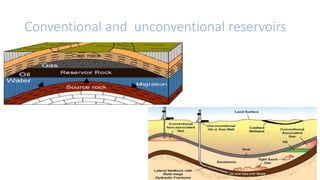
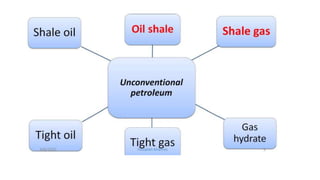
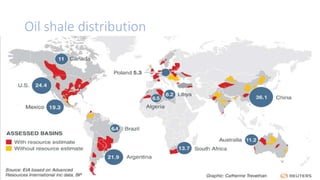
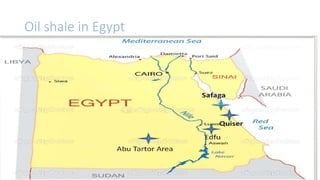
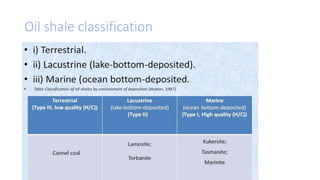
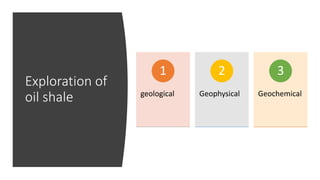
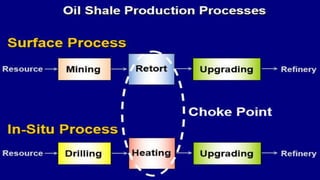
Oil shale is a sedimentary rock containing kerogen, which can be converted to oil. Major oil shale deposits exist in the United States, Russia, Brazil, Estonia, and China. World reserves are estimated at 660 billion tons of oil equivalent, with about 2/3 in the United States. Oil shale exploration involves geophysical and geochemical methods. Extracting oil from oil shale has significant environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions, land disturbance, and water pollution.