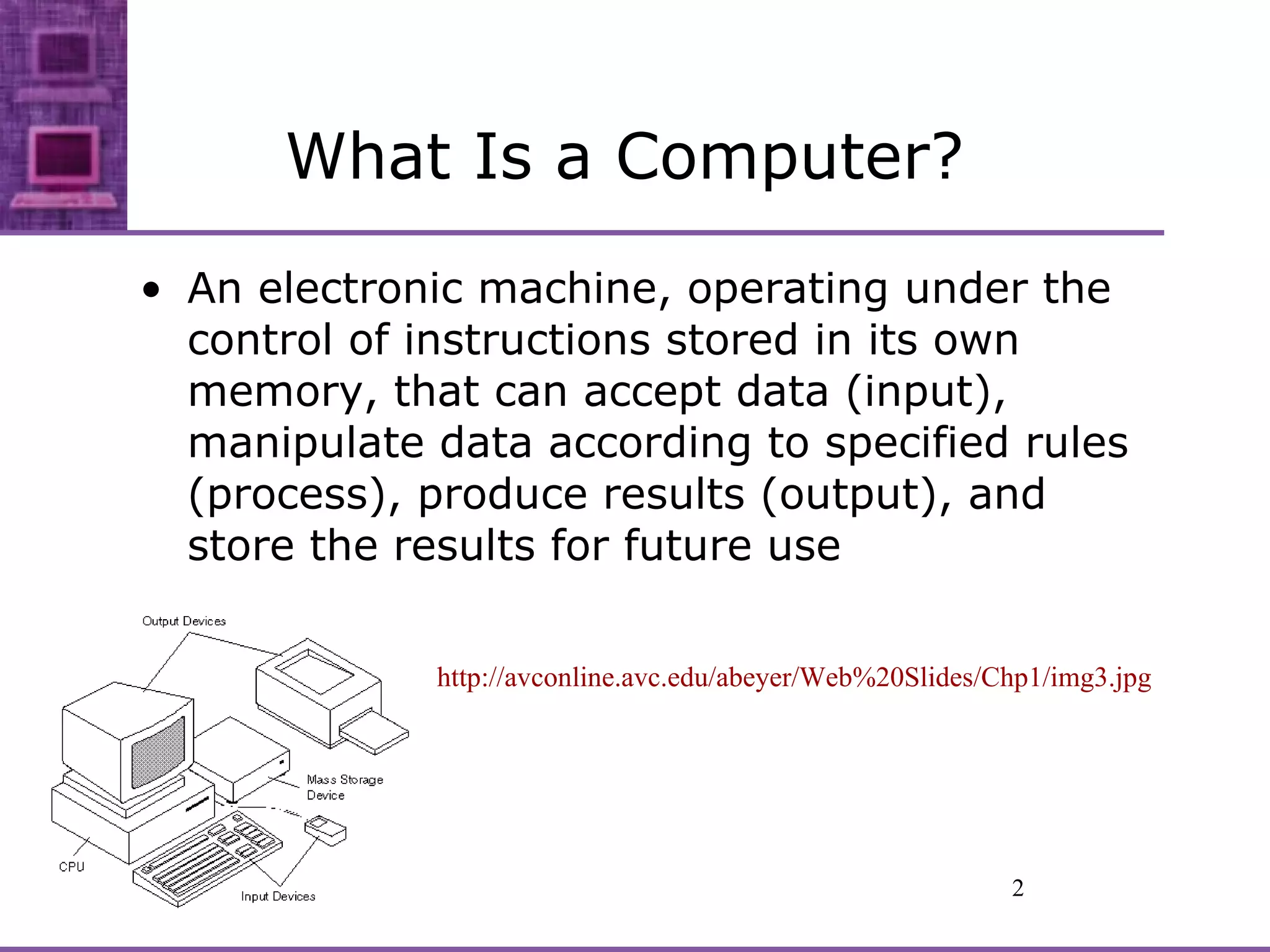
The document provides an overview of the history and definition of computers. It discusses how computers are electronic machines that can accept data as input, manipulate it according to stored instructions, and produce and store output. The definition of a computer is explained in terms of the work it does, the information it handles, and its size/price. Categories of computers include mainframes, PCs, embedded chips, and internet/cyberspace computers. Moore's Law states that chip transistor density doubles every 18 months at constant prices. Computer networks connect two or more computers to share and exchange information and resources. The course objectives are to explore computer applications and their impact/issues in society.