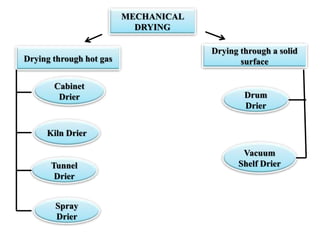
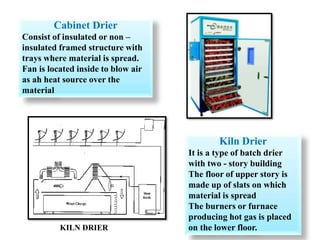
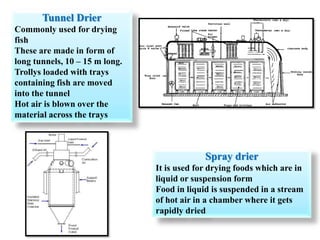
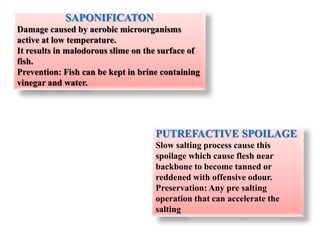
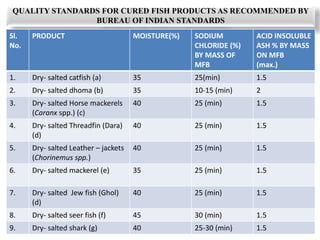
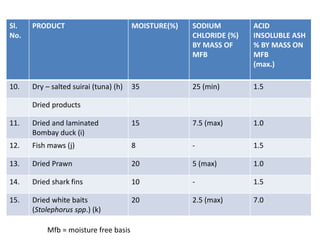
Salting and drying are common preservation methods for fish. Salting involves adding salt which draws water from the fish, lowering its water activity and inhibiting microbial growth. Drying removes water through evaporation via sun or mechanical dehydration methods. Various salting techniques include dry salting, brine salting, and pickle curing. Drying methods include natural sun drying or mechanical techniques using hot air/gas in devices like cabinet driers, kilns, or tunnels. Spoilage risks for salted fish include moulds or bacterial slime if stored in warm, humid conditions. Dried fish can spoil from moulds, insects, or rancidity if moisture levels are too high. Standards specify acceptable moisture