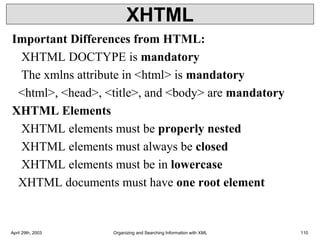
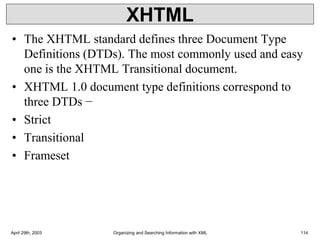
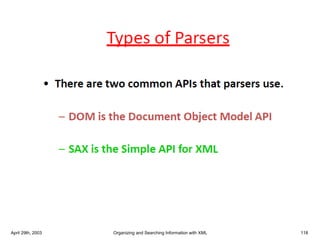
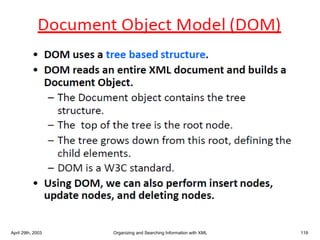
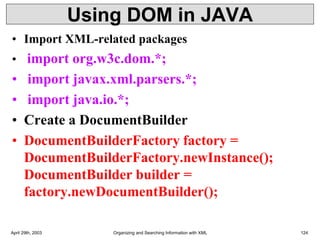
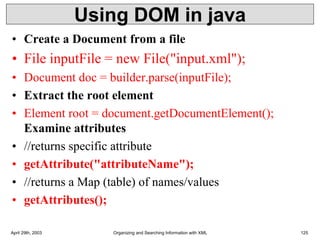
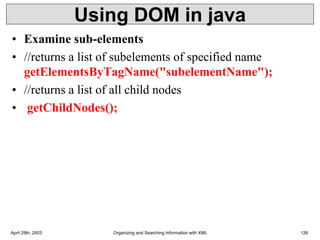
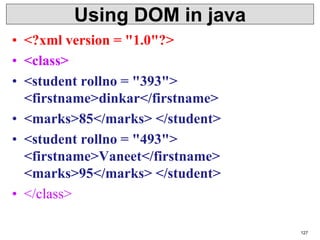
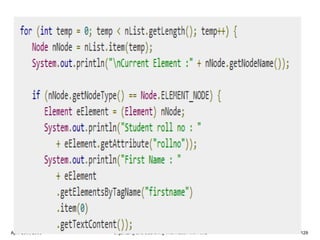
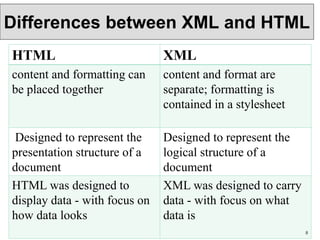
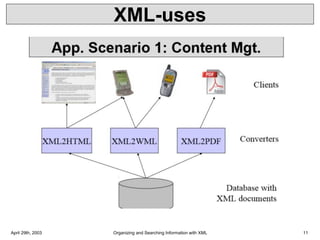
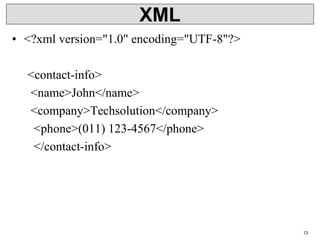
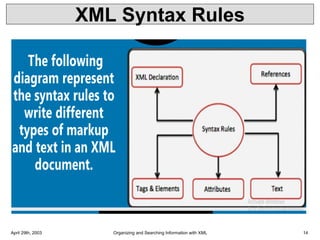
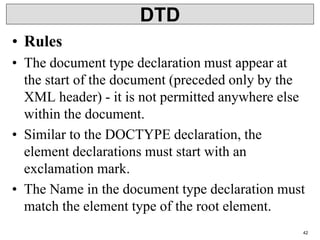
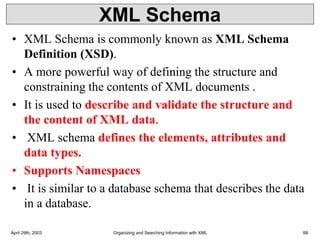
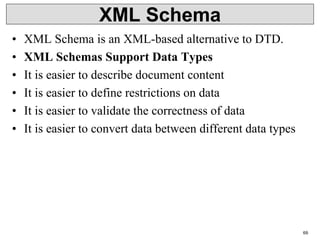
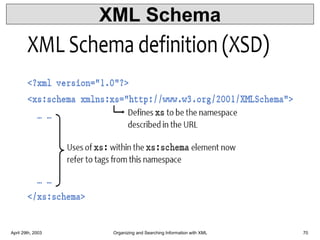
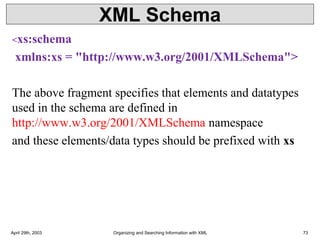
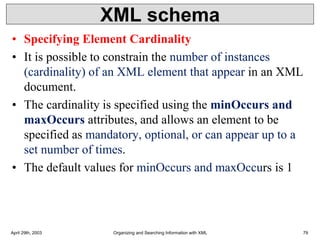
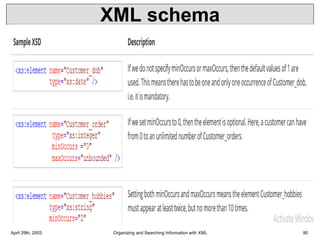
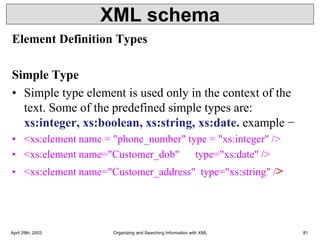
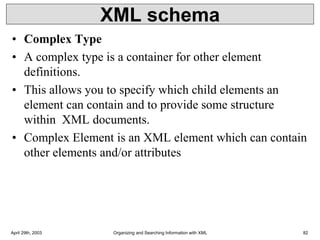
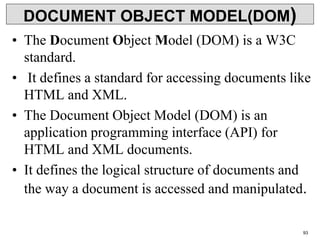
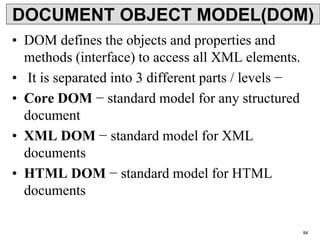
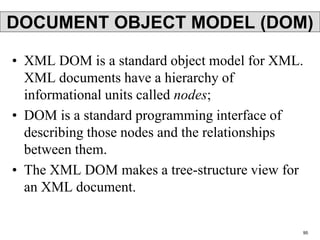
XML is a markup language that defines rules for encoding documents to be both human- and machine-readable. It allows users to define customized tagging structures for different types of documents. A DTD defines the structure and legal elements and attributes of an XML document, ensuring documents conform to the specified rules. XML documents can reference internal or external DTDs to validate document structure. Elements, attributes, and other syntax rules like closing tags help ensure XML documents are properly structured and readable.






















![DTD
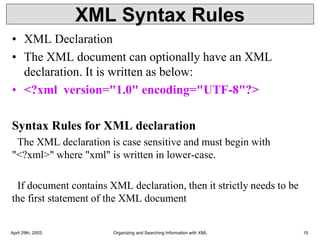
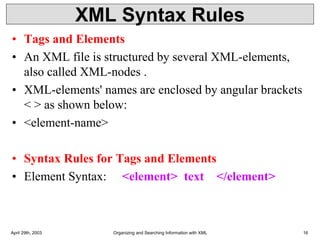
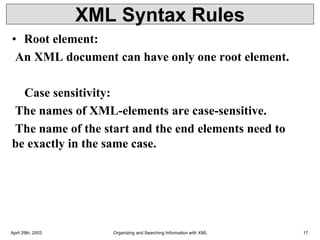
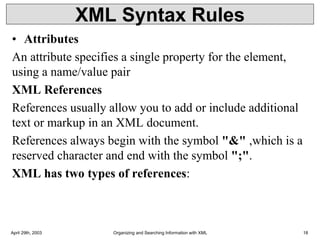
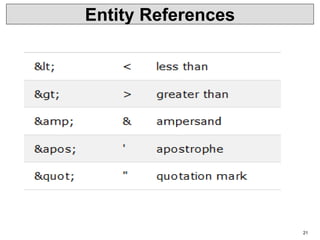
• Syntax
• Basic syntax of a DTD is as follows −
• <!DOCTYPE element DTD identifier
• [ declaration1
• declaration2
• ........ ]>
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-37-320.jpg)
![Internal DTD
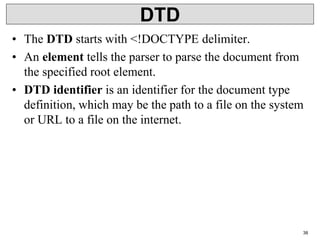
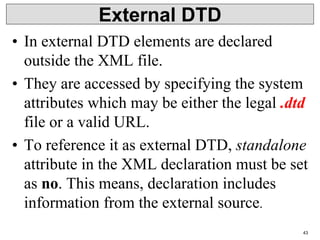
• Internal DTD
• A DTD is referred to as an internal DTD if elements are
declared within the XML files.
• Syntax
• Following is the syntax of internal DTD −
• <!DOCTYPE root-element [element-declarations]>
where root-element is the name of root element and
element-declarations is where you declare the elements.
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-39-320.jpg)
![Internal DTD
• <?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE note [
<!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)>
<!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)>
]>
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend</body>
</note>
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-40-320.jpg)



![External DTD
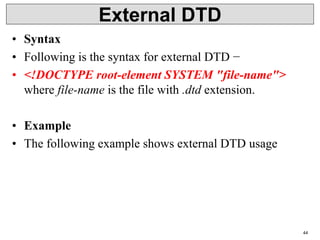
• Types
• Refer an external DTD by either using system
identifiers or public identifiers.
• System Identifiers
• A system identifier enables to specify the
location of an external file containing DTD
declarations. Syntax is as follows −
• <!DOCTYPE name SYSTEM "address.dtd" [...]>
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-47-320.jpg)



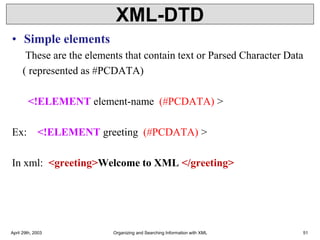



![XML-DTD
• Sequence operator( , )
• <!ELEMENT employee (name , dept, id)>
• Choice Operator ( | )
• <!ELEMENT product (price | discountprice )>
• Composite Operator [ ( ) ]
• <!ELEMENT biodata ( dob , ( company,title)* )>
April 29th, 2003 Organizing and Searching Information with XML 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-55-320.jpg)
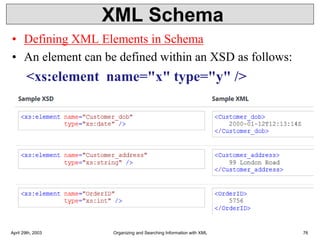
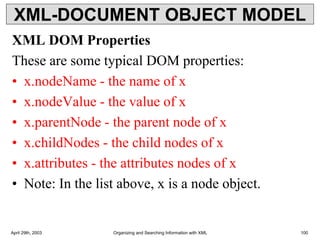
![XML DTD elements
Mixed content example
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" standalone = "yes" ?>
<!DOCTYPE address [
<!ELEMENT address (#PCDATA | name)* >→ mixed content
<!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)>
]>
<address>
Here's a bit of text mixed up with the child element.
<name>
Tanmay Patil
</name>
</address>
April 29th, 2003 Organizing and Searching Information with XML 56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-56-320.jpg)





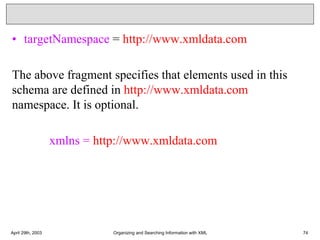








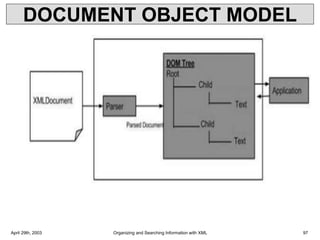





![XML-DOM
xmlhttp.open("GET","note.xml”);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc=xmlhttp.responseXML;
document.getElementById("to").innerHTML=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("to")[0].childNodes[0].
nodeValue;
document.getElementById("from").innerHTML=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("from")[0].childNodes[
0].nodeValue;
April 29th, 2003 Organizing and Searching Information with XML 106](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-106-320.jpg)
![XML-DOM
document.getElementById("message").innerHTML
=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("body")[0].child
Nodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
April 29th, 2003 Organizing and Searching Information with XML 107](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-107-320.jpg)
![txt=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0].
childNodes[0].nodeValue;
code retrieves the text value of the first <title> element
in an XML document:
April 29th, 2003 Organizing and Searching Information with XML 108](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtunit-2xml-230116044106-bfe4a23a/85/WT-UNIT-2-XML-pdf-108-320.jpg)