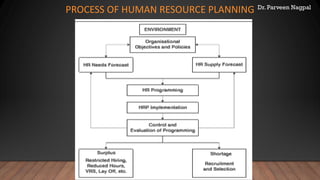
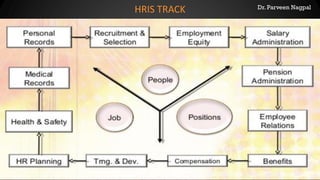
The document provides an overview of Human Resource Management (HRM) and its evolution from Personnel Management (PM), emphasizing the importance of human resources as essential organizational assets. It discusses key features, objectives, and the strategic role of HRM, along with the organizational structure of HR departments and the impact of technology on HR practices. Additionally, it addresses workforce characteristics, challenges in HR planning, job analysis, and the importance of human resource information systems (HRIS).