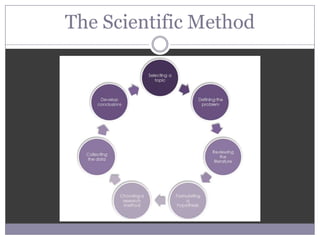
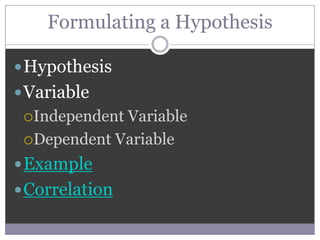
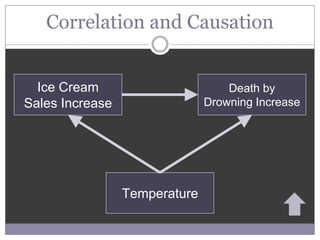
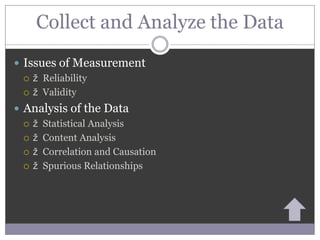
The document outlines the key steps of the scientific method for conducting research, including selecting a topic, formulating a hypothesis, choosing a research method, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. It discusses various research methods like experiments, surveys, ethnography, and existing sources. It also covers important concepts in research like variables, hypotheses, correlation versus causation, reliability, validity, and ethics.