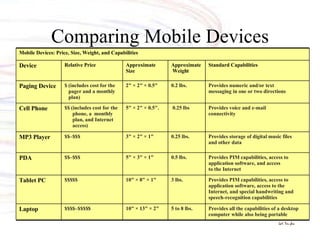
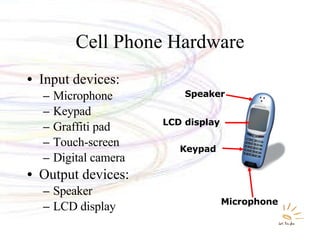
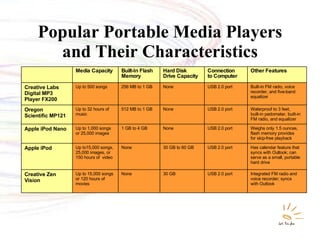
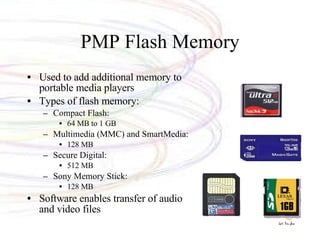
The document discusses various types of mobile computing devices including their key features, sizes, weights and prices. It provides details on laptops, tablets, PDAs, MP3 players and cell phones, comparing their specifications and capabilities. The document also covers operating systems, file transfer methods and convergence of technologies across different mobile devices.






![PMP Ethical Issues Is it illegal to download MP3 files? MP3.com: Song files are on a public server Permission is given by the artist or recording company to place the files on the server A fee is paid to download a file, eg iTunes Napster: A file exchange site Song files were borrowed from users’ computers (peer-to-peer [P2P] sharing) Sued for copyright infringement (wikipedia for details)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08tait-1207199399622459-8/85/08-Tait-12-320.jpg)