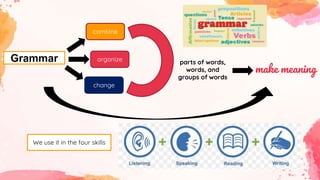
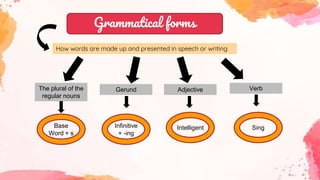
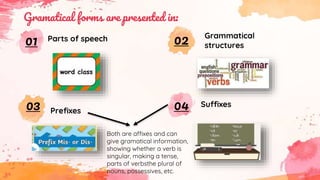
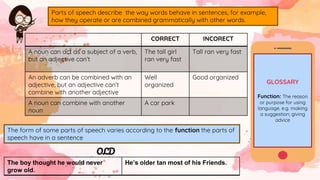
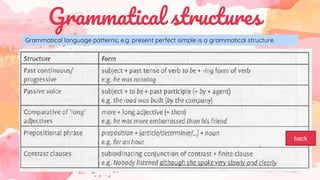
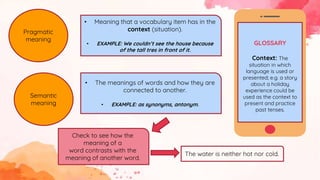
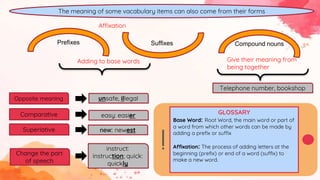
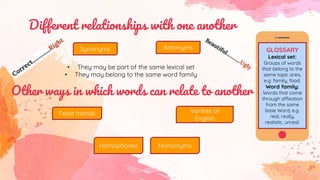
This document provides an overview of grammar and lexis for language learners. It defines grammar as the rules for combining and organizing words, and describes common grammatical forms like parts of speech, prefixes, suffixes, and grammatical structures. It also explains what lexis refers to and discusses different types of word meanings including denotative, figurative, literal, pragmatic, and semantic meanings. Various word relationships are covered such as synonyms, antonyms, false friends, homophones, and homonyms. The document emphasizes that learning vocabulary requires repeated exposure and understanding word forms and meanings. It concludes that keeping vocabulary records can be useful for language learners.