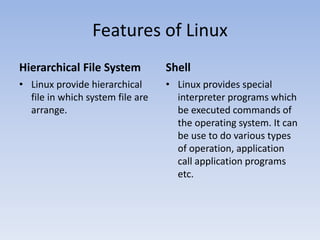
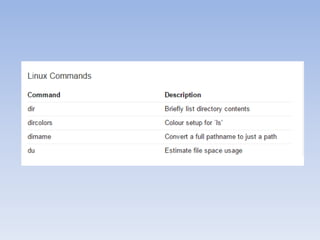
The document provides information about Linux operating system. It discusses the history of Linux, how it was developed by Linus Torvalds as a free and open source alternative to Unix. It describes the key components of Linux like the kernel, types of kernels (microkernel, monolithic, hybrid), features of Linux like portability, open source nature, security etc. It also discusses popular Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Red Hat, Debian, Fedora and SUSE. Finally, it mentions some methods of installing Linux like booting from a USB or burning a live CD.