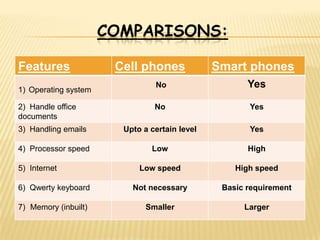
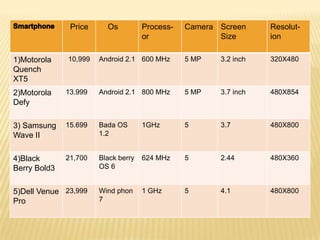
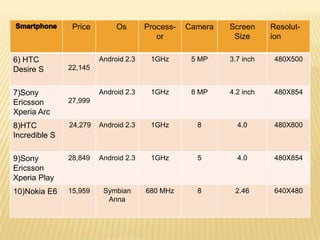
The document discusses the history and features of smartphones. It notes that the first smartphone, the IBM Simon, was released in 1992. Smartphones combine the functions of a cellphone and a personal digital assistant (PDA) by allowing apps, internet access, and integration of phone and computing capabilities. The document lists the operating systems, processors, cameras, and other specs of 10 top smartphones in India and discusses potential future uses of smartphones like mobile banking and medical devices. It concludes by tracing the evolution of smartphones from early clunky models to today's powerful multimedia devices.