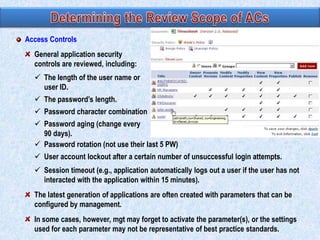
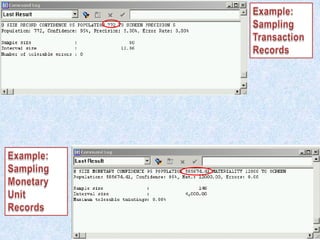
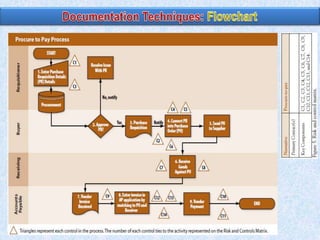
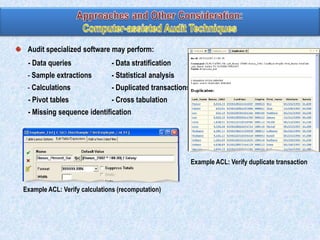
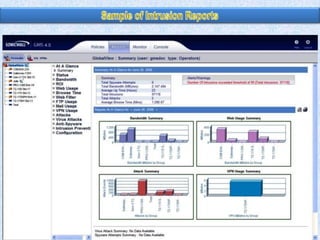
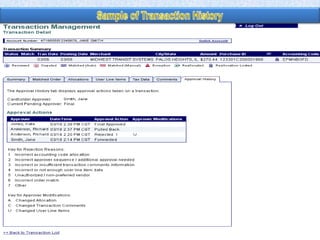
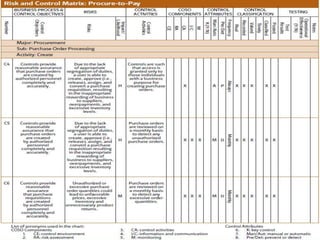
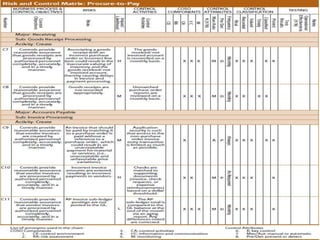
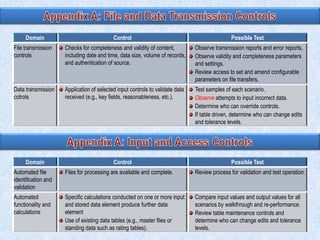
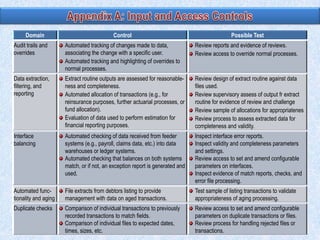
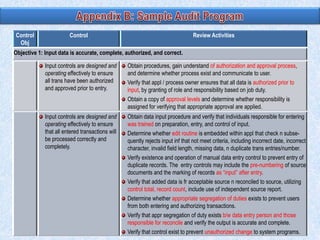
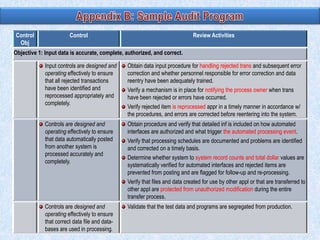
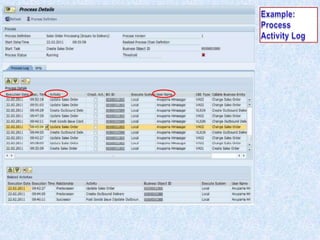
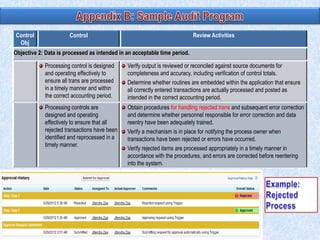
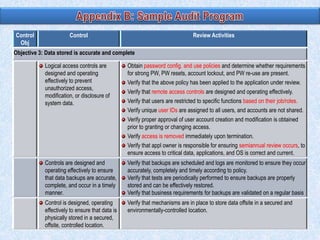
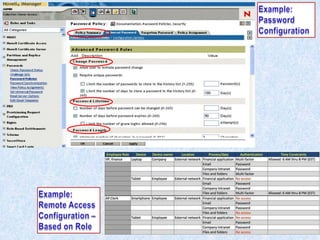
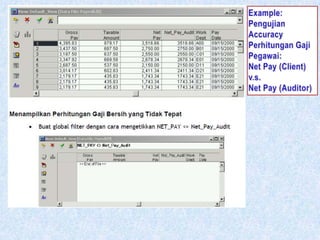
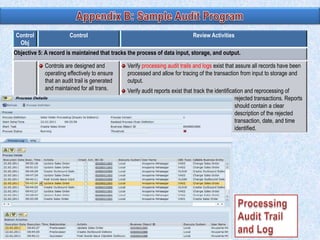
To summarize:
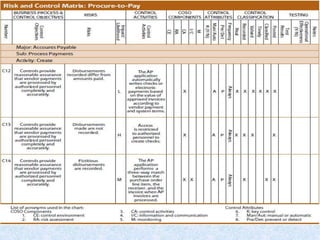
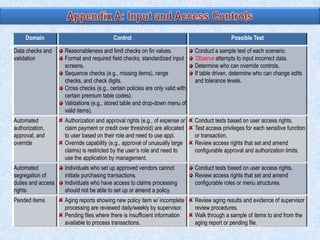
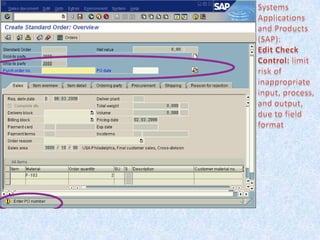
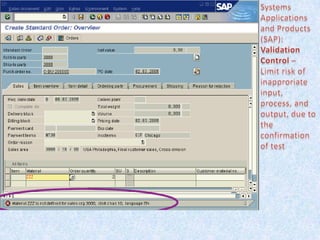
1) Auditors conduct a top-down risk assessment (RA) to determine which applications and controls to review. They document risks and controls in matrices mapped to processes, accounts, and disclosures.
2) The RA involves weighting risk factors, ranking risks, and prioritizing applications for review based on composite risk scores. Applications above a threshold score are included in the review scope.
3) The review scope, approach, and frequency are based on the RA results and resource availability. A business process method breaks processes into levels to structure the control review.

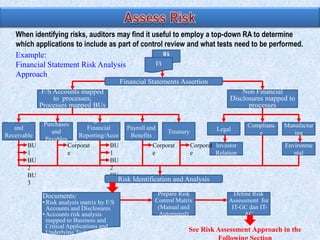

![Composite scores = ∑ (risk factor weight x risk scale) and adding the totals.
The composite score of 375 = [(20 x 5) + (10 x 1) + (10 x 5 ) +…].
For this example, the auditor may determine that the application control review will
include all applications with a score > 200.
Risk Factor Weighting
20
10
10
10
10
10
Applica- Application
Design
PreApp supports Frequency of Complexity
tion
contains
effective- packaded more than one
change
of change
primary ness of the
or
critical business
controls App control developed
process
15
Financial
impact
15
100
Effective- Composite
ness of the
scores
ITGCs
App A
5
1
5
5
3
3
5
2
375
App B
1
1
2
1
1
1
4
2
170
App C
5
2
2
1
5
5
5
2
245
App D
5
3
5
1
5
5
5
2
395
App E
5
1
1
1
1
1
3
2
225](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-140215091550-phpapp01/85/05-2-auditing-procedure-application-controls-4-320.jpg)