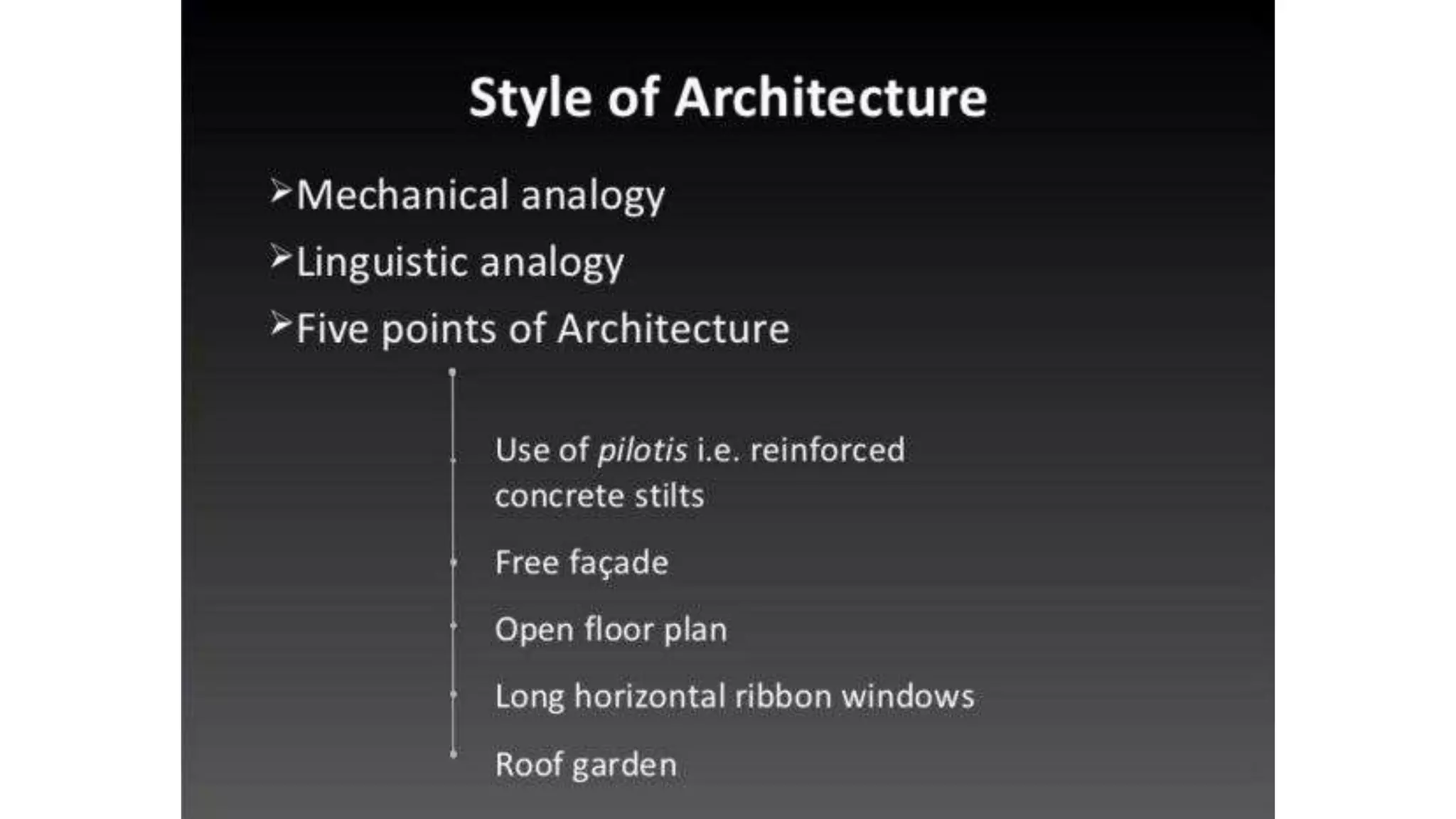
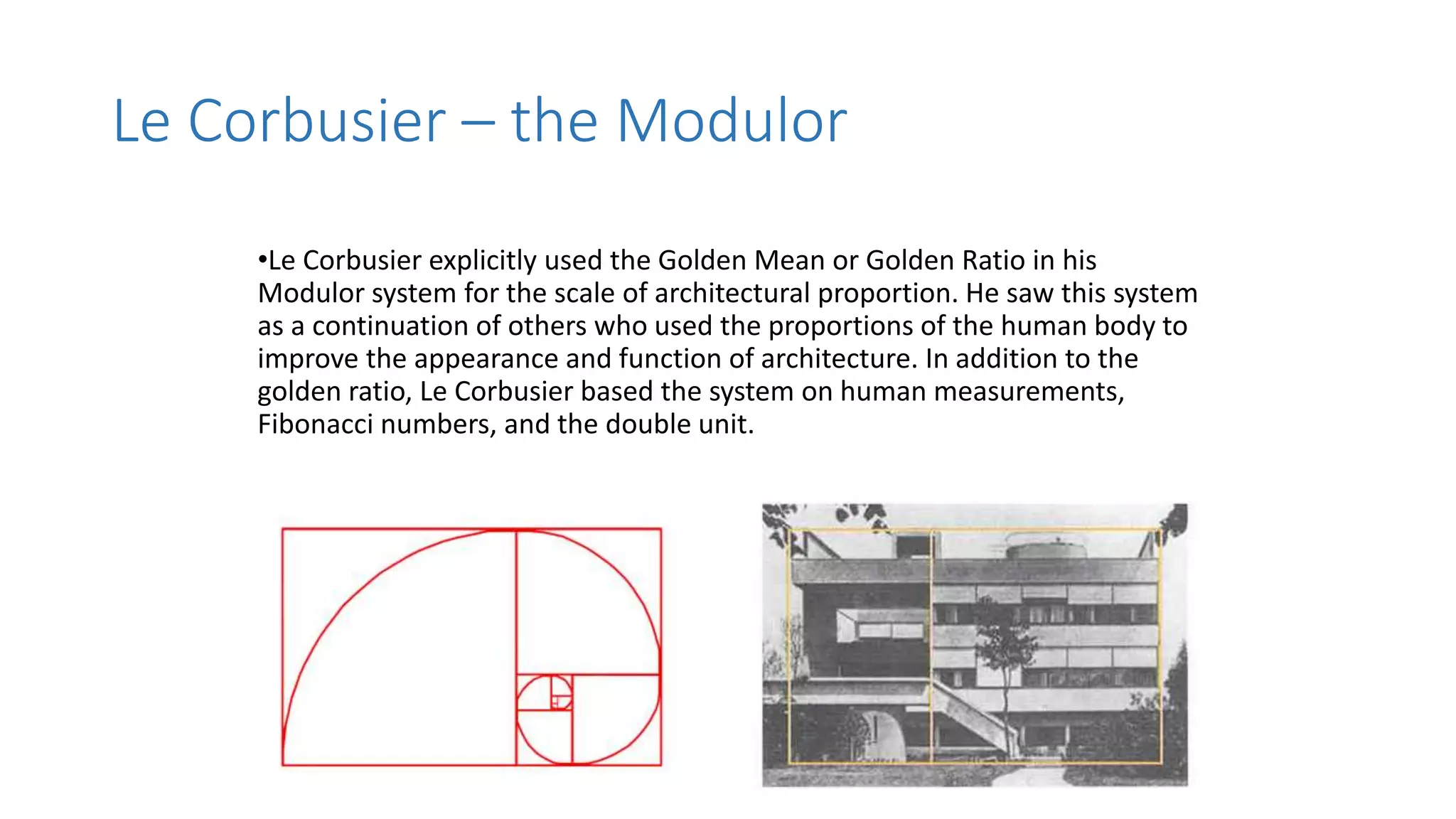
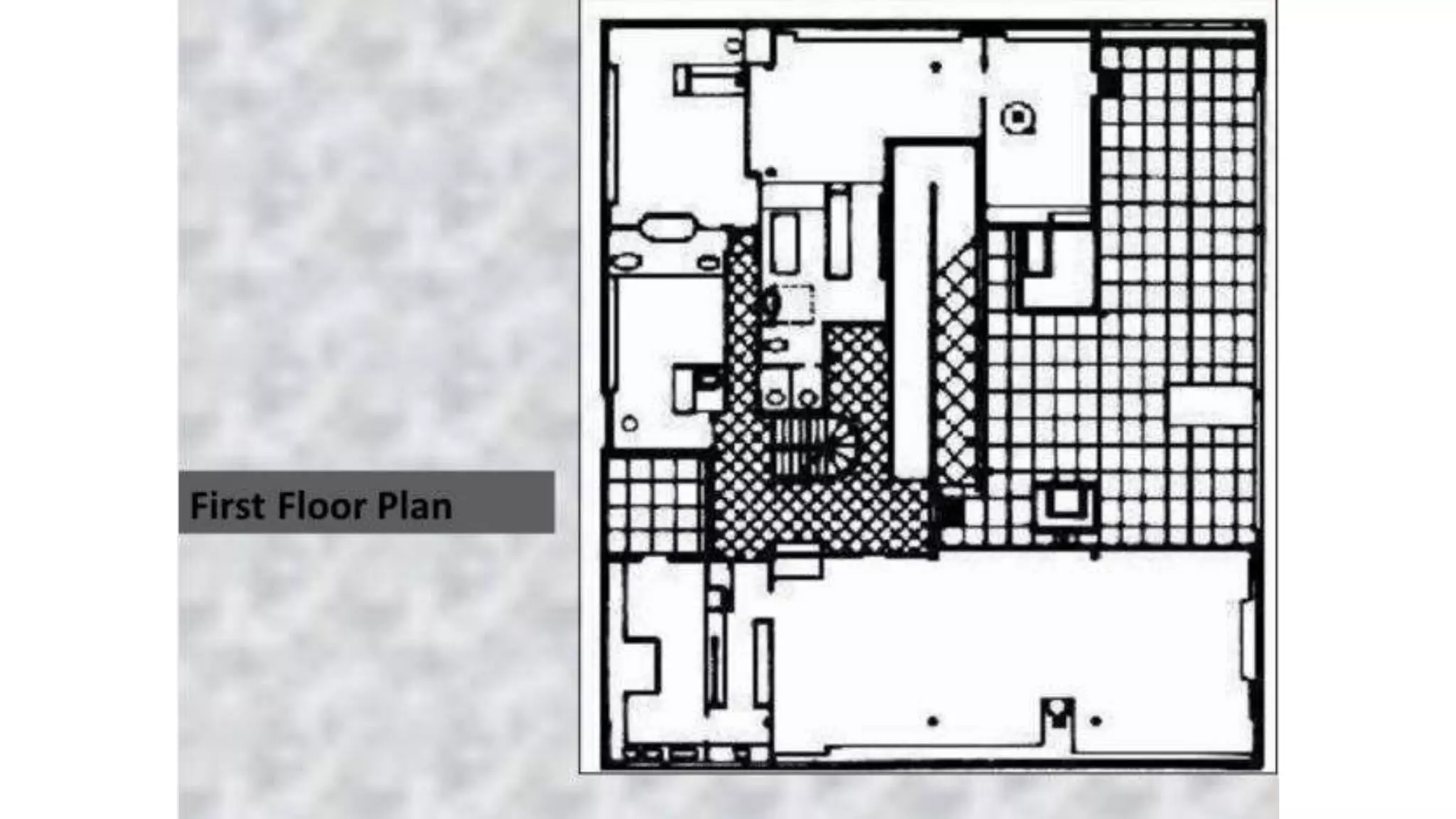
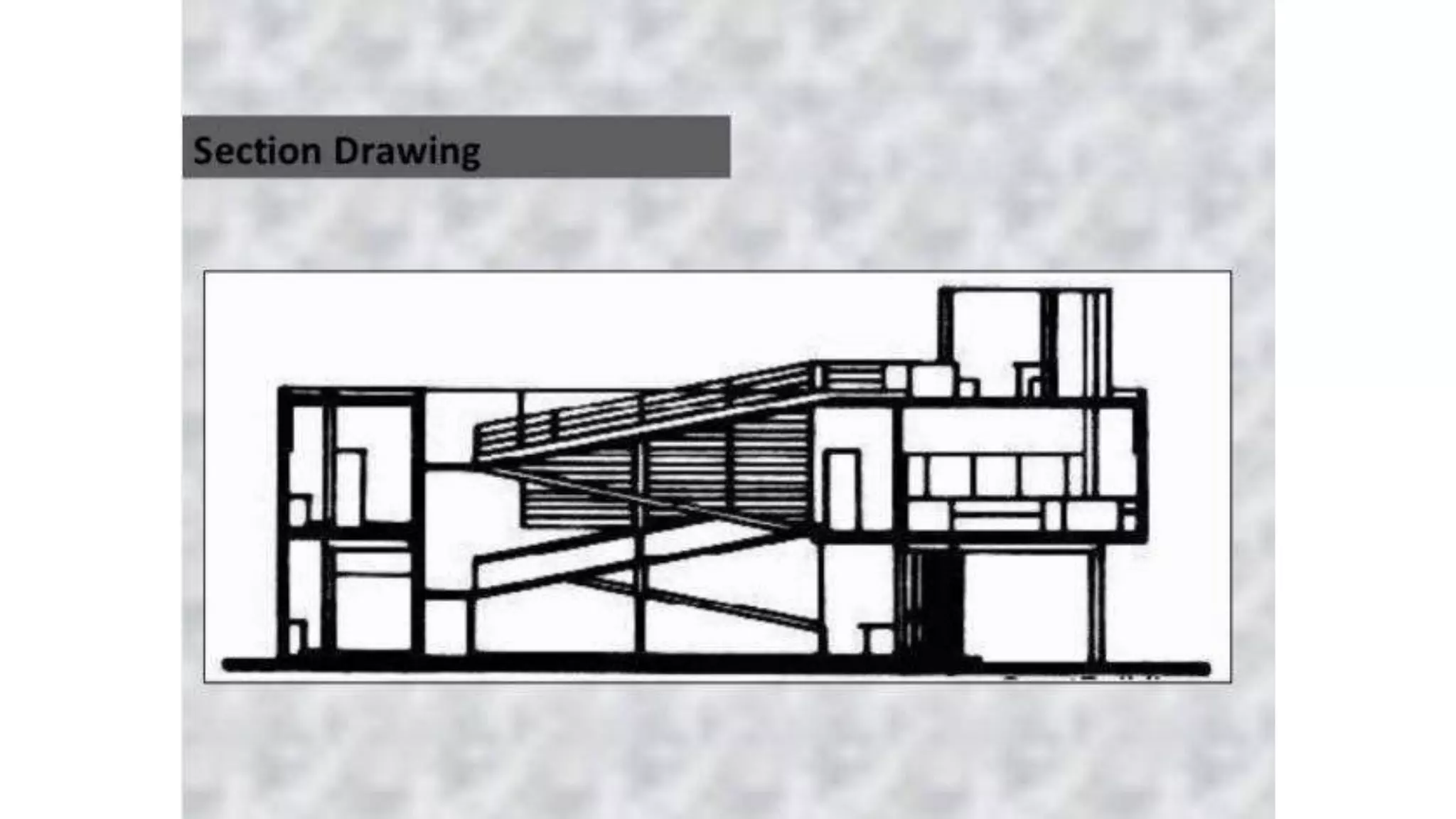
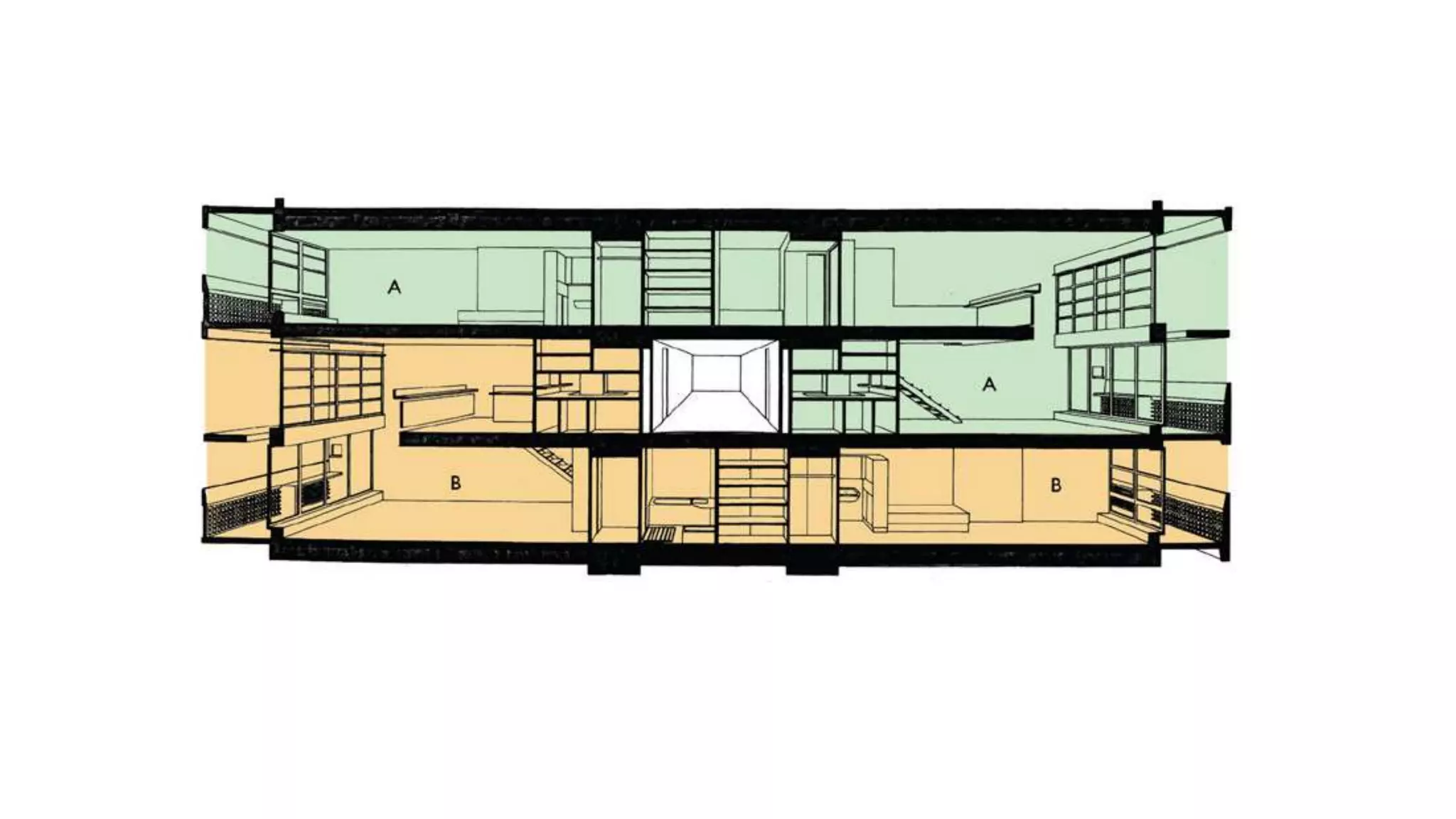
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret-Gris, better known as Le Corbusier, was a pioneering modern architect, urban planner, writer and designer. He was dedicated to improving living conditions in crowded cities through innovative urban planning and architecture. Le Corbusier helped establish the principles of modern architecture through projects like the Villa Savoye, which embodied his five points of architecture. He was also influential in the design and planning of the city of Chandigarh in India.