The document compares and contrasts several software engineering process models:
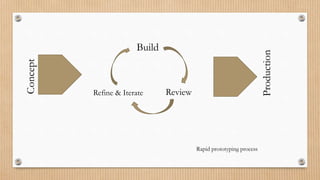
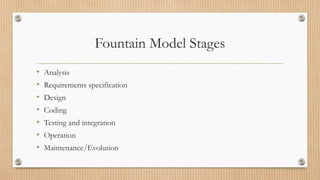
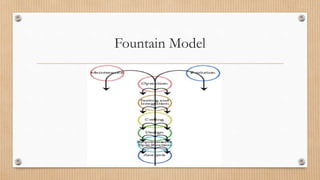
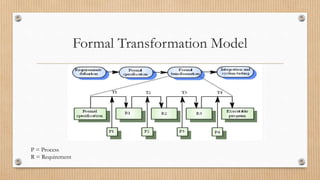
The Waterfall model is a linear sequential model where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It is easy to manage but difficult to change requirements later. Evolutionary models like incremental and spiral models involve user feedback in iterative development cycles to refine requirements. Rapid prototyping creates samples to assess functionality and refine designs based on user feedback. The Fountain model is similar to Waterfall but allows revisiting previous phases. Formal transformation uses mathematics to reduce errors through iterative transformations. The Reuse-oriented approach develops software through existing code and processes to reduce costs and time.