This document discusses types of conformity according to Kelman's (1958) three levels: compliance, identification, and internalization. It provides definitions and examples for each:
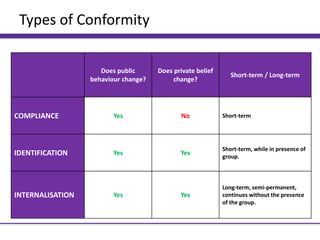
1) Compliance involves public behavior change but not private belief change, and is short-term. An example is eating meat privately while conforming to vegetarian friends.
2) Identification involves public and private belief changes that are short-term while in the presence of the group, like temporarily becoming Christian to please friends.
3) Internalization involves long-term public and private belief changes that continue without the group's presence, such as permanently adopting a friend's fashion views.
It also distinguishes between normative social influence (
















![Application Question
Suggestion: Daniel is demonstrating informational social influence [1]
as he is copying Mila to gain knowledge and/or to be right [1].
In addition, Daniel is demonstrating internalisation [1], as he is
changing both his public behaviour and his private beliefs as he
believes that Mila (who is intelligent) is likely to be right [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xbjmspbhsgoomjmcg7kk-signature-8d7f6ae105fb68a50b755064649f8315d25cfd46c1598ee1fe358b9809ed2d2c-poli-181229215521/85/01-types-of-conformity-power-point-21-320.jpg)