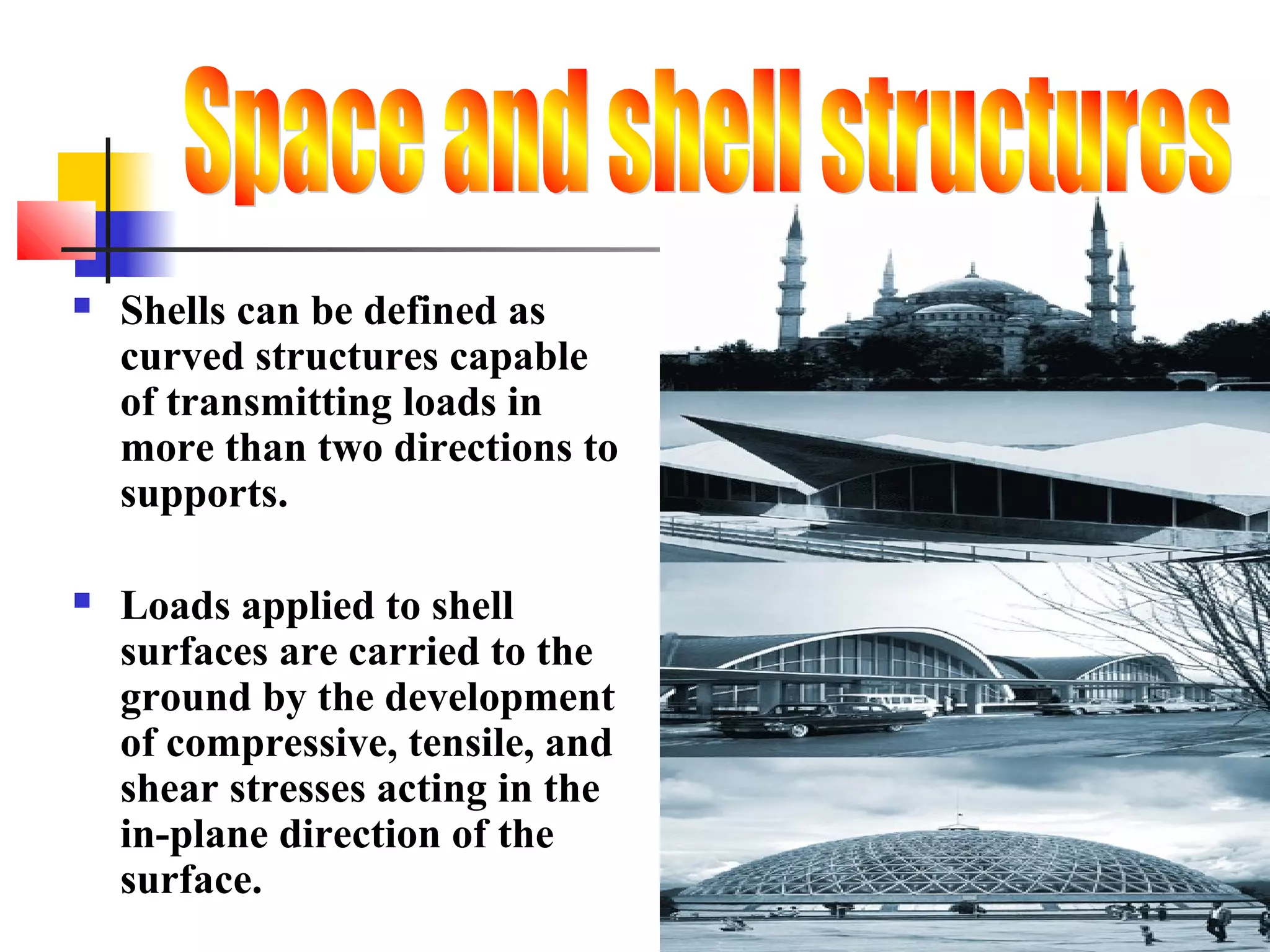
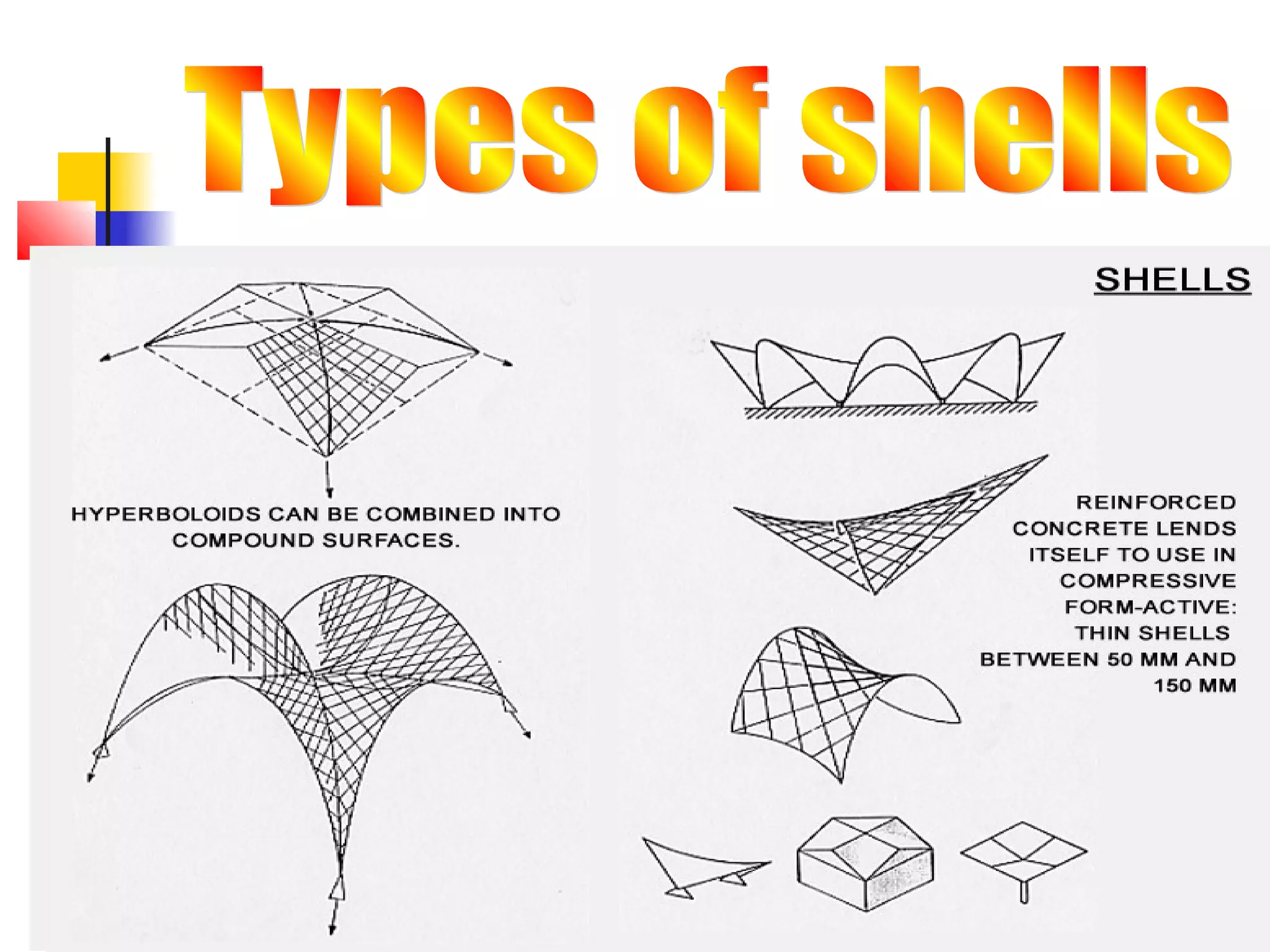
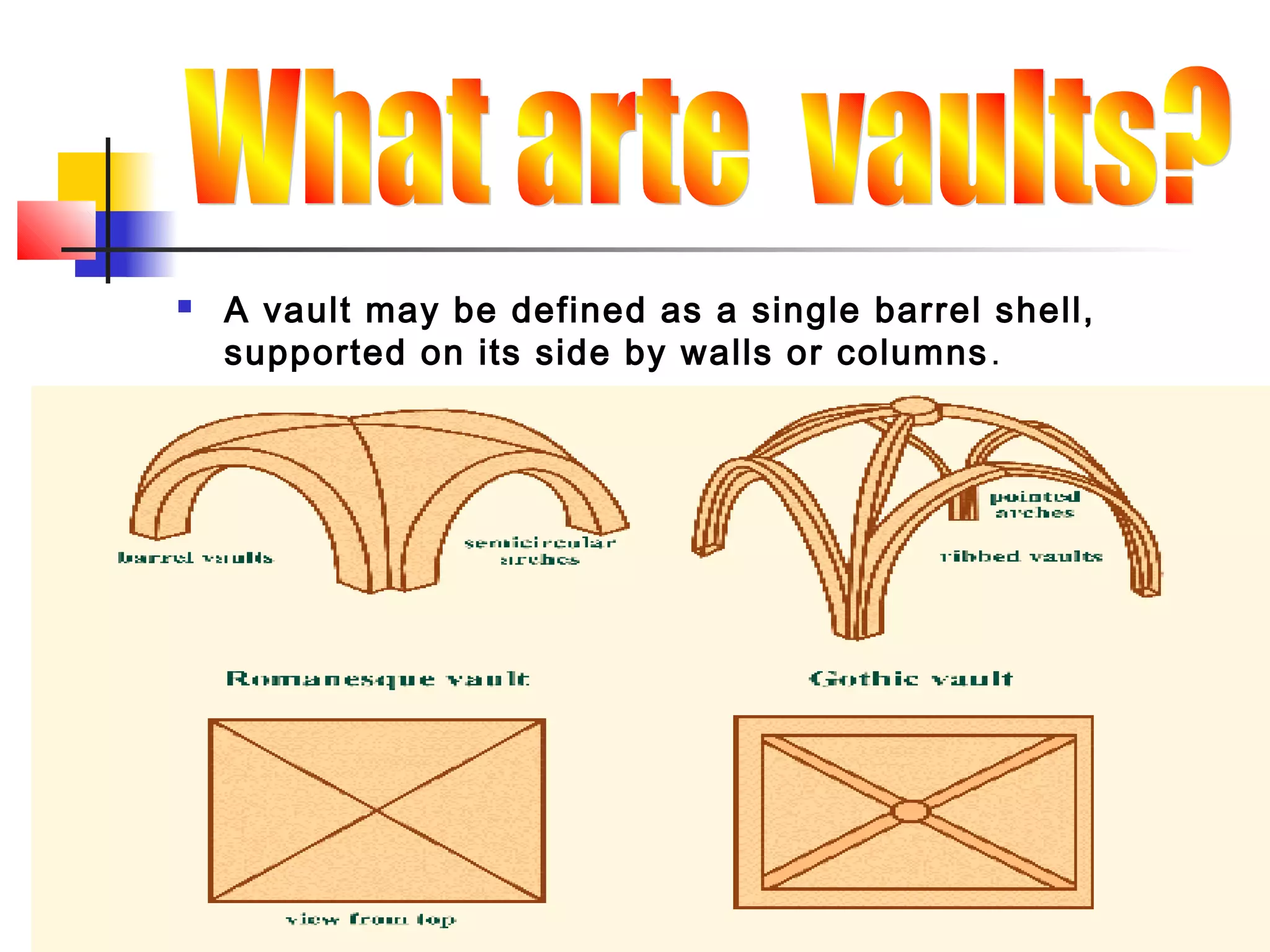
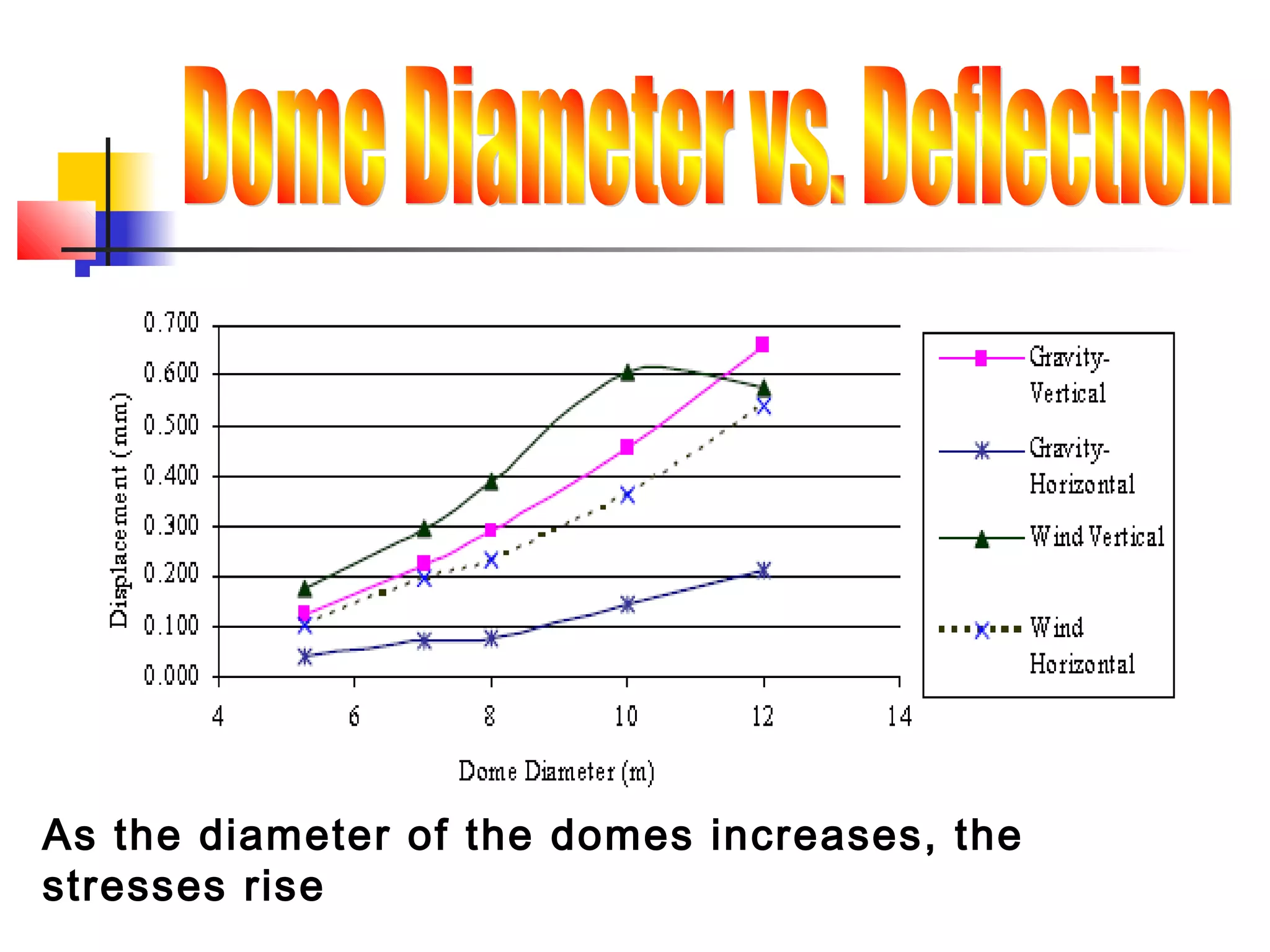
Shells are curved structures that can transmit loads in multiple directions and are constructed using thin materials like concrete or reinforced concrete. They distribute loads across their surfaces through compressive, tensile and shear stresses. Large spherical domes are often constructed using inflated membranes as forms which provide support during construction. Domes over 300 feet require a grid structure to provide sufficient stiffness while minimizing weight. Shells and folded plates are constructed as uniform thin surfaces rather than stacked discrete pieces like frames. Domes, vaults, and barrel shells are examples of shell structures used in building construction.