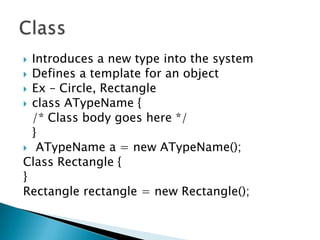
This document introduces the concepts of classes and objects in Java. It defines a class as a template that introduces a new type into the system and defines an object as an instance of a class. The key points covered include:
- Objects are created from classes using the new operator.
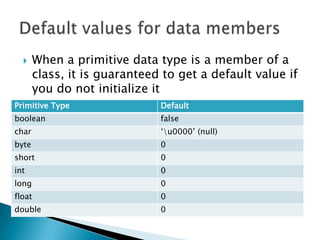
- Objects contain fields to store data and methods to manipulate the data.
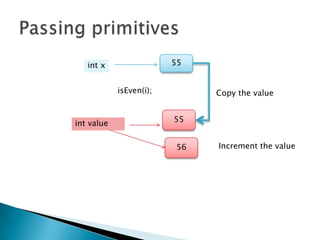
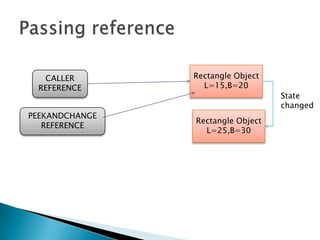
- When passing primitive data types to methods, the value is passed but when passing objects, the reference is passed.
- Methods determine the messages an object can receive including name, arguments, return type and body.





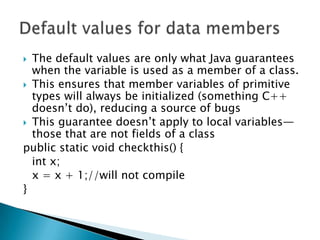


![public class MethodPlayer { public boolean play(intvol) {System.out.println(“Play volume -” + vol); } public static void main(String a[]) {MethodPlayer player = new MethodPlayer();player.play(5); }}Method in Action](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-classandobject-100906020209-phpapp02/85/08-class-and-object-11-320.jpg)