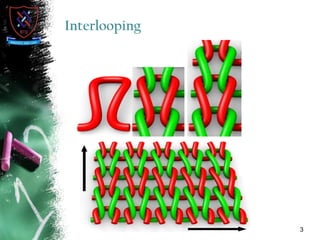
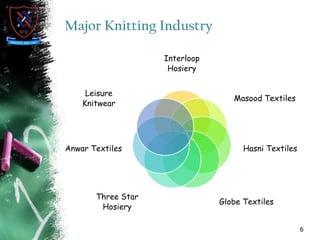
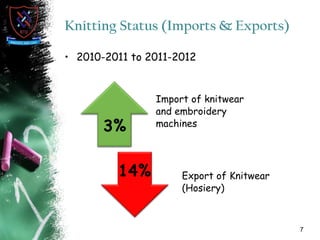
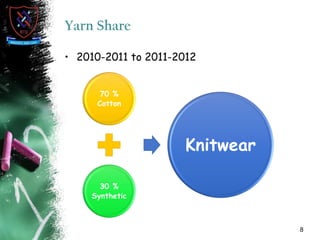
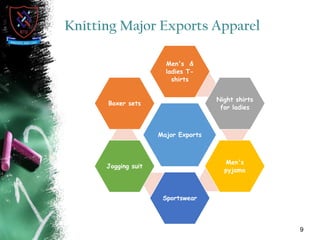
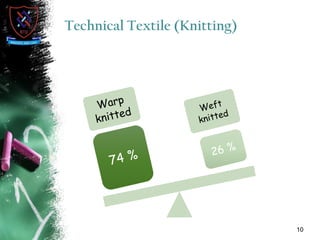
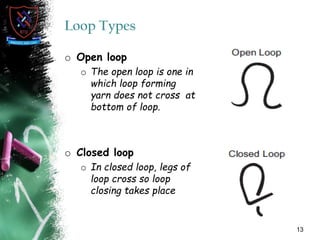
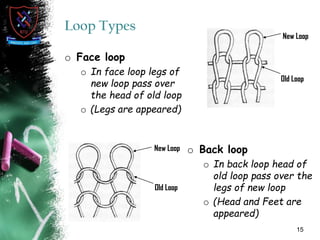
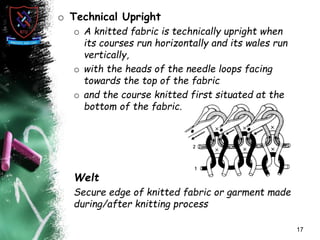
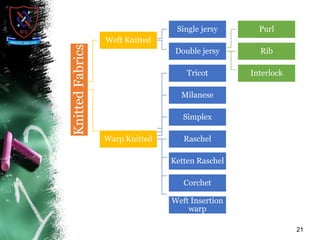
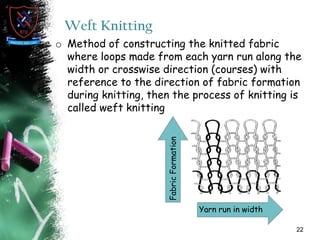
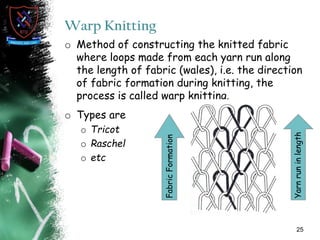
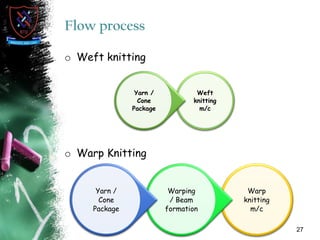
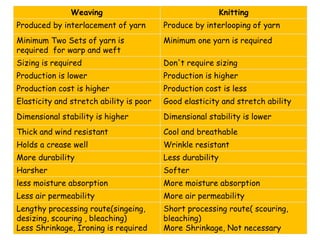
Knitting is the second most popular fabric formation technique where a continuous yarn is looped to form a fabric. There are two main types - weft and warp knitting. Weft knitting forms loops that run horizontally across the fabric width while warp knitting forms loops that run vertically along the fabric length. Knitting has several advantages over weaving like stretchability, softness, and moisture absorption. Pakistan's knitting exports make up a small share of the global and regional markets. The document defines various knitting terminology and examines properties and applications of knitted fabrics.