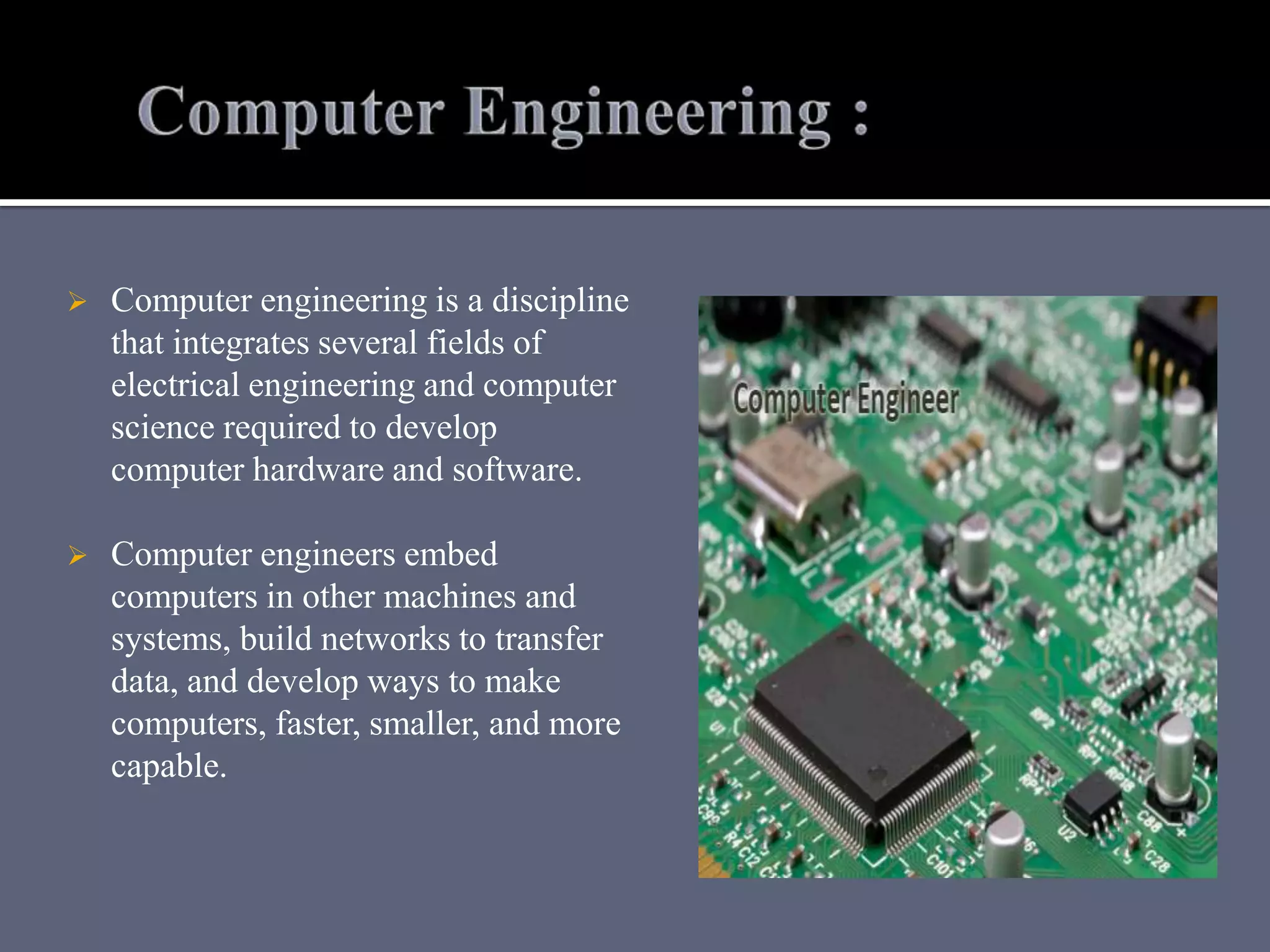
Computer engineering combines electrical engineering and computer science to create hardware and software, while information technology (IT) applies computers in business contexts for data management. Education in computer-related fields prepares students for various roles, including system design, software development, and IT management. The impact of computing and IT is significant across industries, aiding innovations in research, environment sustainability, and creative services.