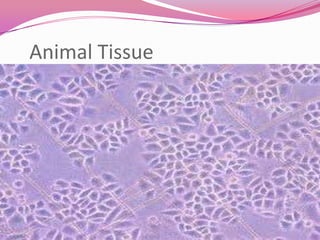
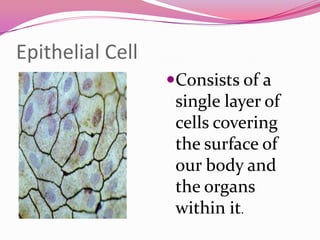
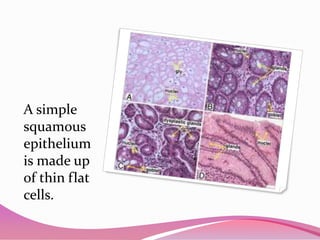
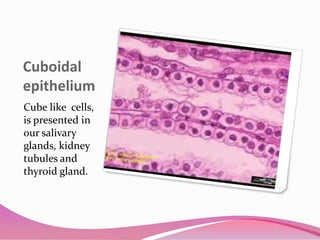
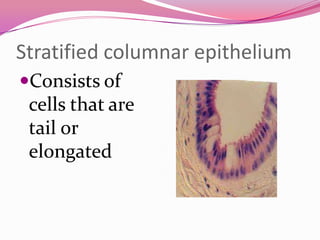
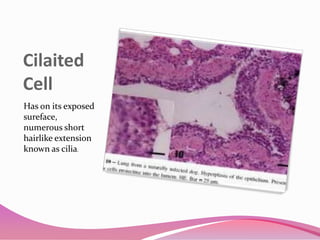
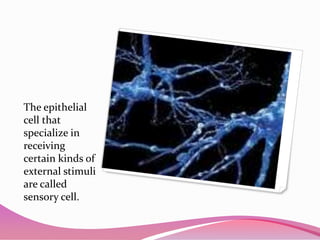
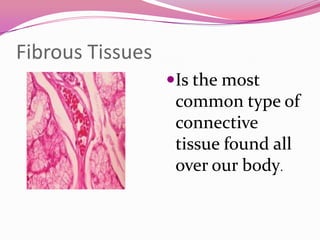
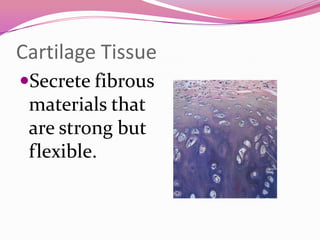
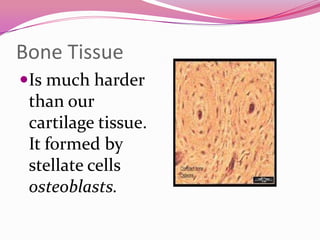
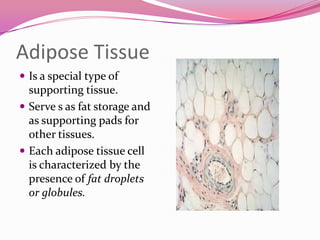
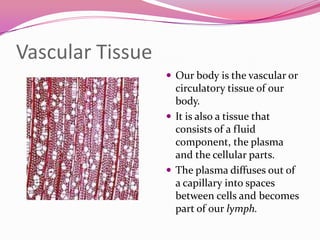
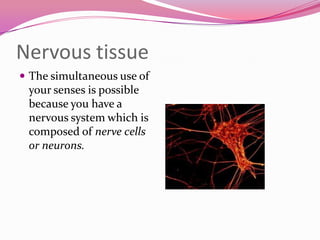
This document describes the main types of animal tissues. It discusses epithelial tissues, which form the outer layers of organs and include squamous, cuboidal, columnar, ciliated, and glandular cells. It also describes the five main connective tissues - fibrous, cartilage, bone, adipose, and vascular tissues. Additionally, it summarizes the three main muscle tissues - smooth, striated, and cardiac muscles - and notes that nervous tissue is composed of neurons.