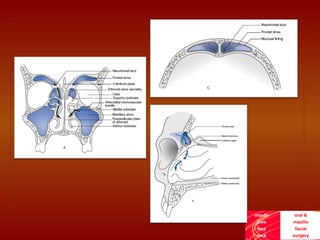
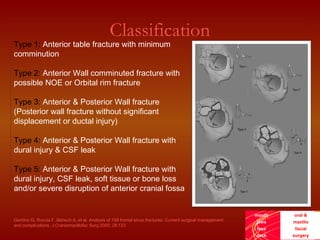
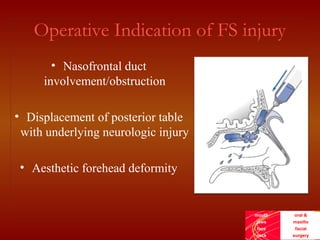
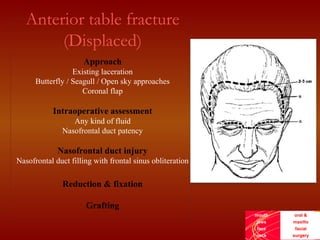
This document discusses the current treatment protocol for fractures of the frontal sinus. It begins by covering the embryology and classification of frontal sinus fractures. Type 1 fractures involve minimal comminution of the anterior table, while type 4 fractures involve injuries to the dura and CSF leak. Management is based on fracture location, dural involvement, and damage to drainage. For nondisplaced anterior table fractures, conservative treatment is used. Displaced fractures may require open reduction, fixation, and frontal sinus obliteration. Posterior table fractures with CSF leak or displacement are treated with frontal sinus cranialization or obliteration. Complications can include infection, mucocele, and brain abscess.