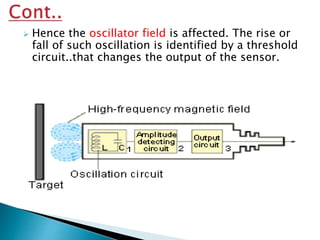
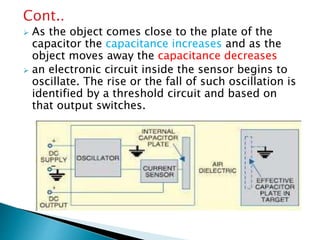
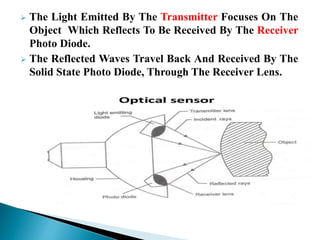
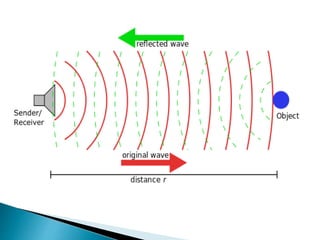
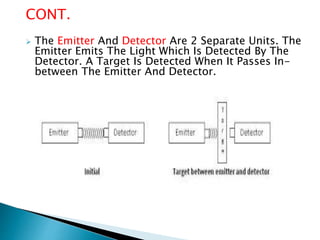
The document provides an extensive overview of proximity sensors, detailing various types such as inductive, capacitive, optical, and ultrasonic sensors, along with their construction, working principles, advantages, and disadvantages. It explains how these sensors detect the presence of objects without physical contact and discusses their applications in industries like automotive and machine tools. Additionally, the document outlines the expected growth of the proximity sensor market across various sectors.