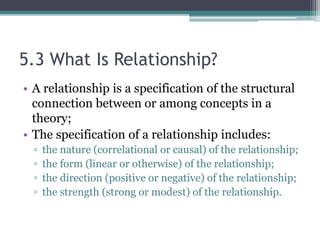
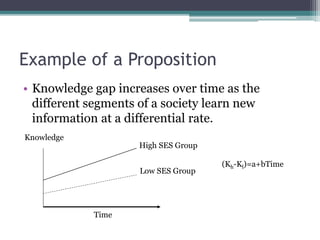
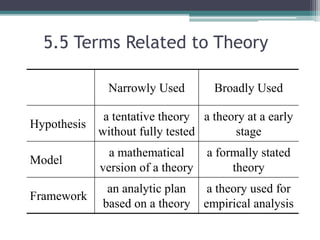
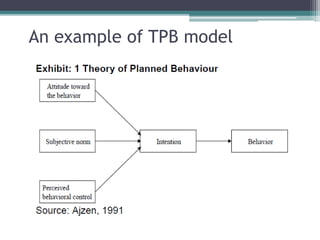
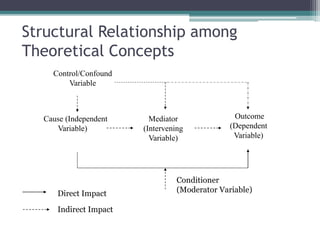
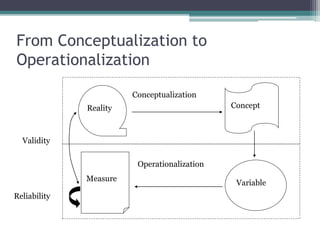
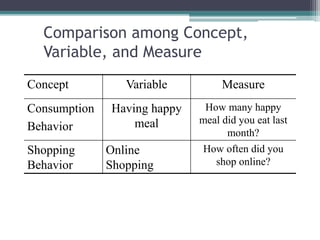
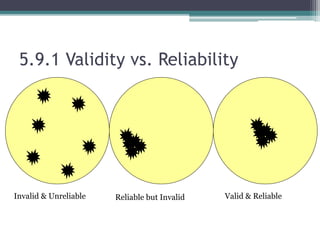
The document provides an overview of quantitative research methods, clarifying the nature and purpose of scientific research, the research process, and the characteristics distinguishing it from other knowledge acquisition methods. It explores different research techniques, including surveys and experiments, while discussing concepts such as validity and reliability in measurement. Additionally, the document emphasizes the significance of theory, conceptualization, and operationalization in conducting research.