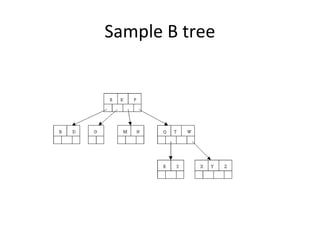
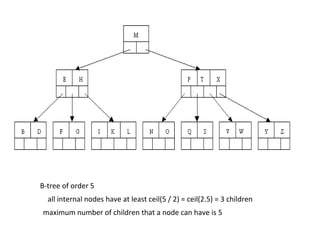
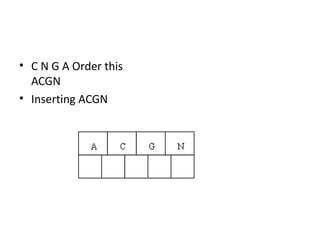
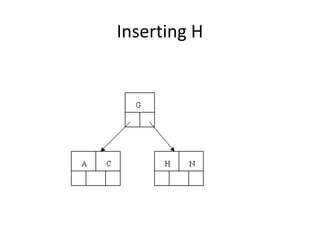
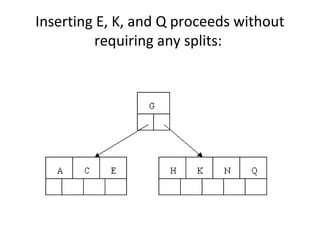
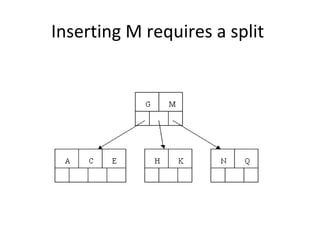
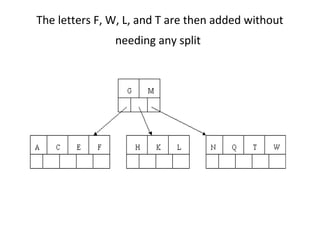
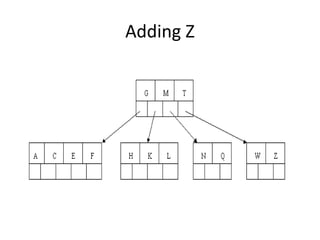
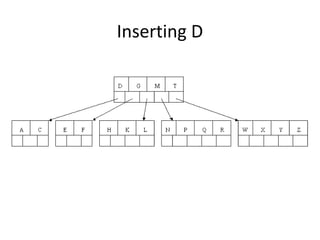
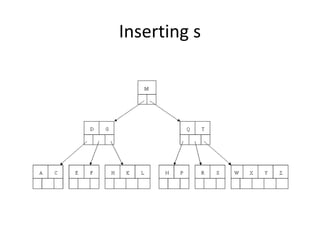
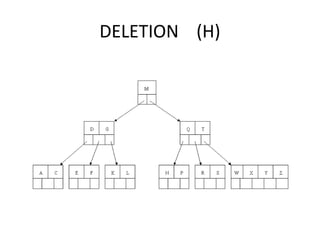
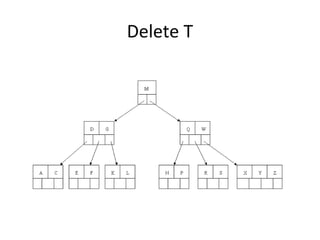
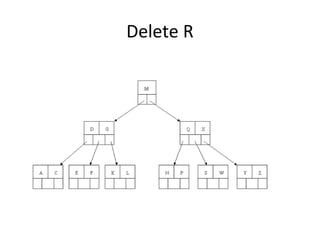
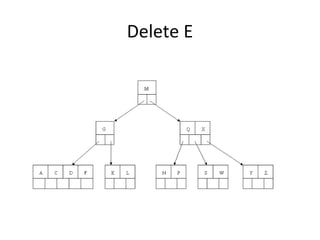
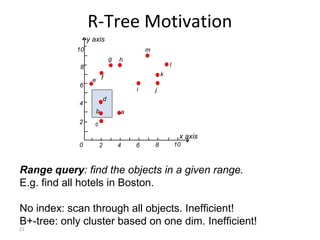
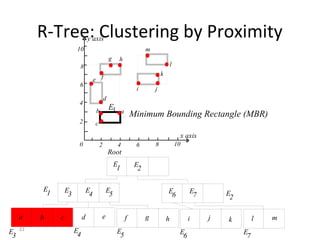
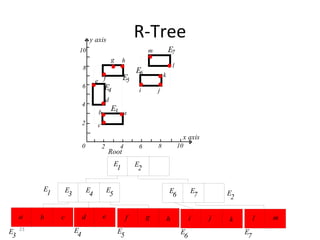
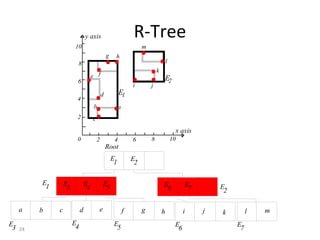
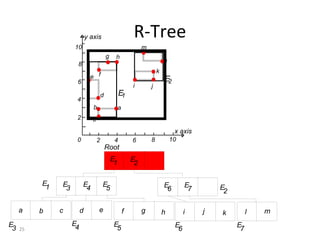
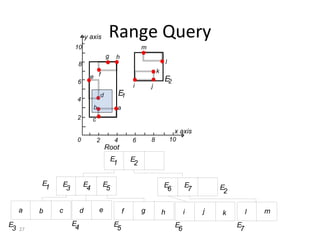
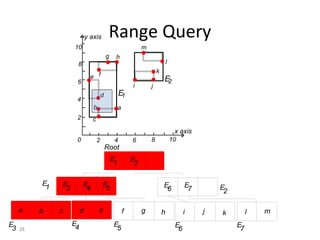
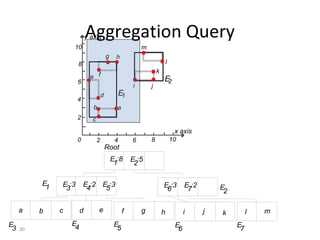
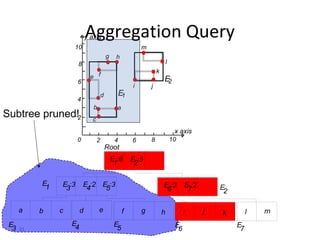
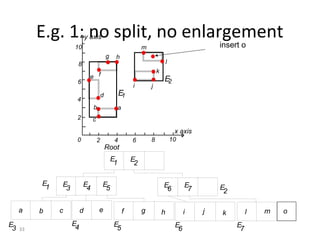
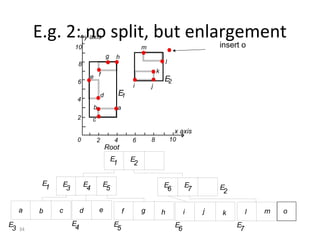
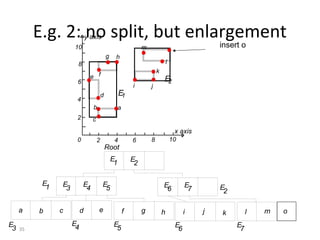
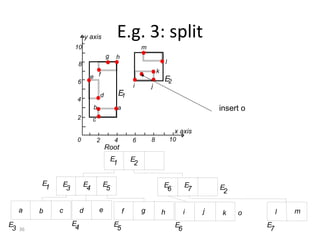
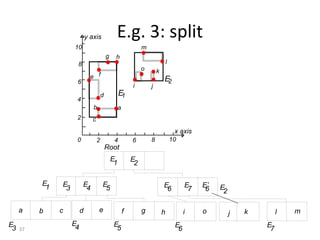
B-trees are tree data structures that allow efficient retrieval of records from disk storage. They are commonly used in databases and file systems. R-trees are a type of tree data structure used for indexing multi-dimensional spatial data like geographic coordinates. B-trees organize data by keys, allowing efficient insertion, deletion, and retrieval of records. R-trees cluster data objects based on their proximity to each other to support spatial queries.