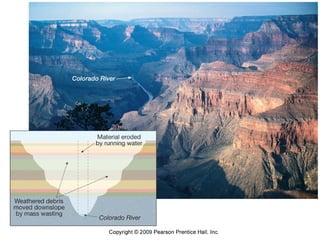
This document provides an introduction to Earth science. It discusses the four main parts of Earth's system: the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. These parts are interrelated - for example, clear cutting forests can impact the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere. The document also introduces some key concepts in Earth science, such as uniformitarianism, the scientific process, and the idea that science aims to understand and explain natural events by collecting data and discovering patterns.