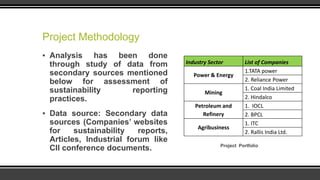
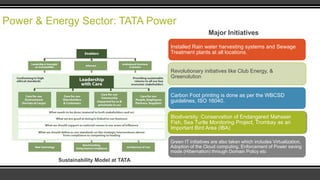
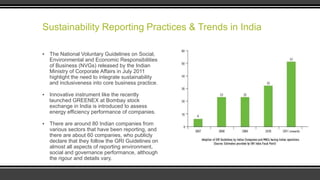
The document explores sustainable development practices across various industry sectors in India, emphasizing the need for economic growth alongside environmental protection. It outlines initiatives undertaken by companies in power & energy, mining, petroleum, and agribusiness, while analyzing the role of different stakeholders and measuring efficacy through sustainability indices. Despite progress from companies like Tata and Reliance, challenges remain for wider adoption of sustainable practices in alignment with global standards.