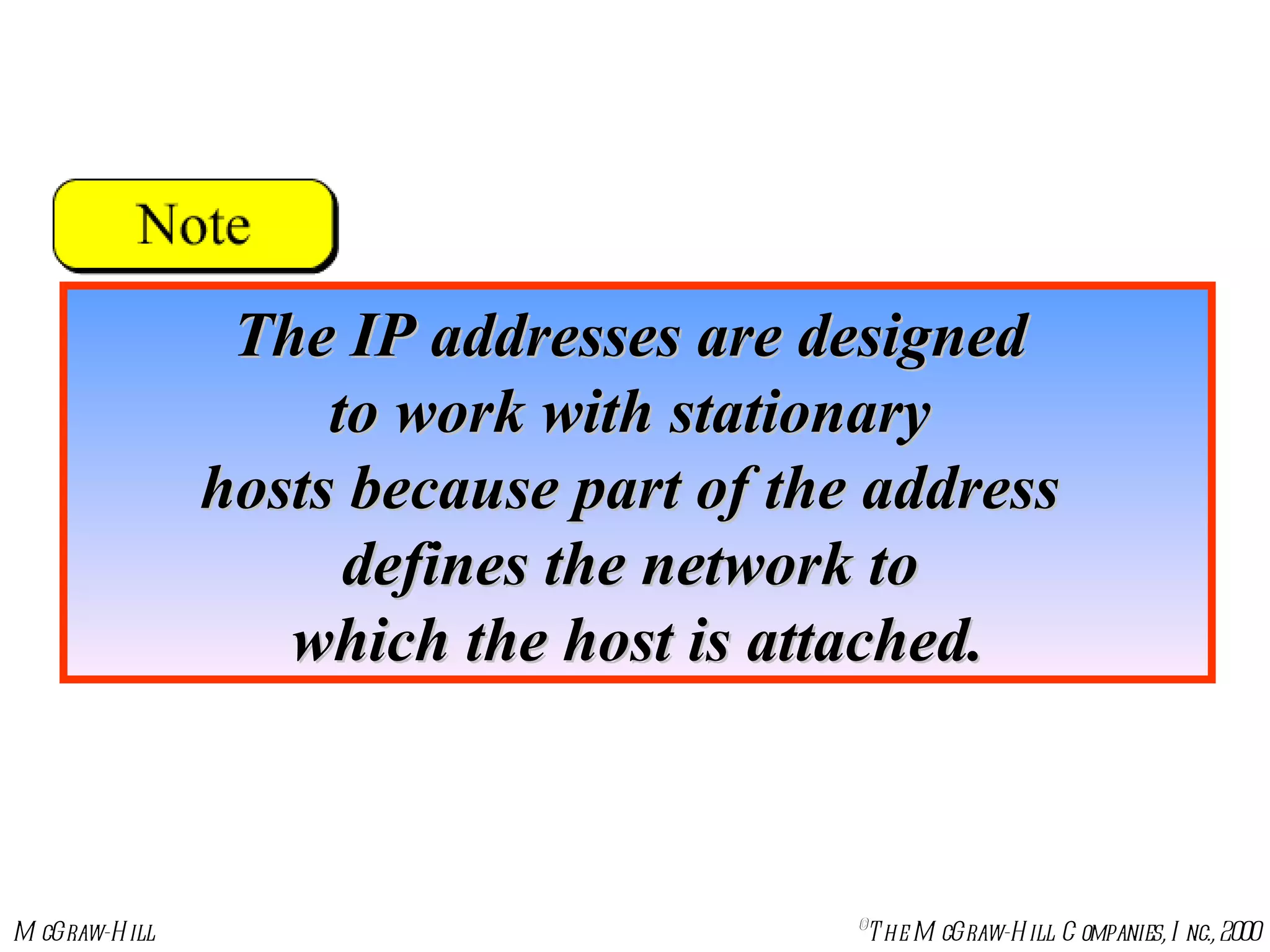
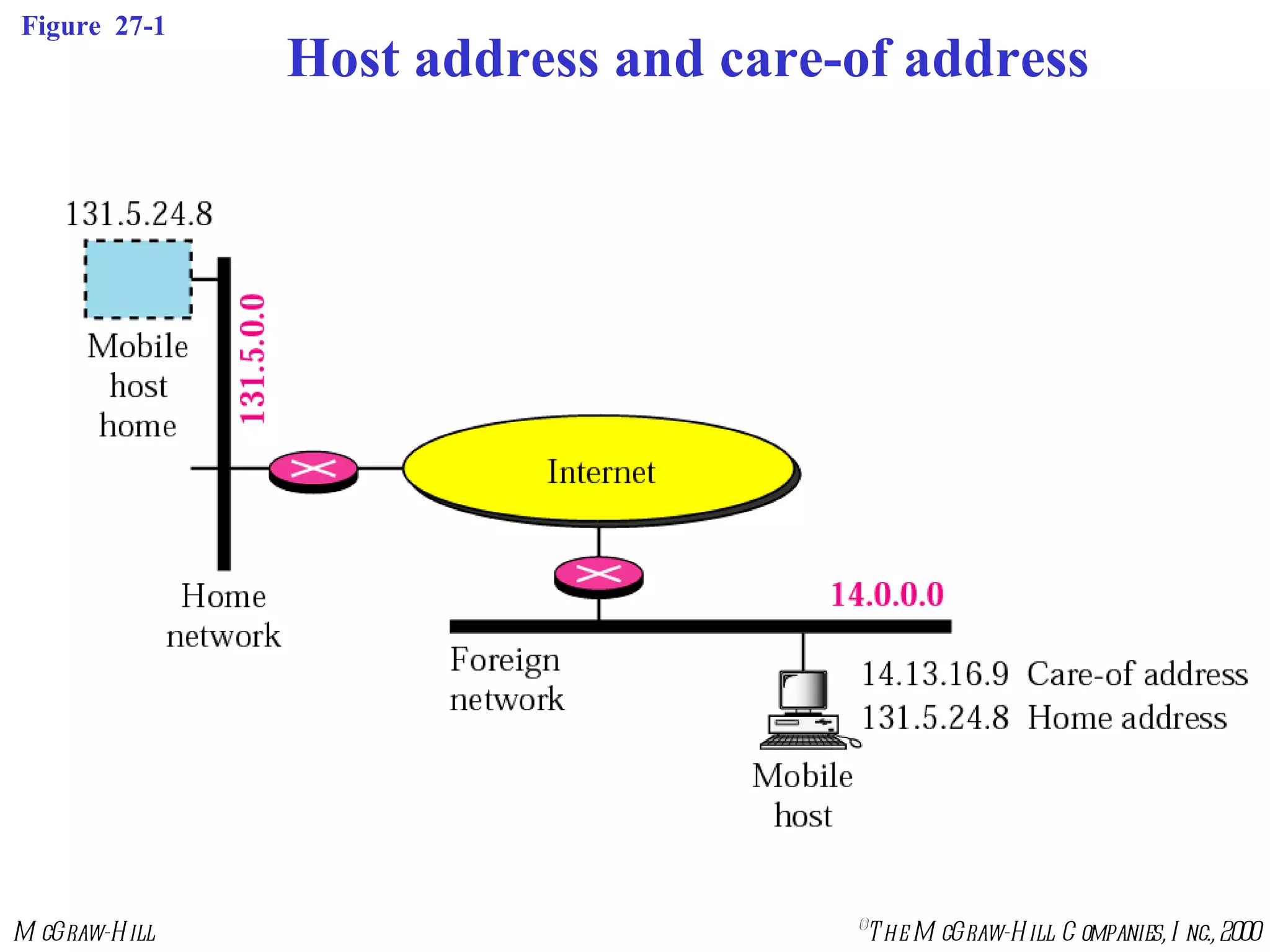
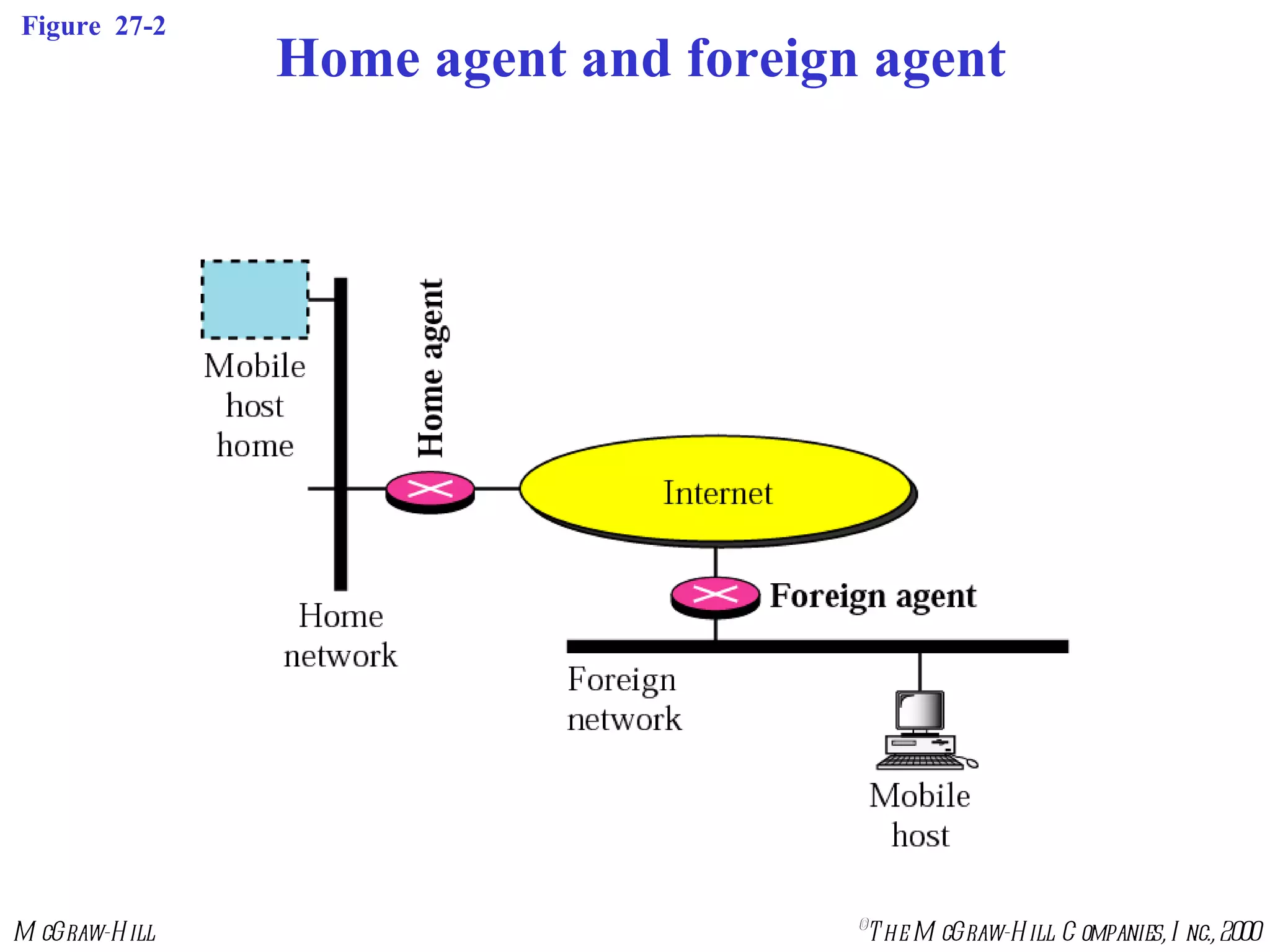
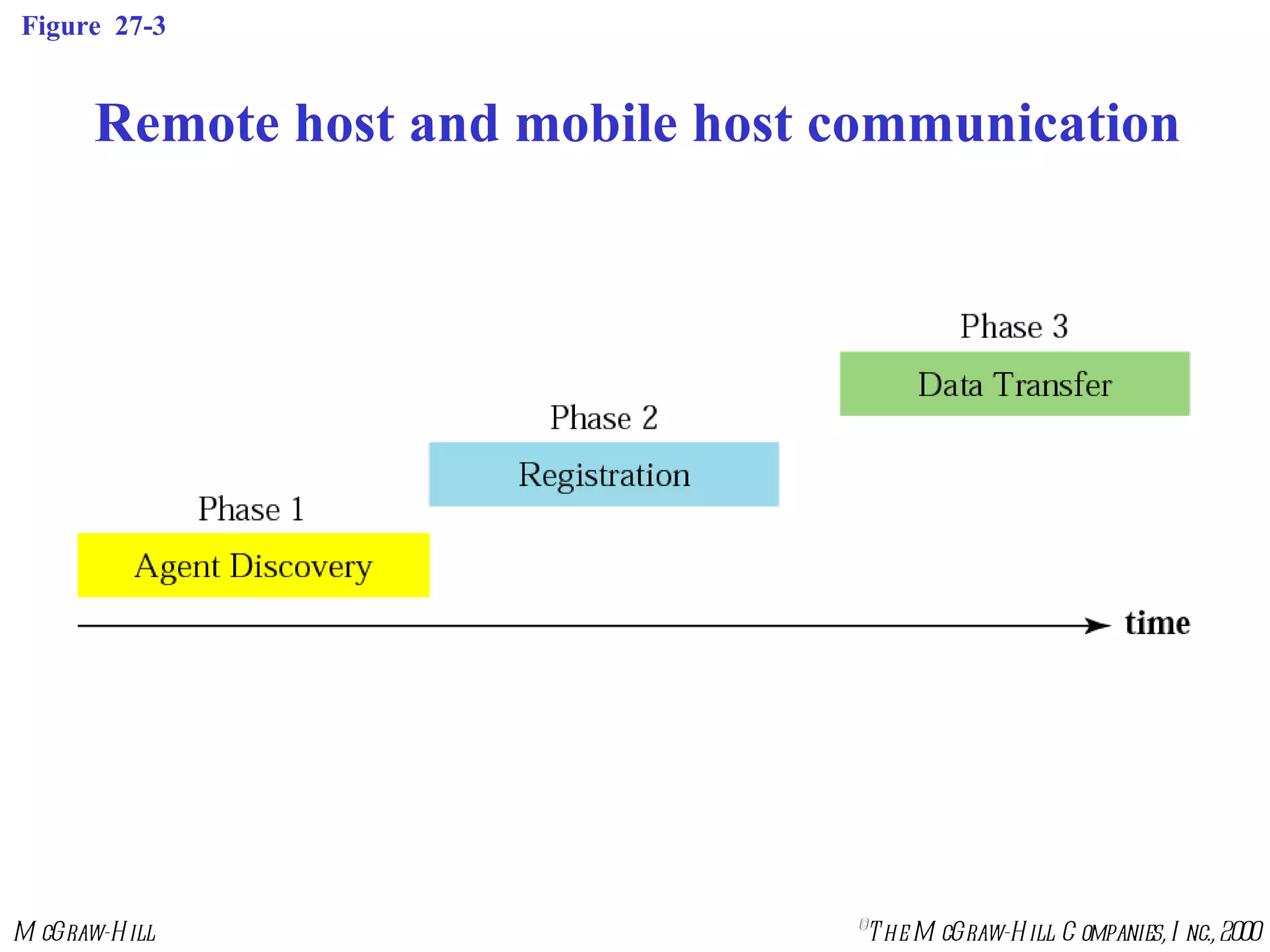
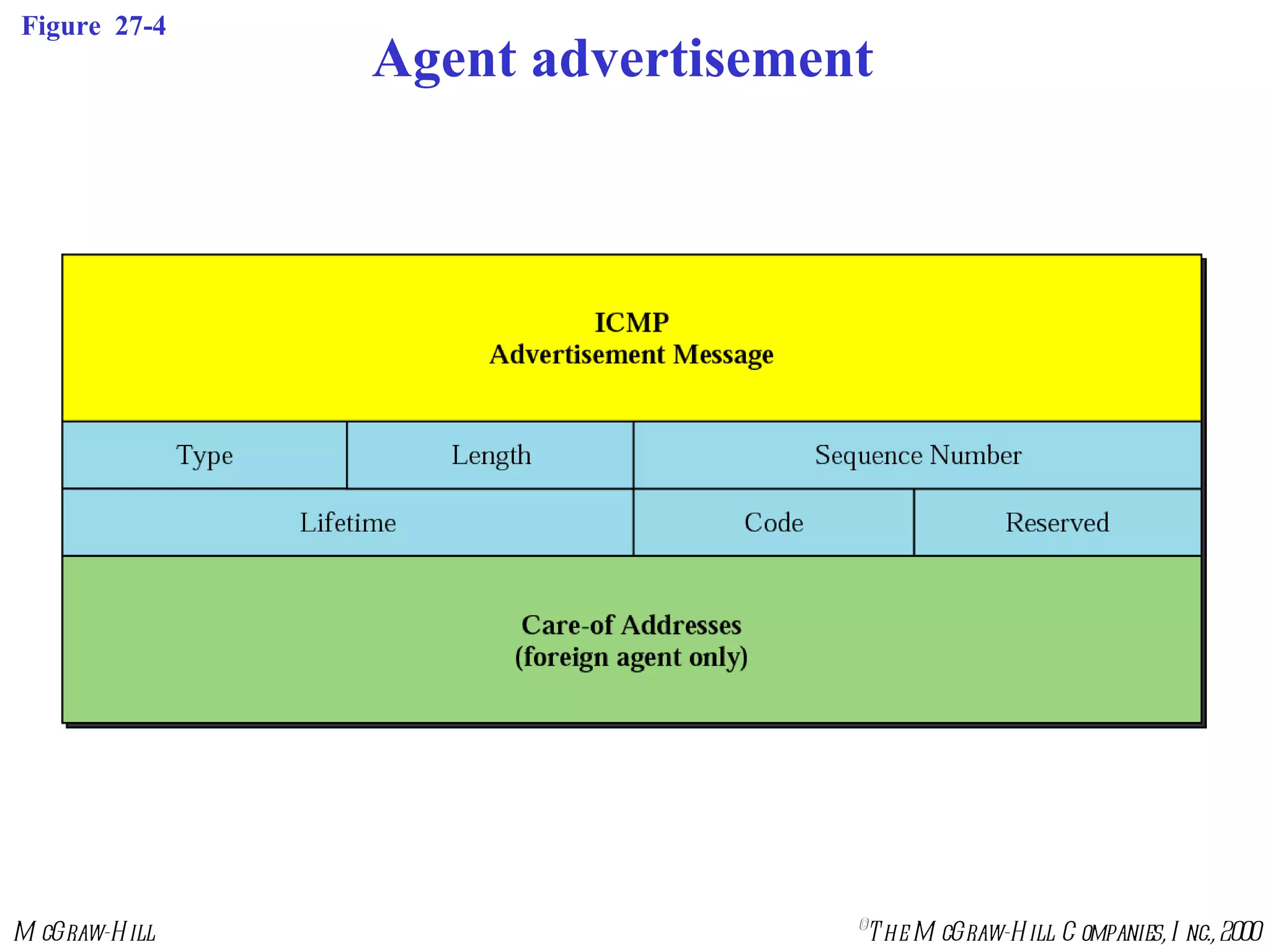
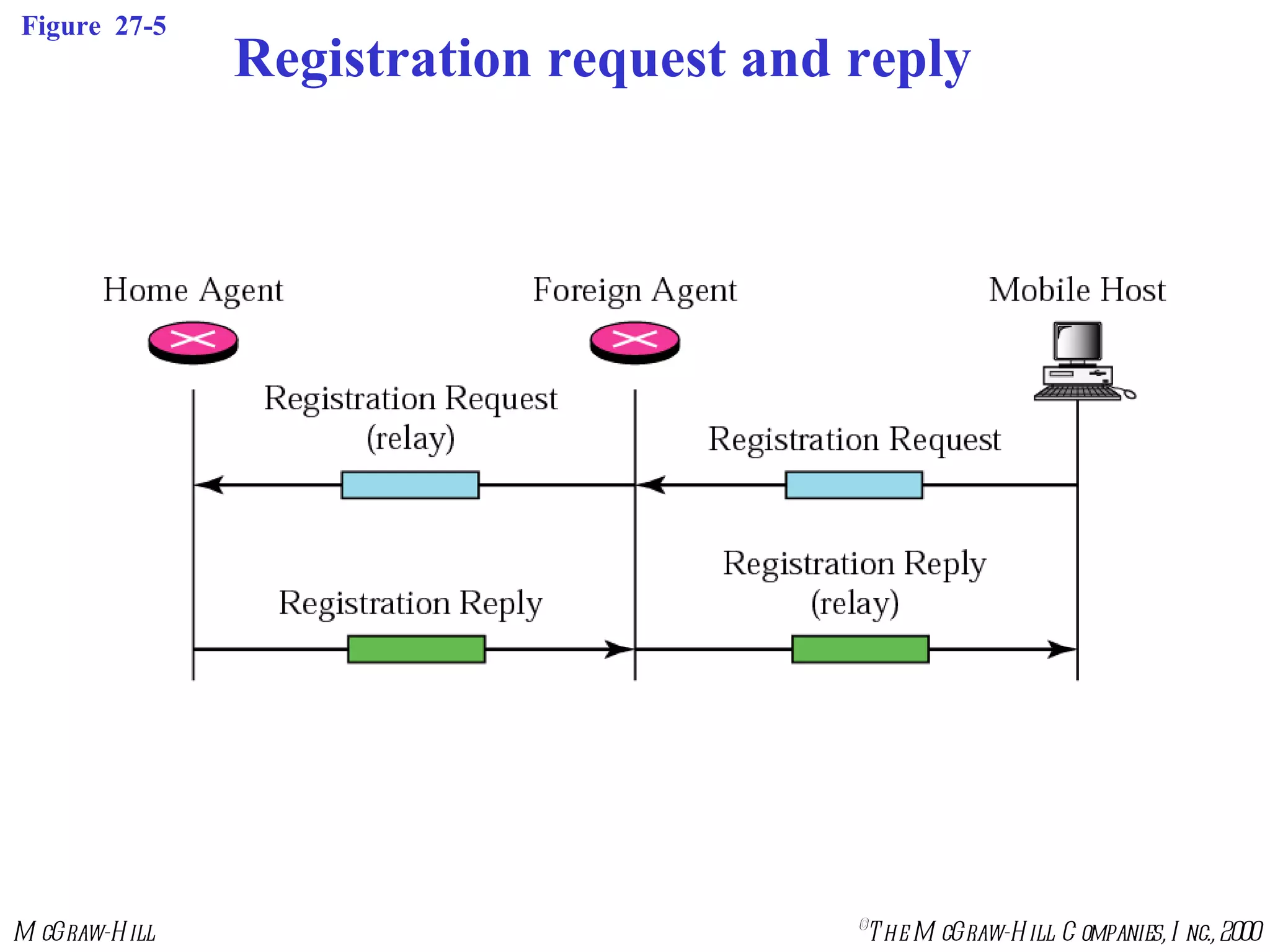
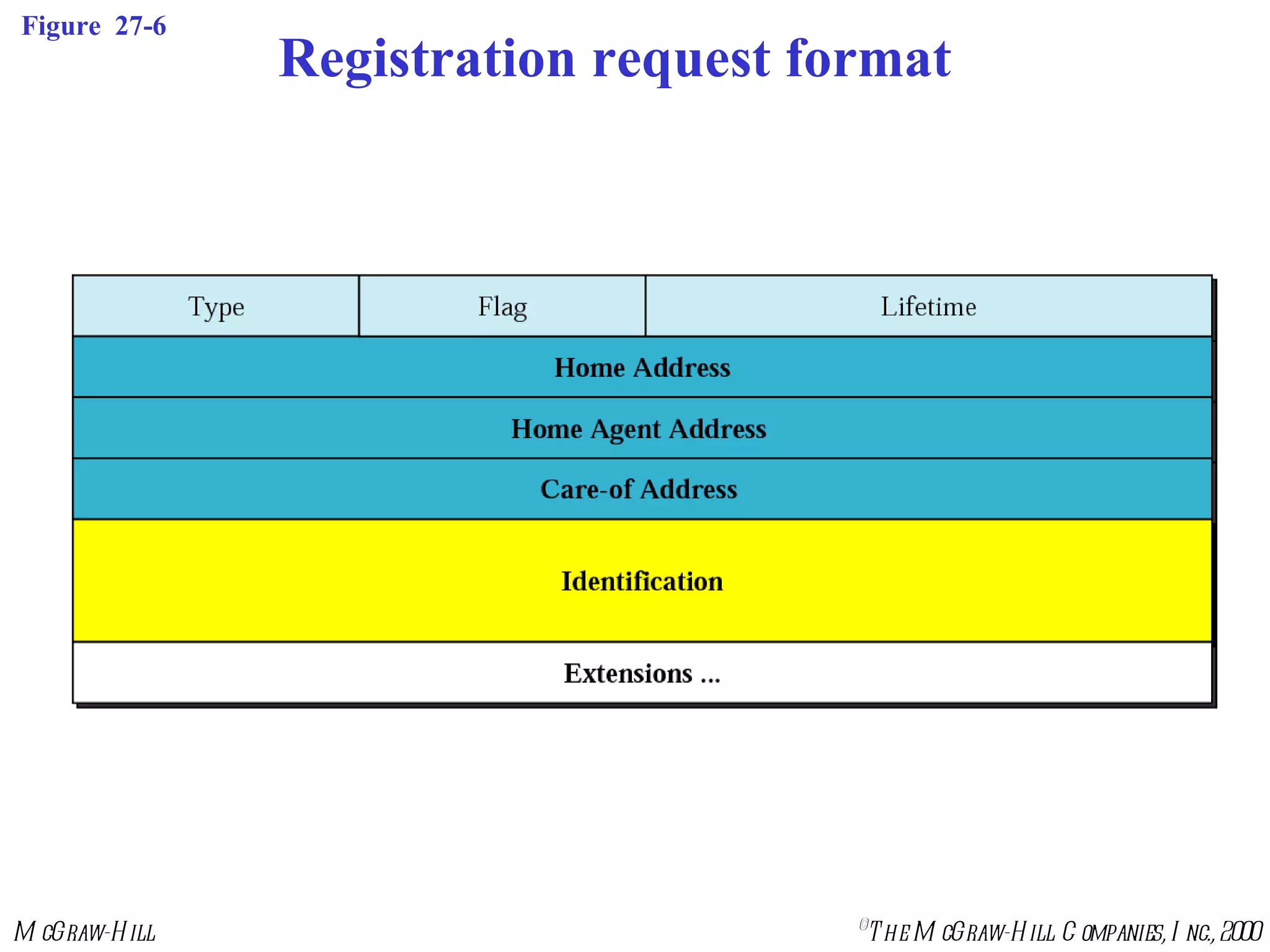
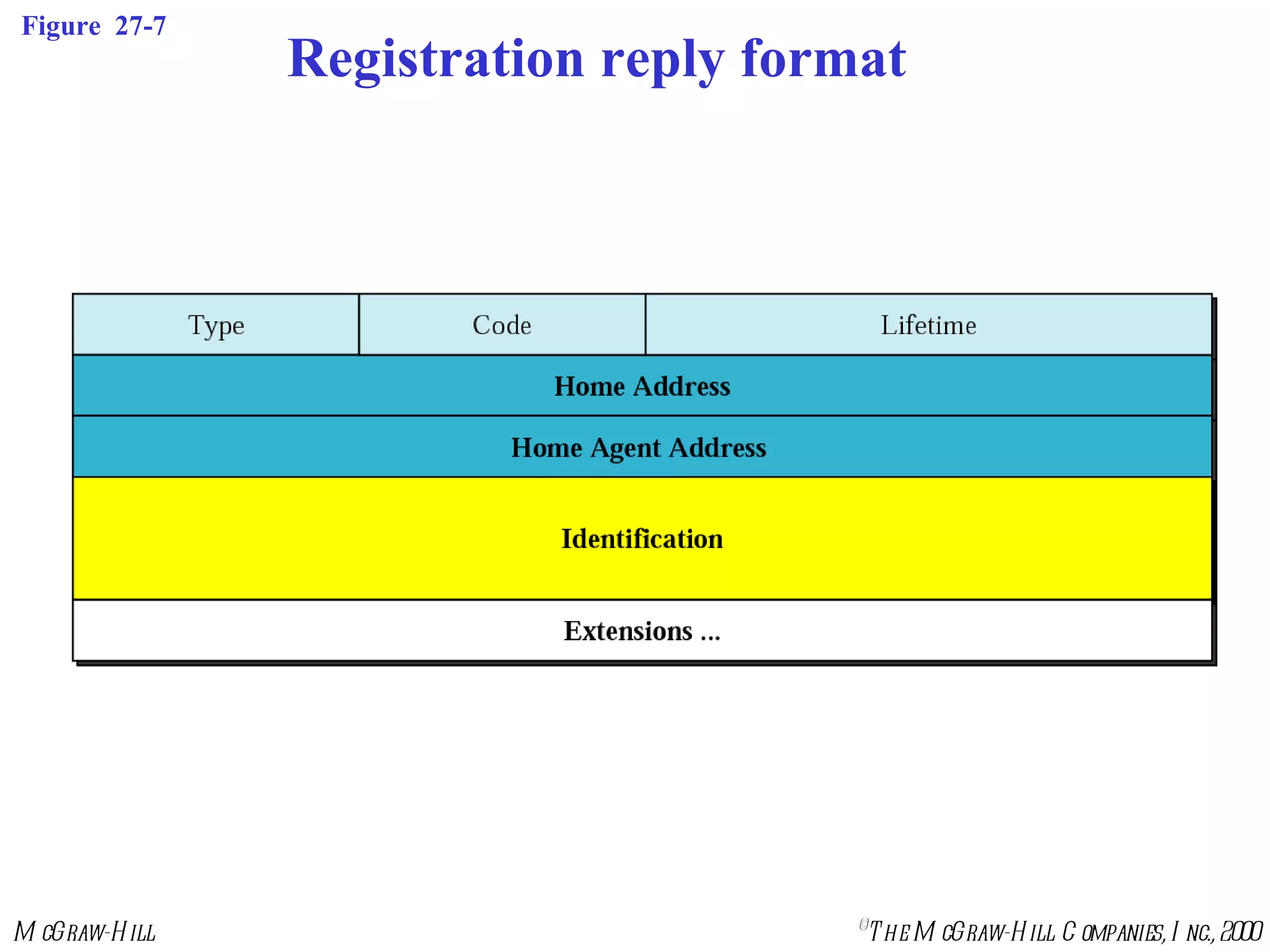
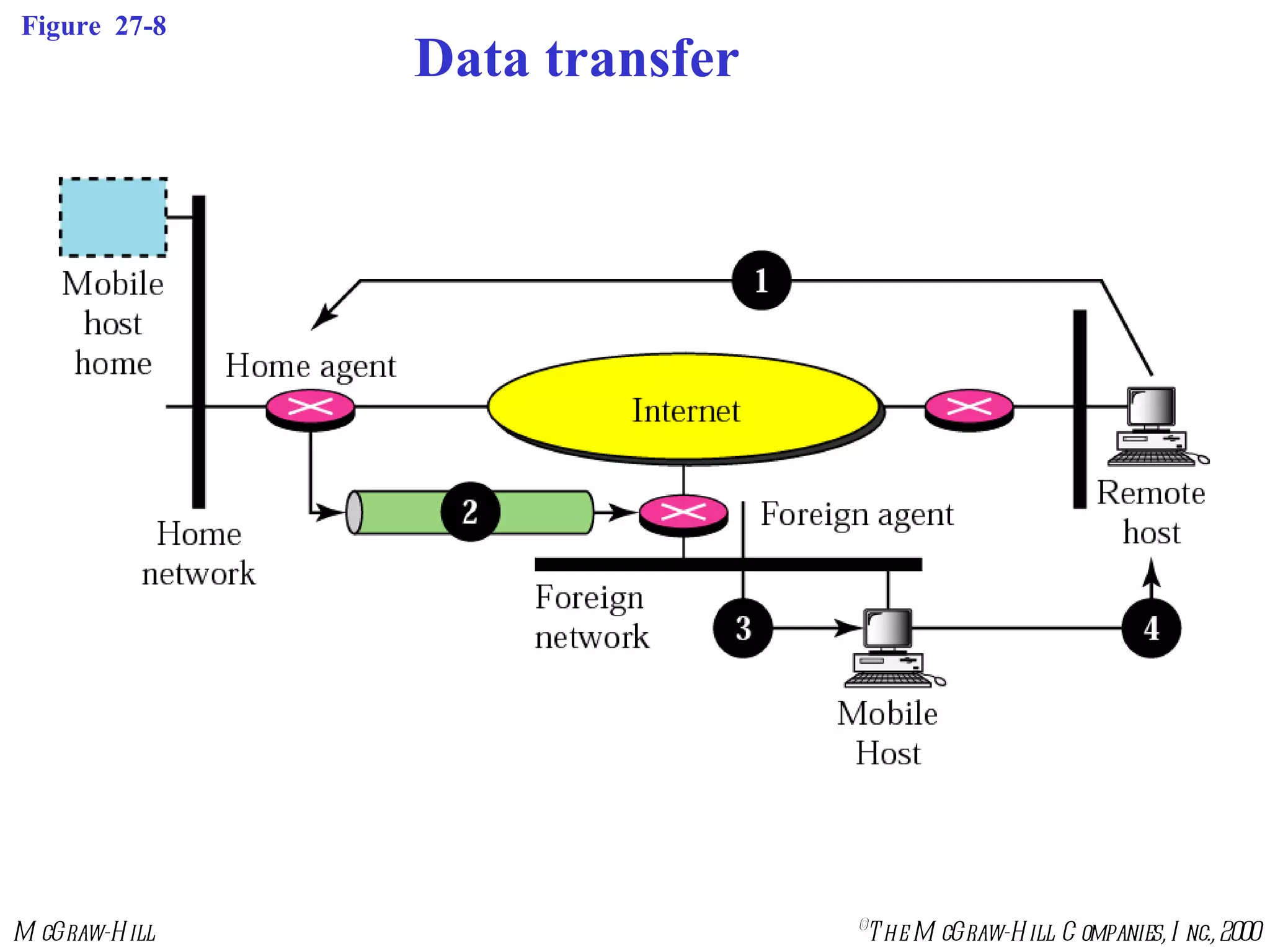
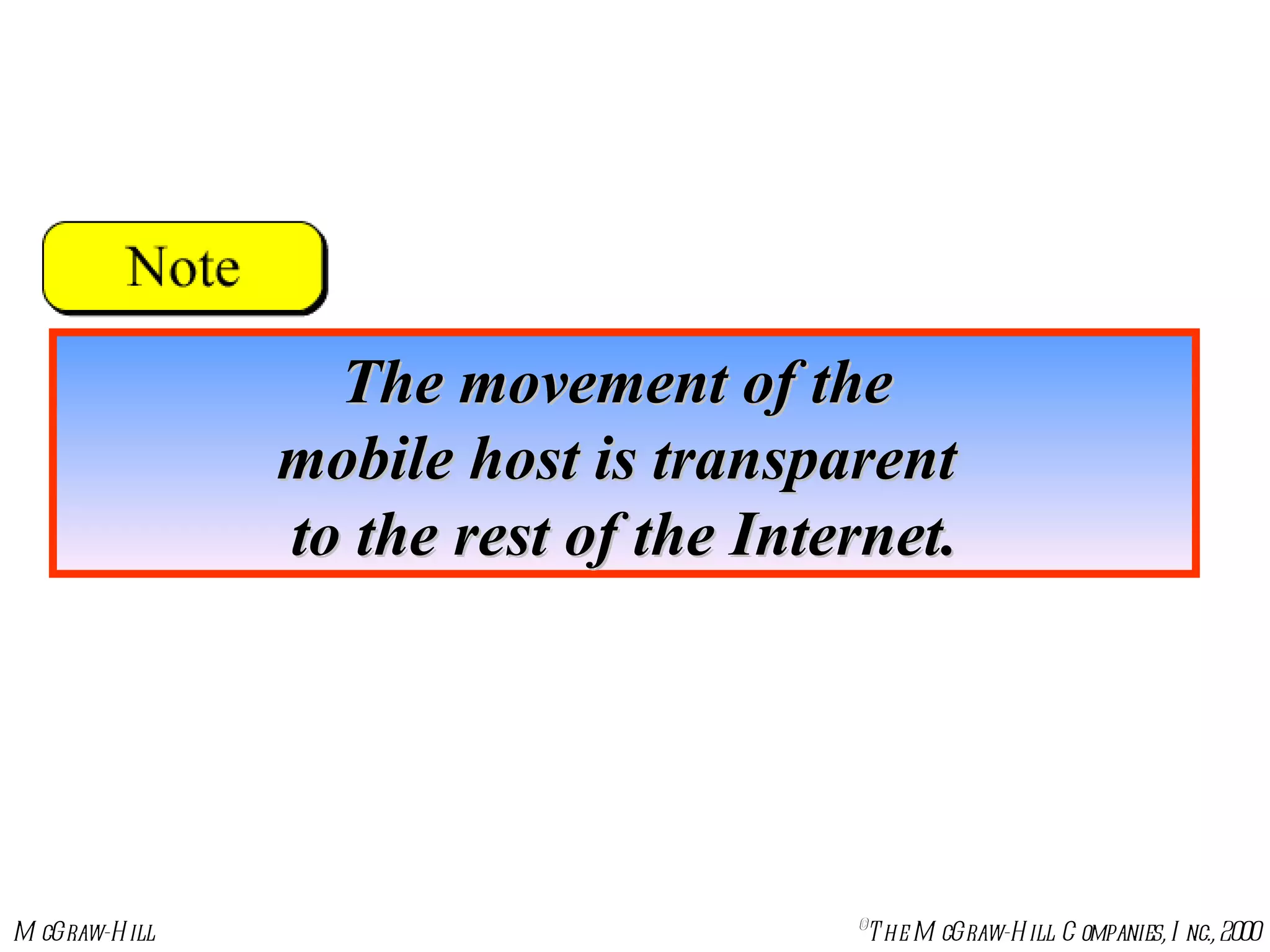
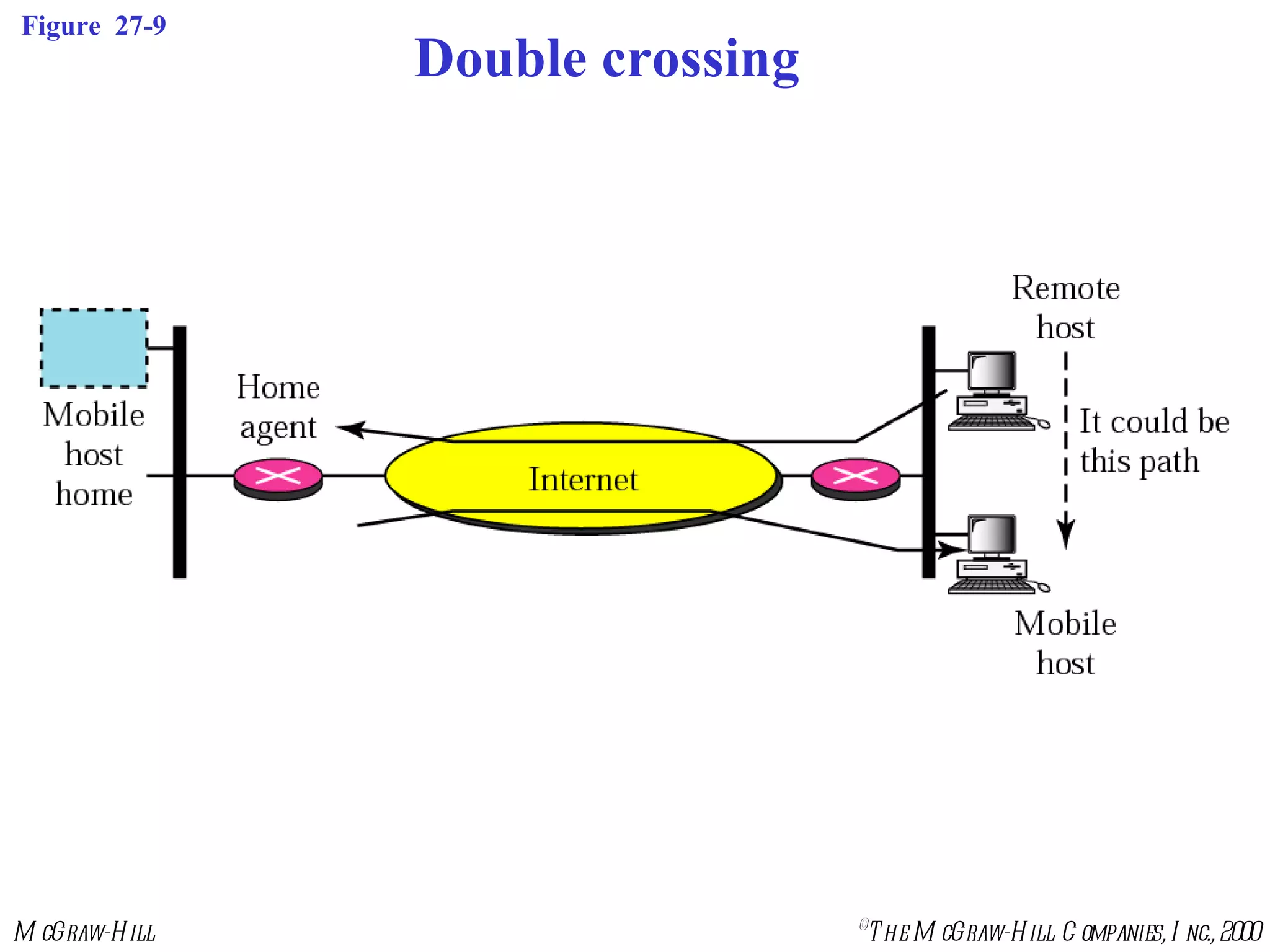
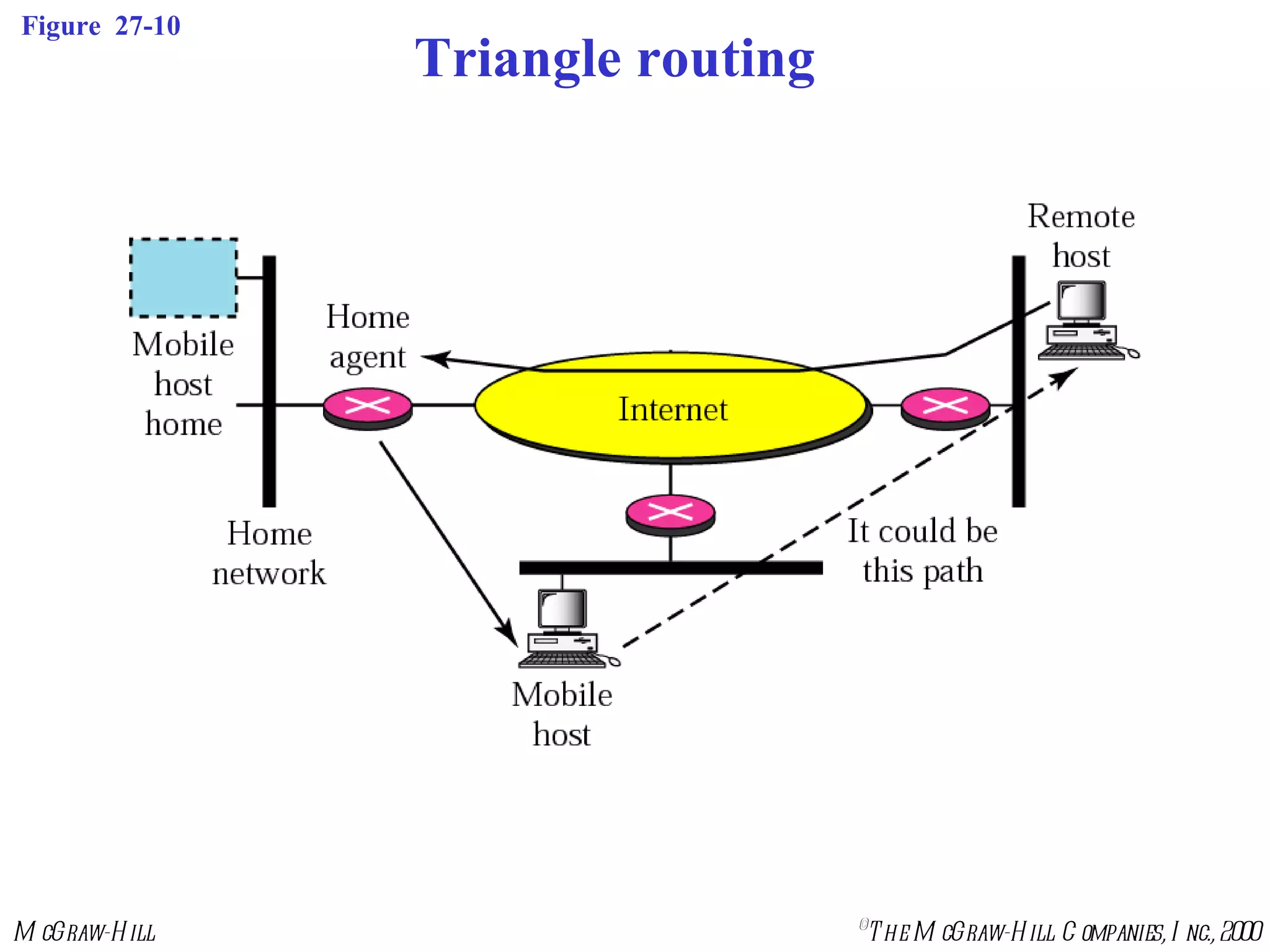
Mobile IP allows mobile hosts to move between networks while maintaining the same home IP address. It uses two IP addresses for each mobile host - a permanent home address and a care-of address that changes as the host moves. The three phases of Mobile IP are agent discovery, registration, and data transfer. During registration, the mobile host registers its current care-of address with its home agent so that data packets can be tunneled or redirected to the mobile host's current location. However, Mobile IP introduces some inefficiency in routing packets to mobile hosts.