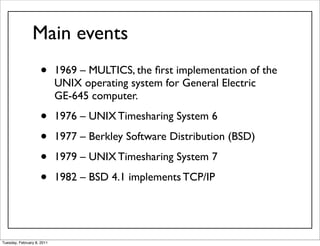
This document provides an overview of Unix basics and system software. It discusses the history of Unix from its origins in 1969 to modern implementations. Key topics covered include Unix terminology, common properties such as portability and multitasking, the software conception of "do one thing well", and components like the kernel, shell, file system hierarchy, and manual pages.




























![Common syntax
$ app_name [options] [parameters]
Options begin with - or --
-o1 [value] -o2 -o3 [value]
or
-o1o2o3
Examples:
$ tar -x -j -v -f archive.tar.gz
$ tar -xjvf archive.tar.gz
Parameters are usually required.
$ rdesktop -f -u UserName 192.168.0.124
Tuesday, February 8, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-1unixbasics-110207222202-phpapp01/85/1-Unix-basics-Part-1-30-320.jpg)





