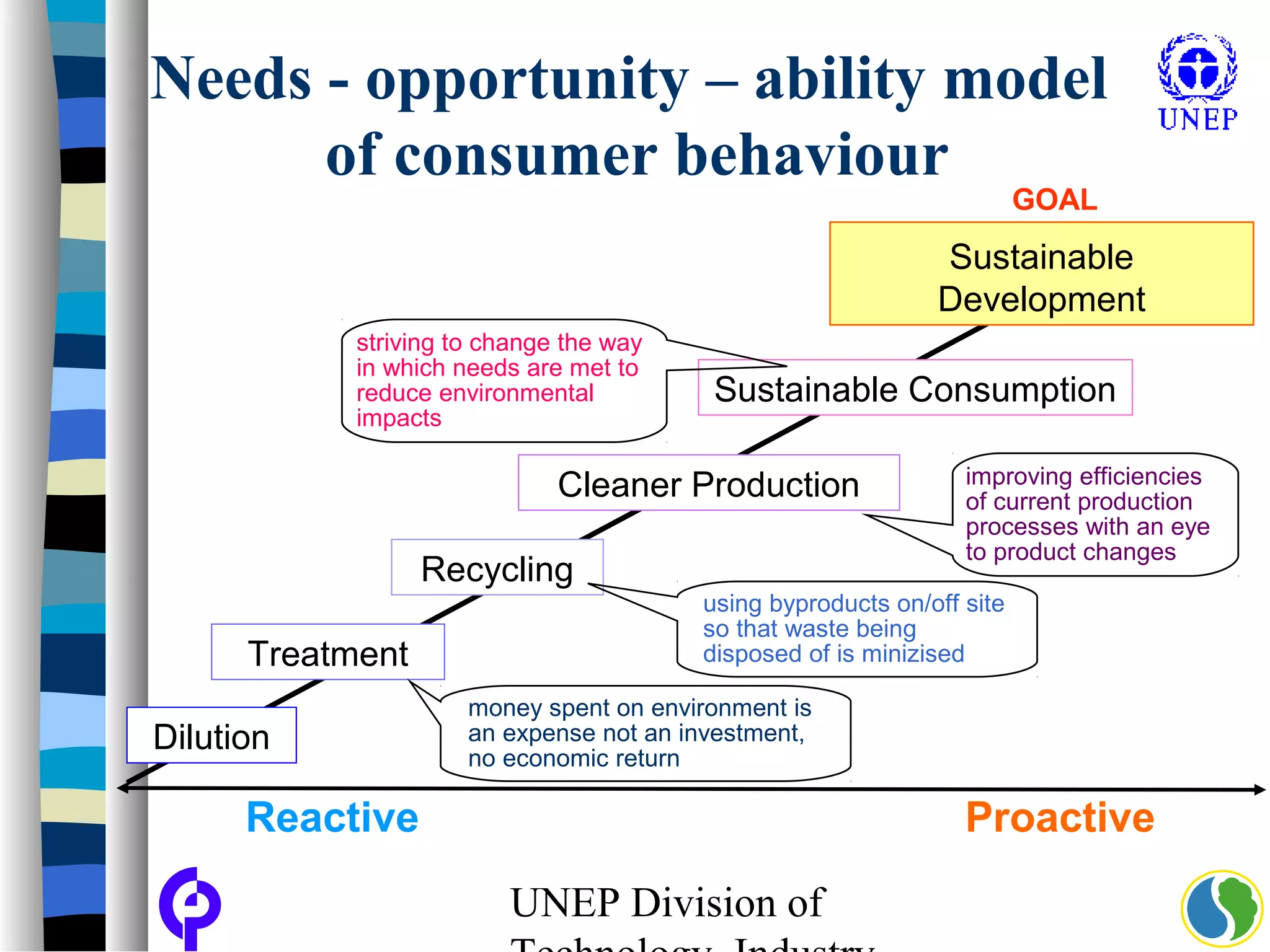
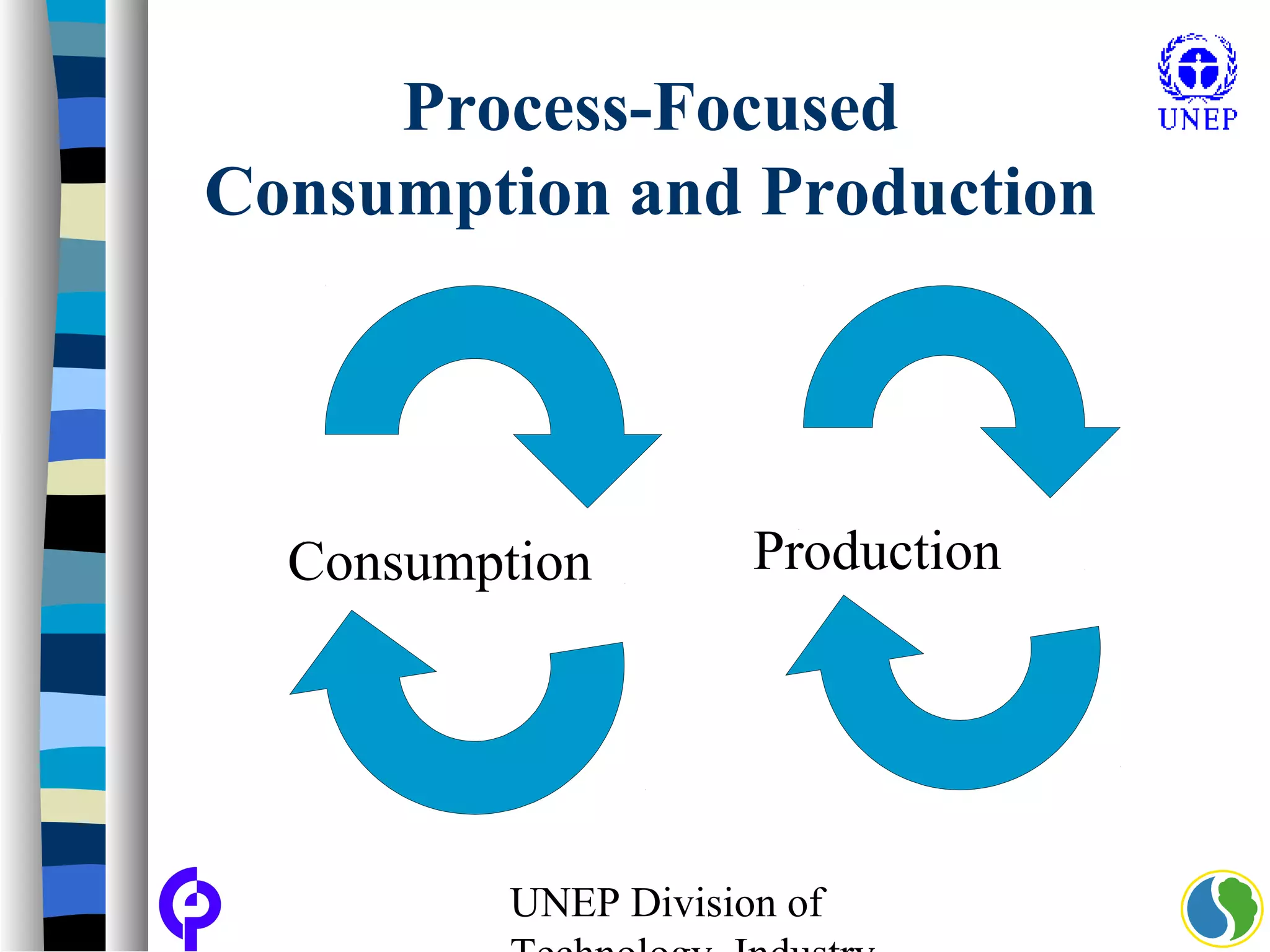
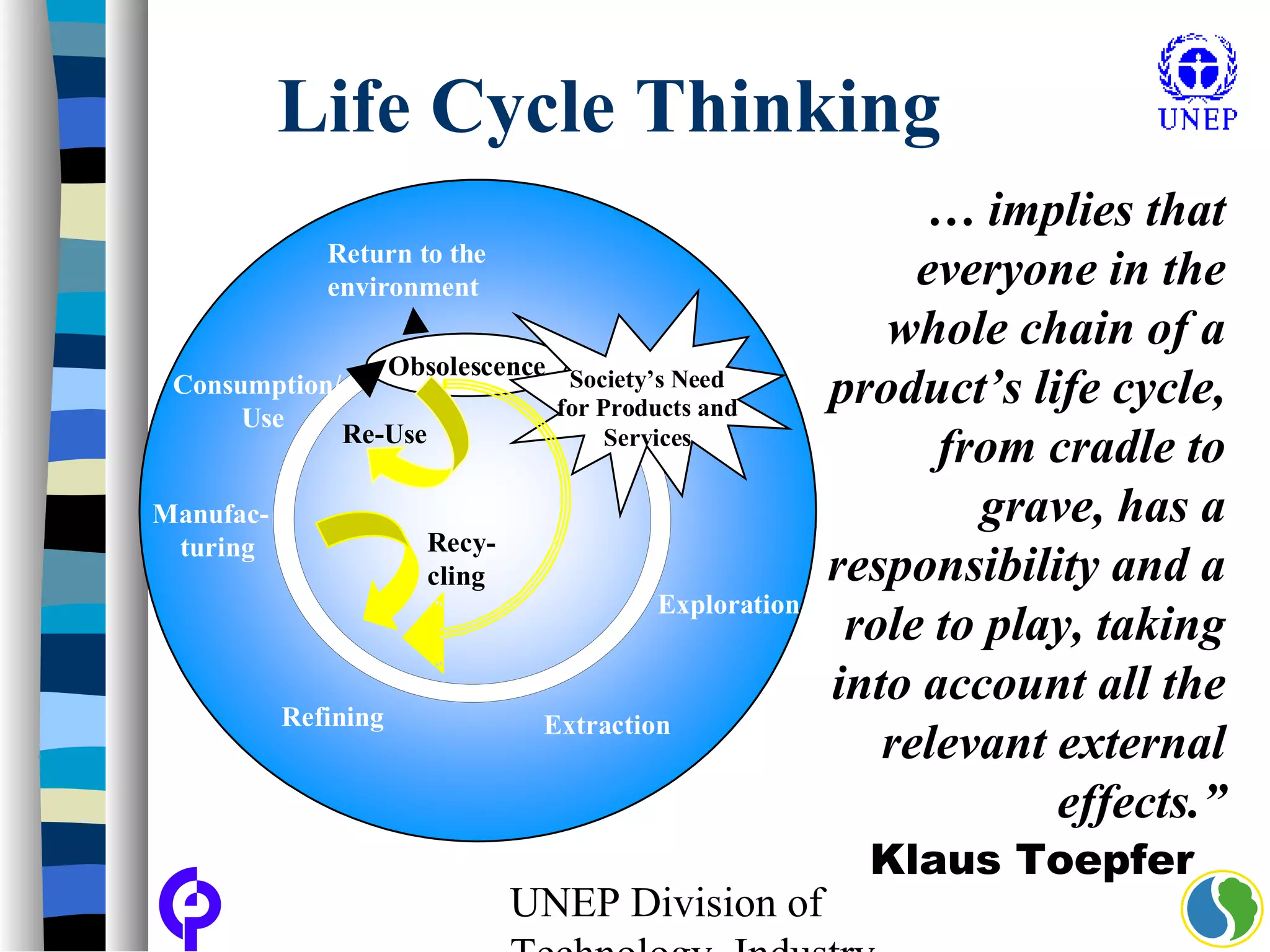
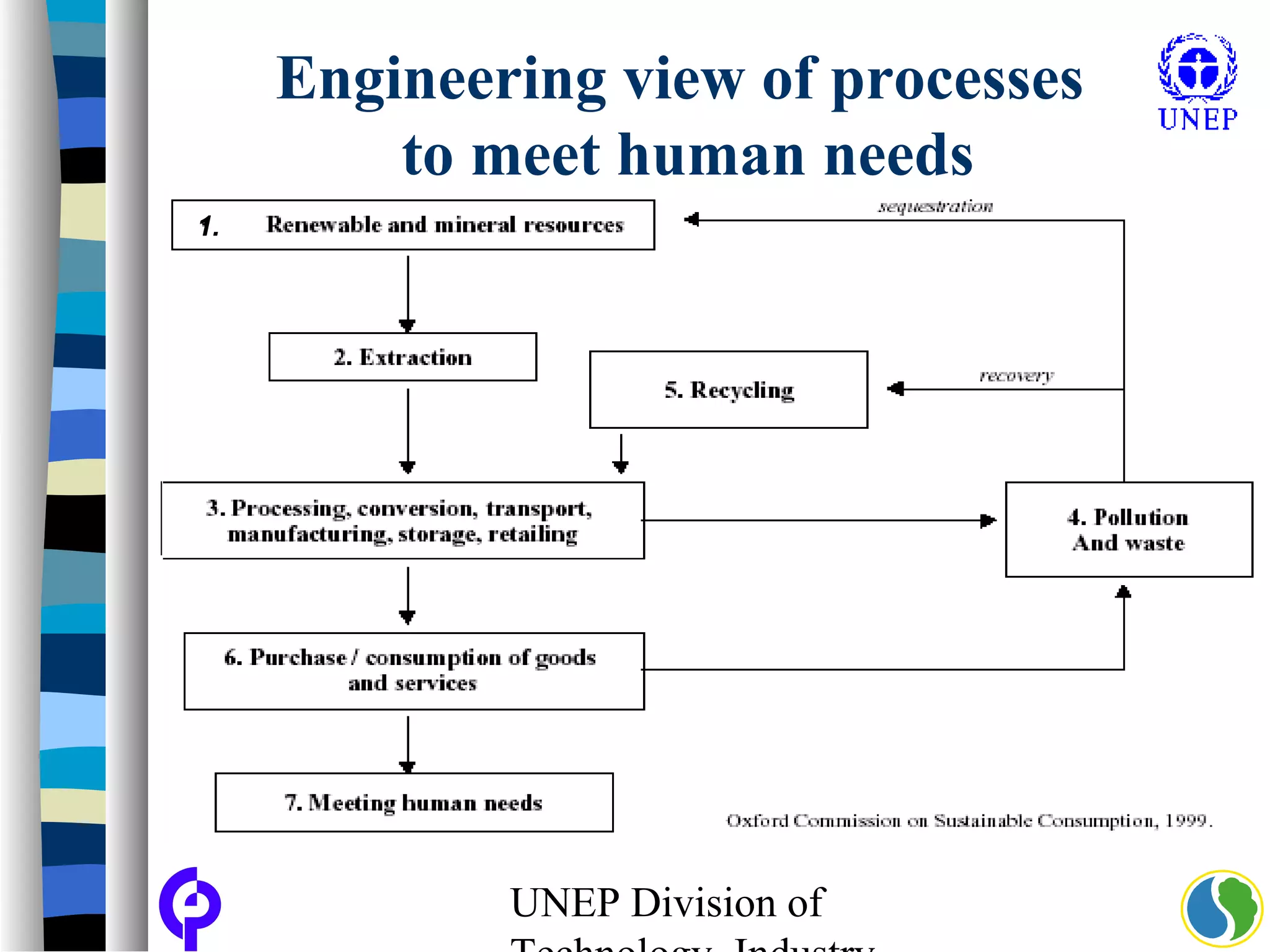
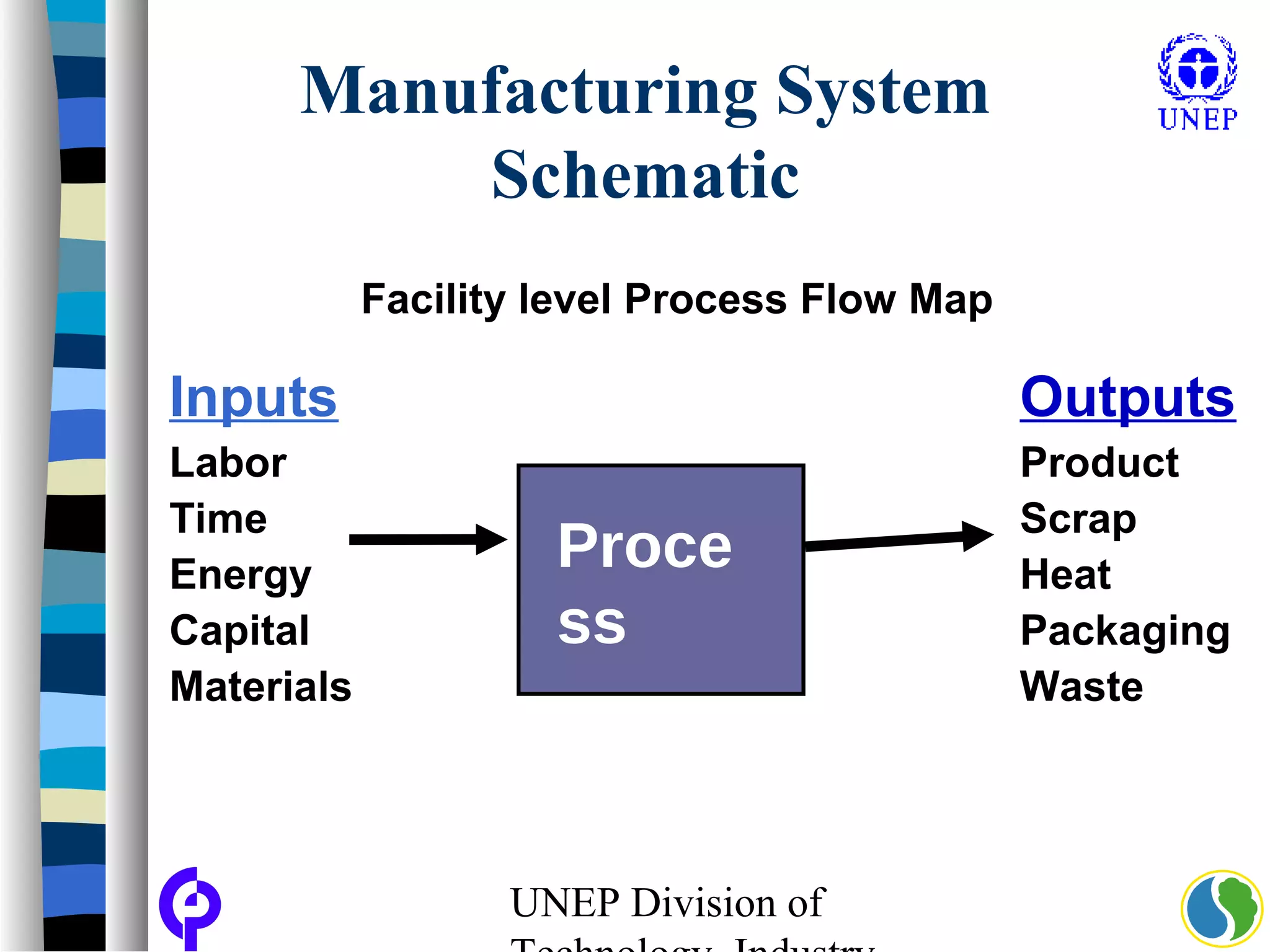
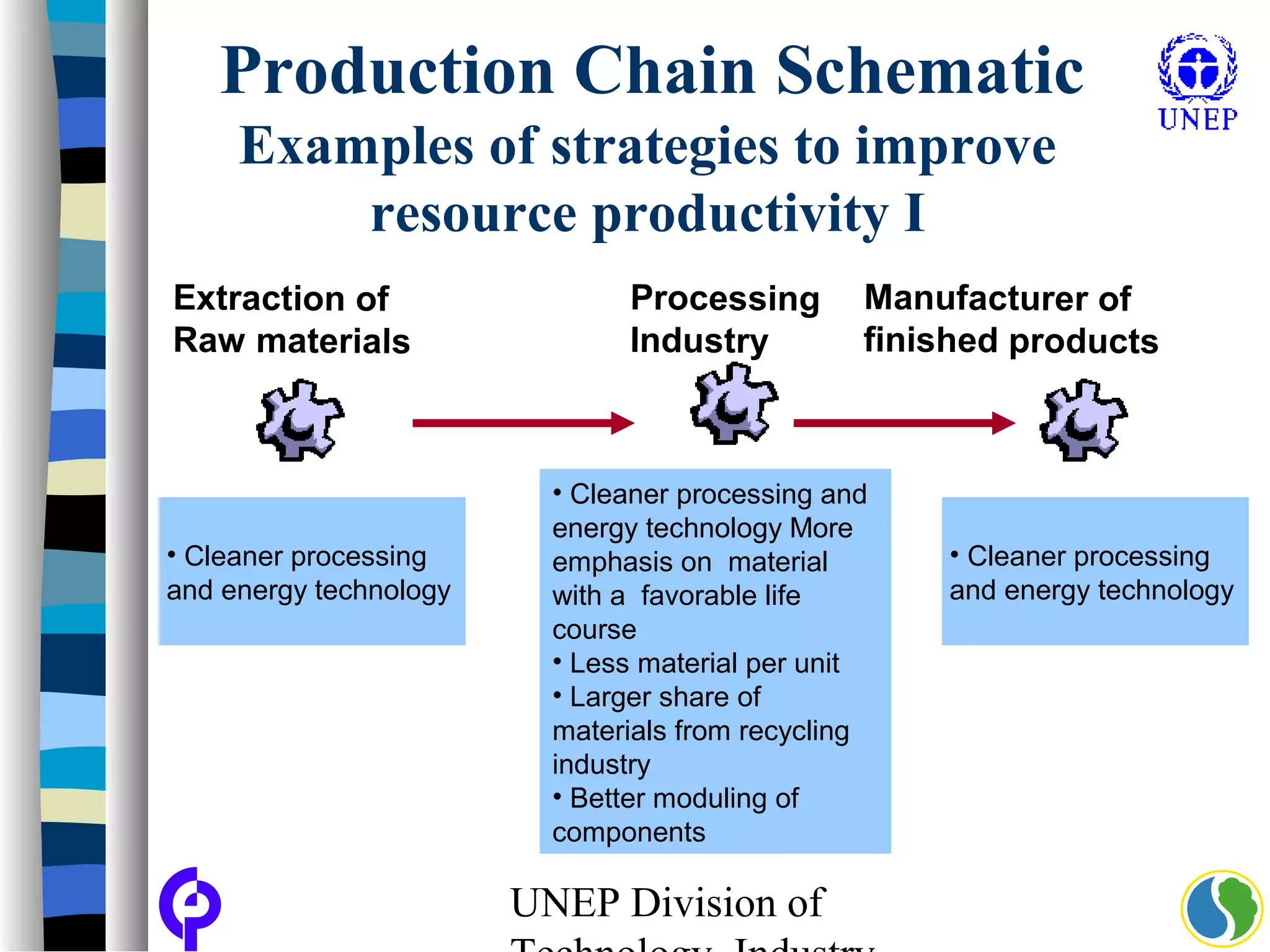
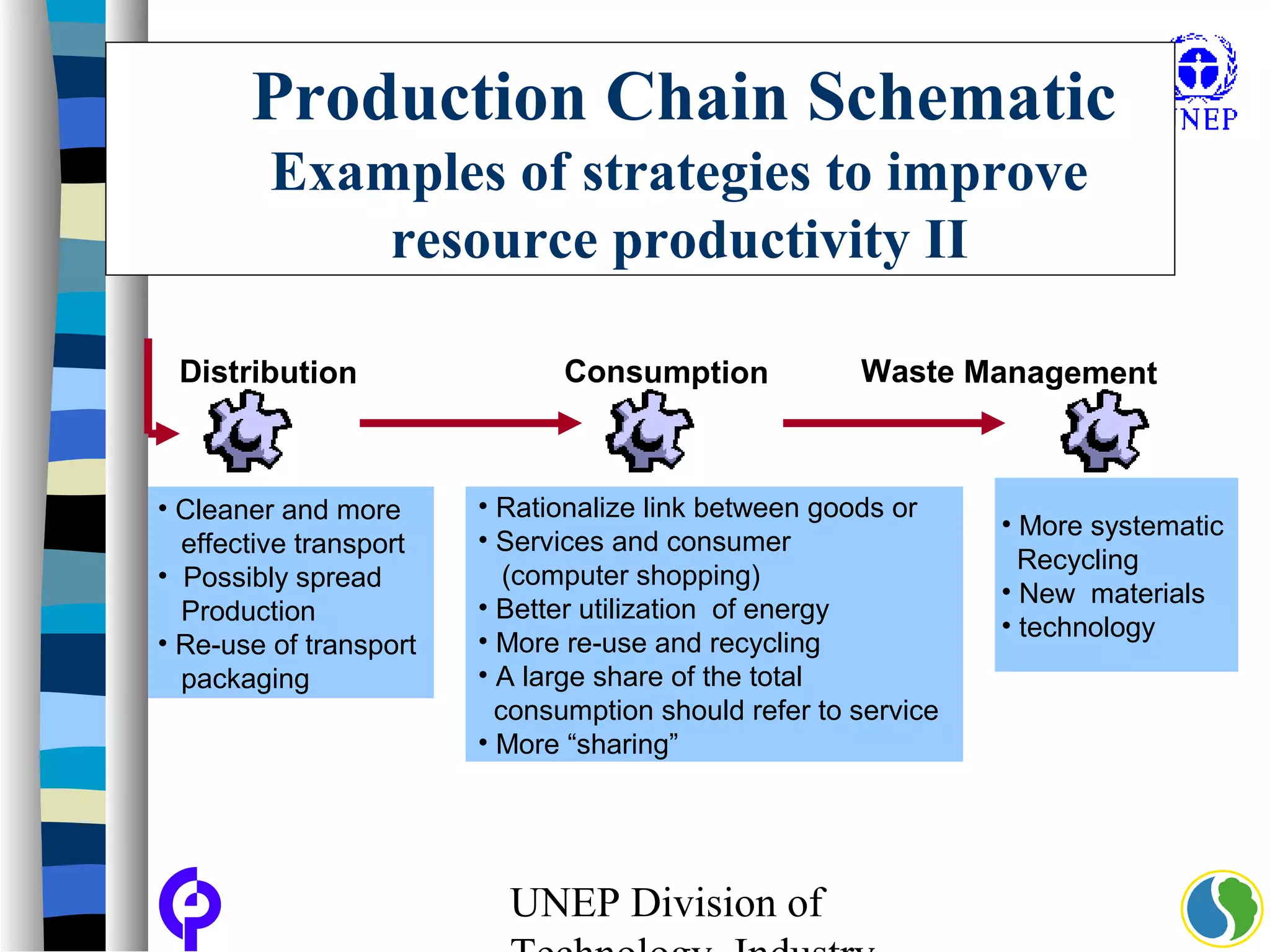
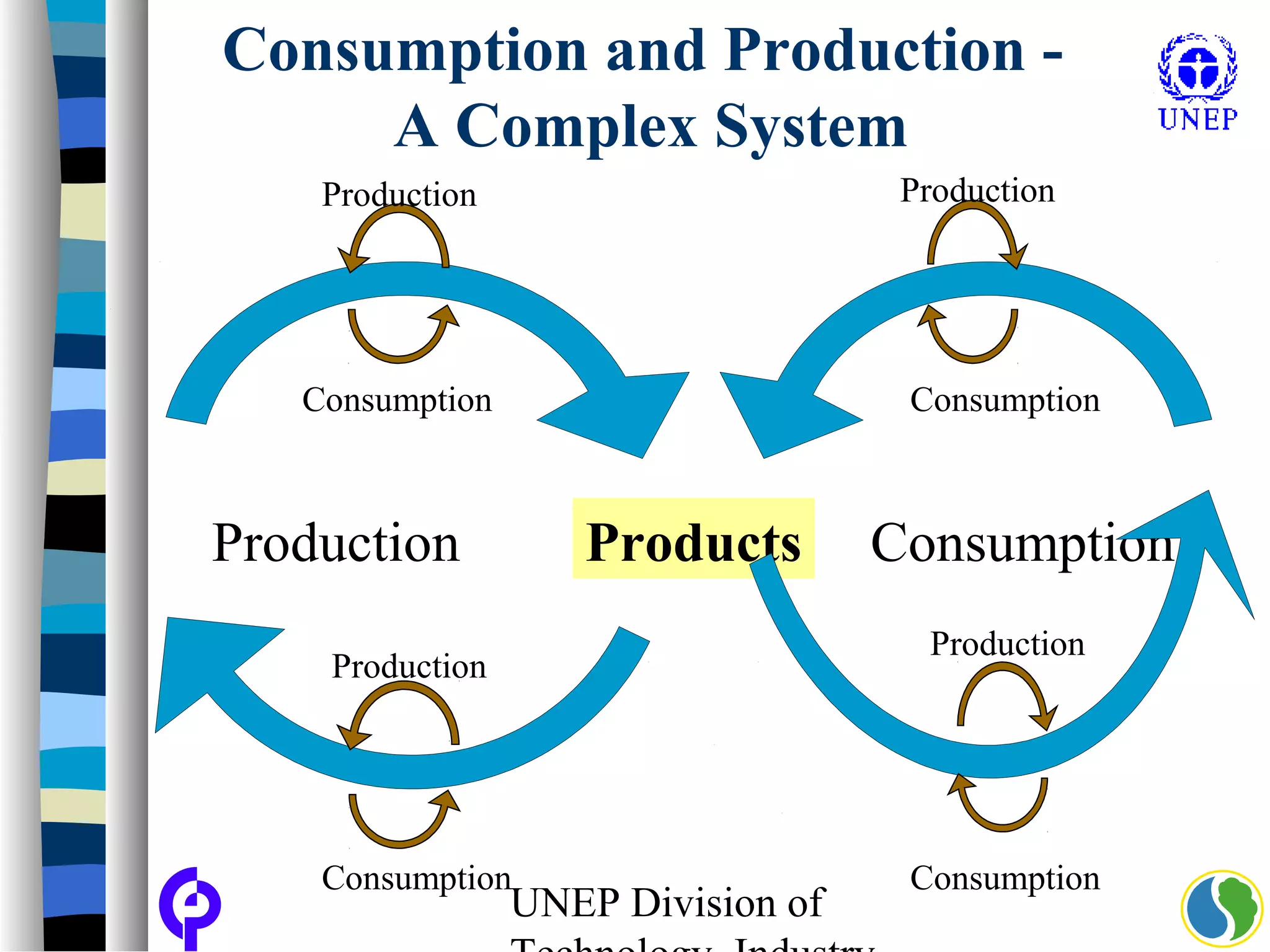
The document discusses sustainable consumption and production and the need to integrate the two concepts. It provides definitions for sustainable consumption, cleaner production, and sustainable consumption and production. It outlines the interrelated nature of consumption and production activities and emphasizes the importance of a life cycle approach and stakeholder engagement across the full consumption and production system to minimize environmental impacts.