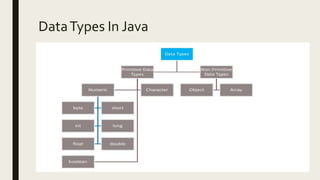
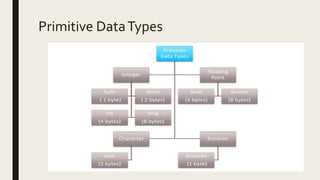
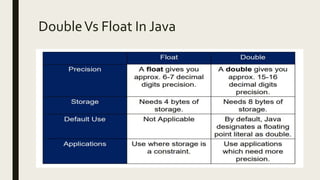
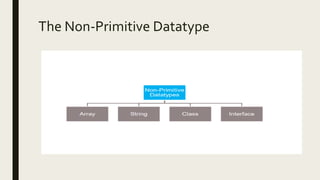
This document discusses Java data types including primitive data types like integers, floating points, booleans, characters and non-primitive data types like classes, strings, and arrays. It provides details on each data type, such as their size, range of values, and examples of declaration and usage. Key primitive data types covered are byte, short, int, long for integers, float, double for floating points, boolean for true/false values, and char for single characters. Non-primitive types discussed include classes for defining custom types, strings for text, and arrays for storing multiple values.










![Arrays In Java
■ Arrays are used to store multiple homogeneous values in a single variable. Note, in
Java array indexes start from zero.
■ String fruits[] = {“apple”,“banana”,”mango”};
■ System.out.println(“The third fruit is” + fruits[2]); //outputsThe third fruit is mango](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javadatatypes-210326175006/85/Java-data-types-16-320.jpg)
