Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times



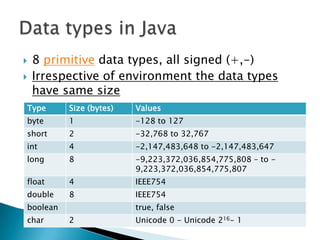





The document discusses data types in Java programming, including primitive data types like integers and longs, as well as variables which store values of a specific data type and how they are declared and named. It also covers literals, which are fixed values assigned directly to variables without computation, and provides an exercise to declare and assign literal values to variables for age, credit card number, and bank balance.








