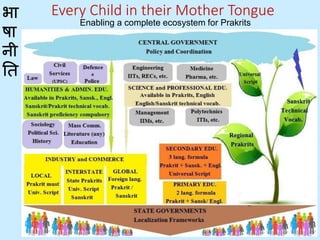
This document proposes a new language policy for India to address current issues and maximize human resource development. It argues that India's current English-focused policy has led to declining language proficiency and barriers to education. It recommends adopting a comprehensive, nationally coordinated policy that promotes Indian languages as mediums of instruction while still teaching English as a second language. Key aspects include developing each Indian language for professional education, courts, and laws while coordinating technical vocabulary based on Sanskrit. The aim is to boost the economy by increasing access to education without language discrimination.