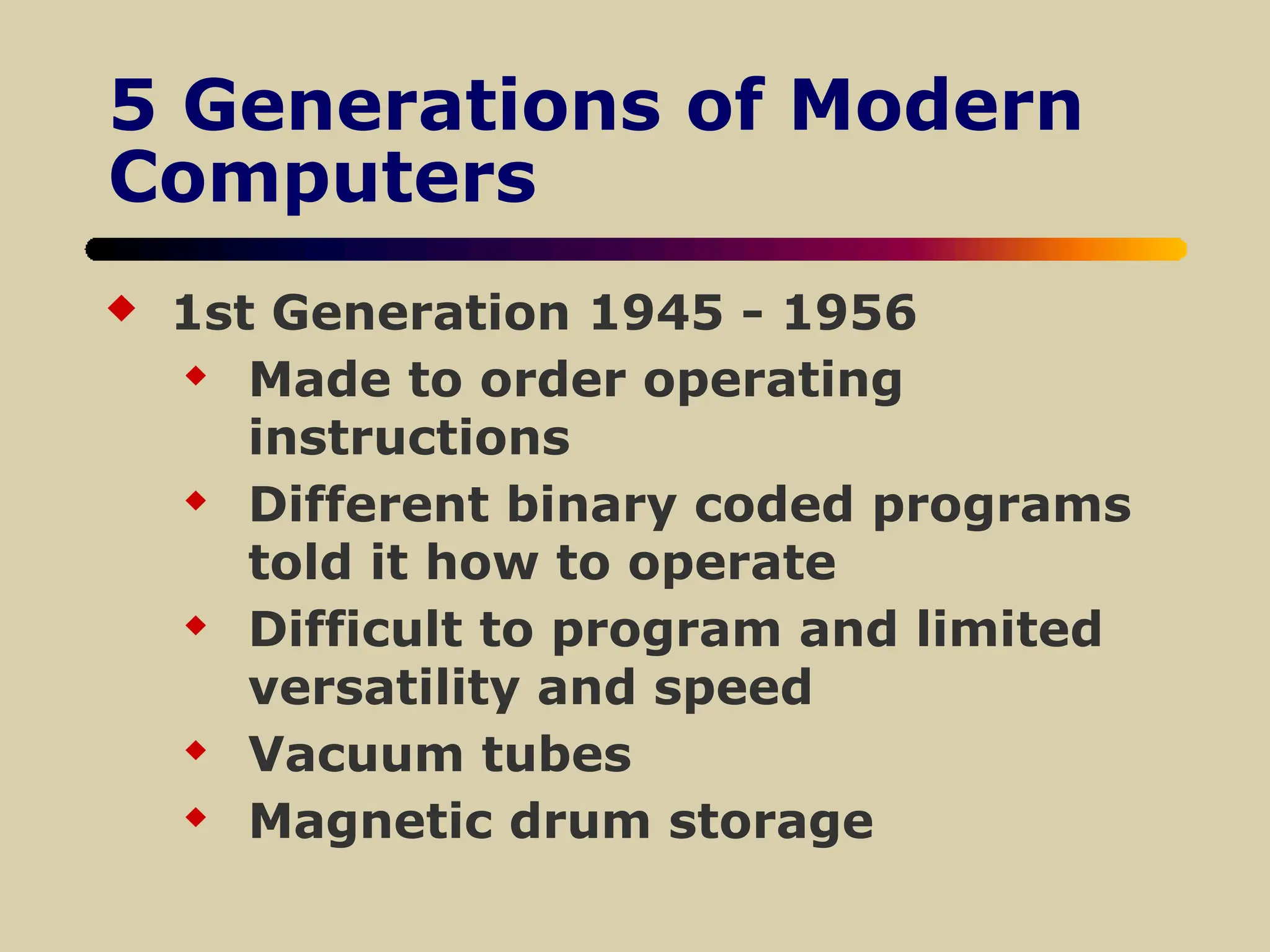
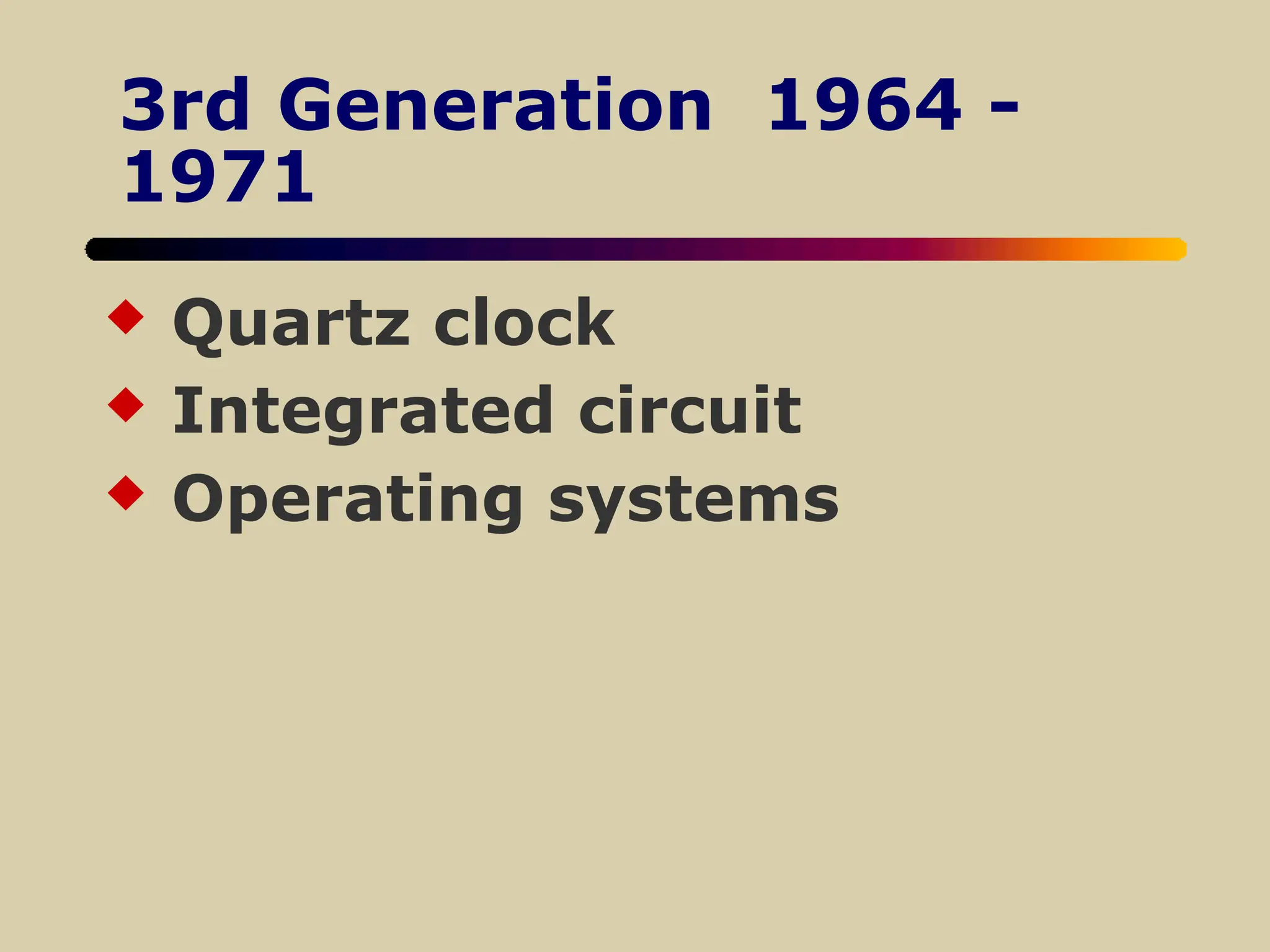
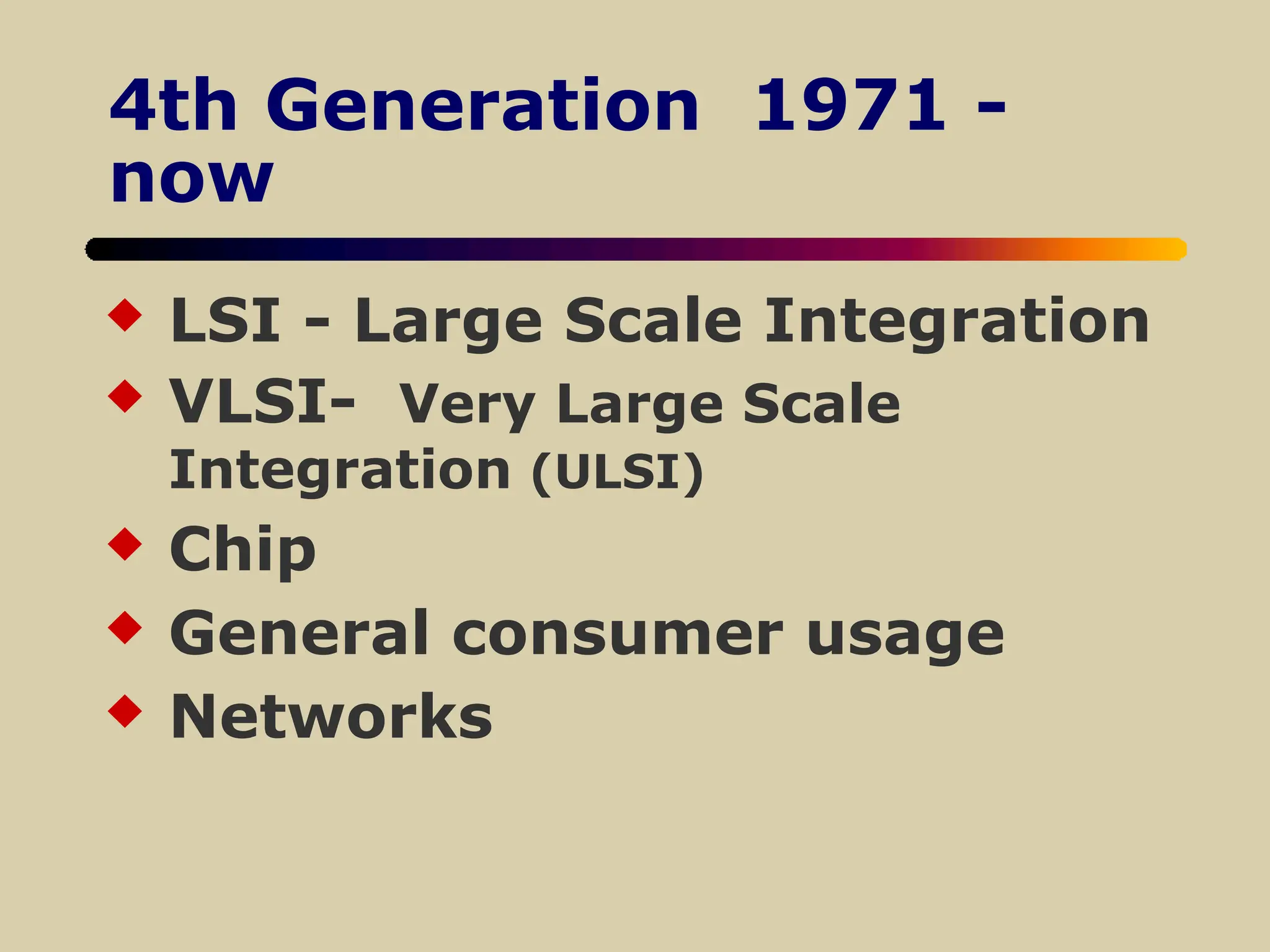
The document discusses the evolution of computers, defining them by their functions and the advancements in technology, such as increasing memory capacity and processing speed. It explores how computers and networks impact various societal components like education, government, and business, highlighting both benefits and challenges, including issues of privacy and job displacement. Additionally, it outlines the history of computing pioneers and significant machines across five generations of development, concluding with a discussion on the societal implications of technological changes.