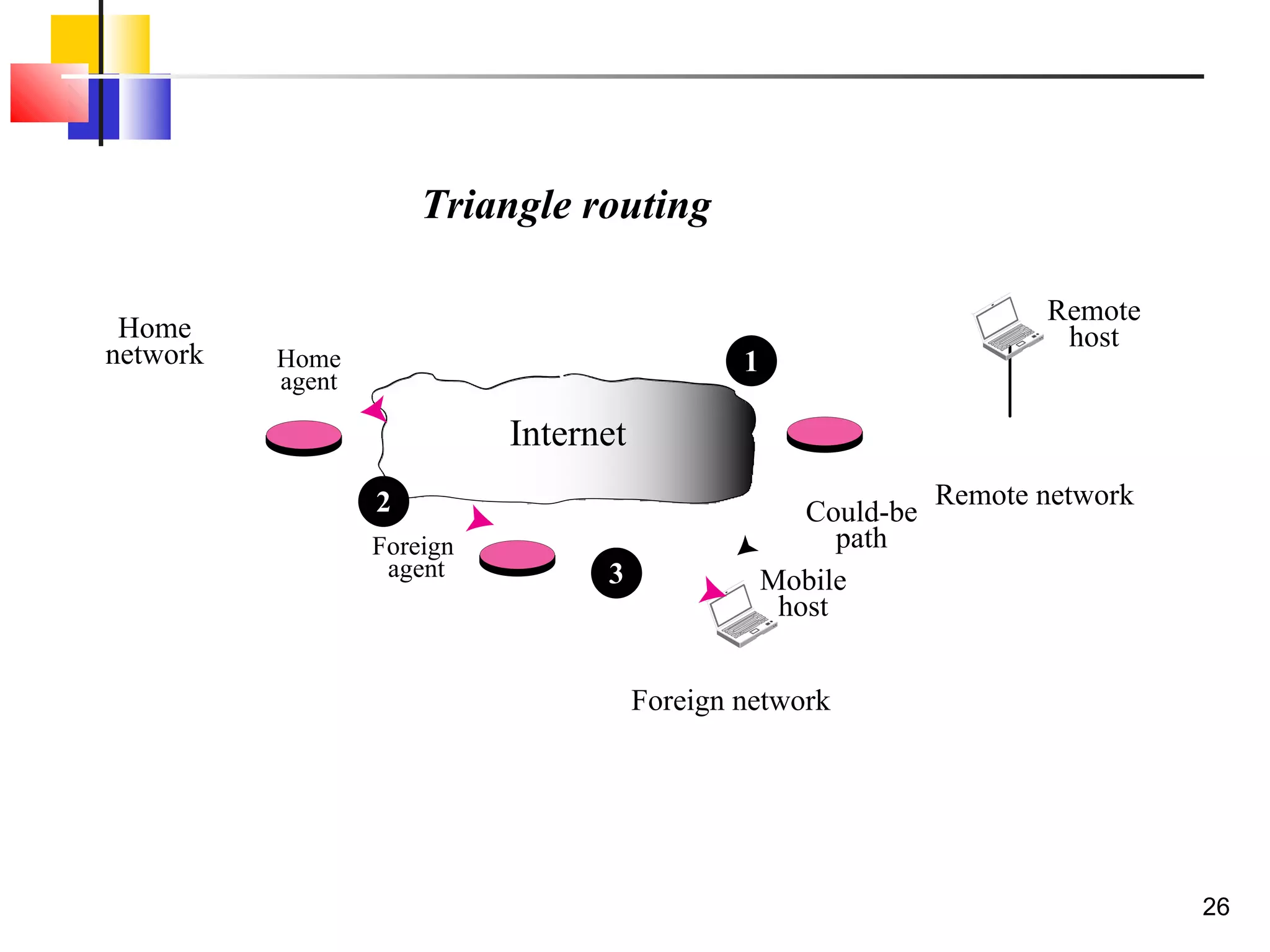
This document discusses the key aspects of mobile IP, including addressing, agents, communication phases, and inefficiencies. It explains that mobile IP uses two addresses - a home address and care-of address. Agents (home and foreign) are used to route traffic to mobile hosts as they change locations. Communication involves three phases - discovery, registration, and data transfer. Inefficiencies can occur through double crossing routing or triangle routing rather than more direct paths.