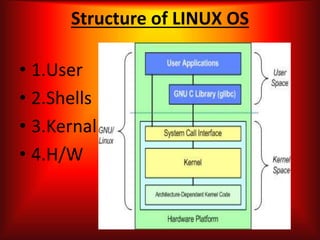
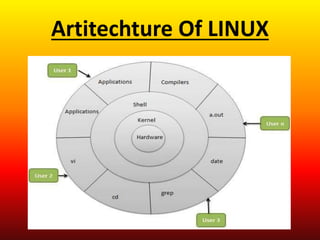
The document provides an introduction to the Linux operating system. It discusses the history of Linux, noting it was developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 based on UNIX and intended to be open source and free. It describes Linux as a free operating system that includes software applications. Popular Linux distributions are then listed such as Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, and Gentoo. The core components of the Linux operating system structure are outlined as the user, shells, kernel, and hardware. Key features of the kernel and shells are defined. Security advantages of Linux and popular text editors in Linux like Vi and Emacs are also summarized.